Fernando de Noronha Archipelago: Rocas Atoll (Brazil)
Fernando de Noronha is a volcanic archipelago located off the northeast coast of Brazil in the South Atlantic Ocean. The archipelago comprises 21 islands and islets, the most significant being Fernando de Noronha. In addition, Rocas Atoll is a circular coral reef that encloses a lagoon.
Fernando de Noronha
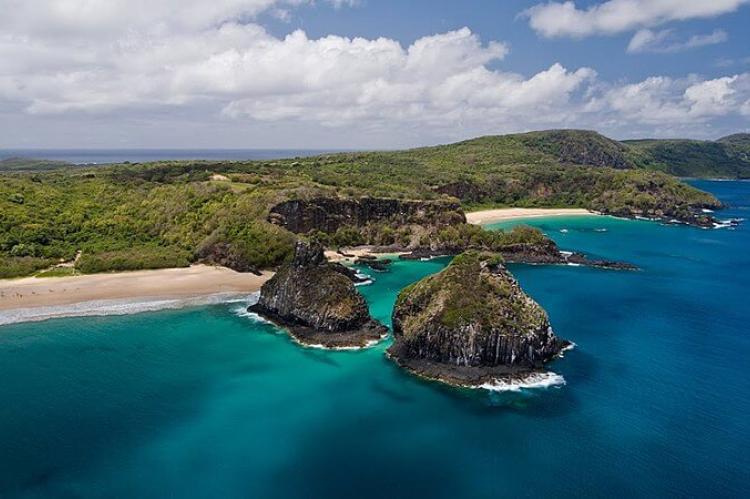
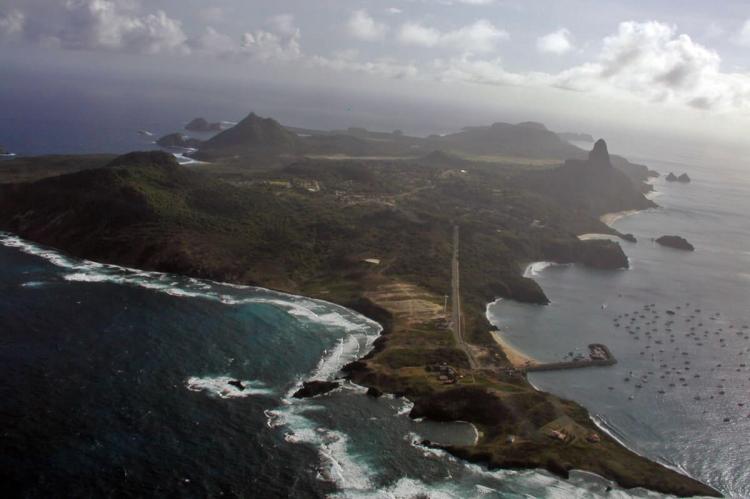
Fernando de Noronha is a volcanic archipelago located off the northeast coast of Brazil, in the South Atlantic Ocean, approximately 354 km (220 mi) from Natal. The archipelago comprises 21 islands and islets, the most significant being Fernando de Noronha.
Fernando de Noronha is known for its stunning natural beauty, crystal-clear waters, pristine beaches, and diverse marine life. The archipelago has several protected areas, including a Marine National Park and a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Visitors to Fernando de Noronha can enjoy various outdoor activities, such as diving, snorkeling, surfing, and hiking. In addition, the archipelago's beaches, such as Baía do Sancho and Praia do Leão, are among Brazil's most beautiful and popular destinations for locals and tourists.
