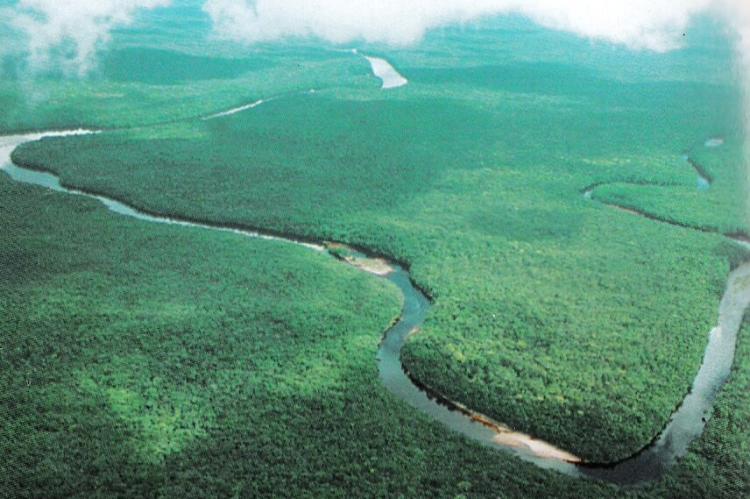
The Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests: A Wetland Wonderland
Nestled along the northeastern coast of Venezuela and extending into Guyana, the Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests ecoregion is a remarkable tapestry of flooded forests, wetlands, and meandering waterways. This expanse of inundated landscapes testifies to nature's resilience and adaptability.
The Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests: A Wetland Wonderland
Nestled along the northeastern coast of Venezuela and extending into Guyana, the Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests ecoregion is a remarkable tapestry of flooded forests, wetlands, and meandering waterways. This vast expanse of inundated landscapes, stretching from the southern reaches of the Paria Peninsula to the Waini River, is a testament to nature's resilience and adaptability.
Geographic Features
A Landscape of Little Relief
Geographically, the Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests ecoregion is characterized by a terrain of slight relief, with soils almost entirely composed of alluvial deposits originating from the distant Colombian and Venezuelan Andes. These sediments, carried by the mighty Orinoco River and its tributaries, have shaped the region's intricate network of rivers, oxbow lakes, and alluvial fans.
A Labyrinth of Waterways
The ecoregion is intricately woven with a complex matrix of wetlands, mangroves, and inundated moist forests, crisscrossed by a labyrinth of waterways. Permanent wetlands and marshes, known as the Orinoco Wetlands ecoregion, coexist with large rivers, small gallery streams, levees, and the iconic delta alluvial fan.
As the Orinoco River branches outward towards the Atlantic Ocean, its distributaries become increasingly partitioned and disjunct, forming numerous islands before converging again in the delta's easternmost reaches.
Climate and Hydrology
A Tropical, Humid Environment
The climate of the Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests ecoregion is quintessentially tropical, with high temperatures averaging around 26°C (79°F) and a relative humidity of approximately 70%. The region experiences two distinct seasons: a dry season and a wet season.
The wet season, which typically begins in April or May and lasts through December, is characterized by irregular rainfall patterns. Precipitation levels vary significantly throughout the region, increasing from 500-2,000 mm (20-80 inches) in the north to 8,000 mm (300 inches) in the southernmost reaches.
Biodiversity: A Treasure Trove of Life
Flora
The swamp forests of the Orinoco (Amacuro) Delta are essential habitats for a diverse array of plant life, including many endemic species. Common hardwood trees in these forests include the Guiana chestnut, mahogany, kapok, wild pigeon plum, shimbillo, greenheart, padauk, and billygoat plum.
Numerous palm species also thrive in this ecoregion, such as the açaí palm, troolie palm, and the iconic moriche palm, which is well-adapted to the flooded conditions.
Fauna
The Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests ecoregion is a haven for wildlife, supporting a rich avian fauna of over 175 species, including 39 species of aquatic birds and 13 species of wading birds, such as the striking scarlet ibis and roseate spoonbills.
These wetland forests provide essential habitats for threatened and endangered species, including the Orinoco crocodile, Amazon river dolphin, jaguar, bush dog, giant river otter, Orinoco goose, and the majestic harpy eagle.
Conservation Efforts
Protected Areas and Biosphere Reserve
Recognizing the importance of this unique ecosystem, portions of the Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests ecoregion are protected through three designated protected areas, encompassed within the larger Delta del Orinoco Biosphere Reserve.
Challenges and Threats
Despite its relative inaccessibility and poor soil conditions, which have historically safeguarded the region's pristine forests, recent oil exploration and extraction projects have encroached upon these once-untouched landscapes, posing potential threats to the delicate ecological balance.
Conclusion
The Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests ecoregion is a true ecological marvel, where the forces of water, sediment, and life have converged to create a unique and diverse wetland ecosystem. From the towering hardwood trees and graceful palms to the myriad of wildlife species that call these flooded forests home, this ecoregion is a testament to the resilience of nature and the importance of preserving such biological treasures for generations to come.
Map depicting the location of the Orinoco Delta swamp forests (in purple).