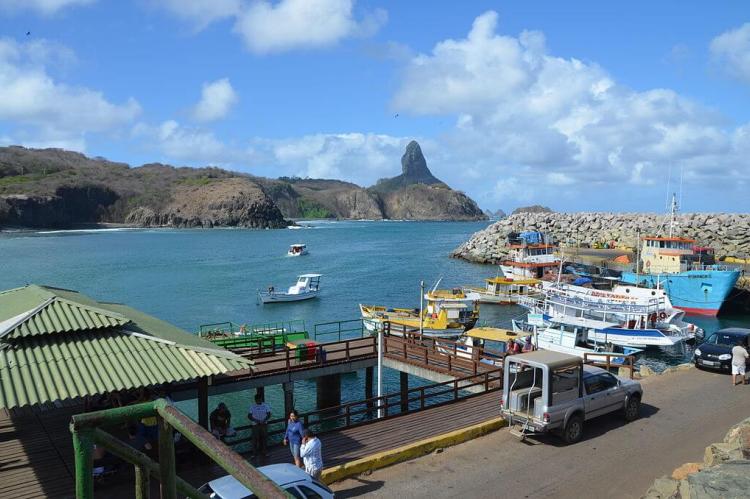
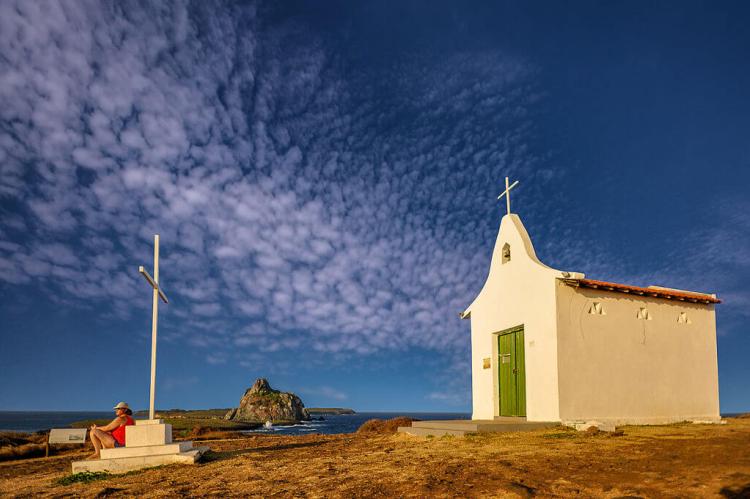
In addition to its natural attractions, Fernando de Noronha has a rich history and cultural heritage. The Portuguese first discovered the archipelago in the 16th century. It has been used for various purposes, including as a prison, a military base, and a scientific research station.
Today, Fernando de Noronha is a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world who come to experience its natural beauty and unique culture. However, the number of visitors is limited to preserve the delicate ecosystem and maintain the island's sustainability.
Rocas Atoll
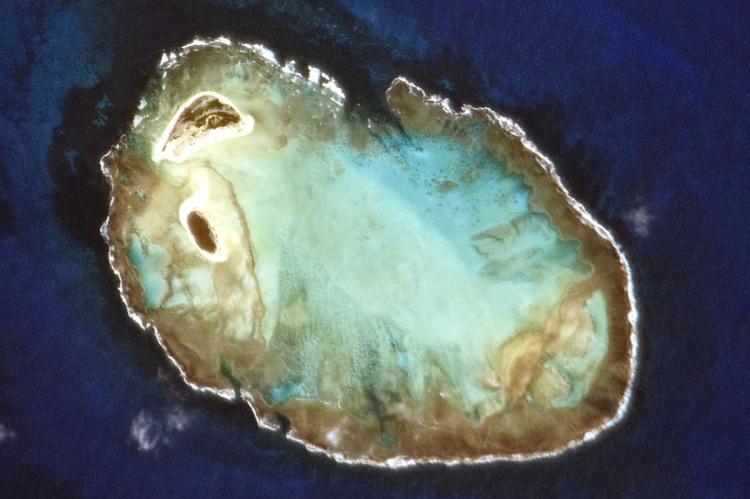
Rocas Atoll (Atol das Rocas) is a Brazilian atoll located in the Atlantic Ocean, approximately 267 km (166 mi) northeast of Natal, the capital of Rio Grande do Norte state. It is one of the few atolls in the South Atlantic and a significant ecological reserve.
An atoll is usually a circular or oval-shaped reef structure with a lagoon. These structures typically form around a volcanic island that has subsided while the coral grows upward. These reef structures are self-contained environments that create ideal conditions for diverse habitats. As a result, coral reefs are considered among the most diverse ecosystems in the world.
Rocas Atoll is a circular coral reef that encloses a lagoon. The reef has a diameter of approximately 3.7 km (2.3 miles) and is composed of limestone rock and coral. The atoll is uninhabited, except for a small Brazilian Navy base used for scientific research and marine environment monitoring.
Rocas Atoll is home to diverse marine life, including fish, sharks, sea turtles, and seabirds. In addition, the waters around Atol das Rocas are considered a breeding and feeding ground for several species of marine mammals, including humpback whales, dolphins, and manatees.
Due to its ecological importance, Rocas Atoll was declared a Biological Reserve in 1979 and is now part of the National Parks System of Brazil. It is also a designated Ramsar Site, which means it is recognized as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
The Brazilian government strictly controls access to the atoll to protect its delicate ecosystem and ensure biodiversity conservation.