Paraguay's Aquatic Landscapes: From Pantanal to Paraná
Paraguay is a landlocked country in South America, shaped by its major rivers and water resources. Its geography includes the Pantanal wetlands and powerful dams that make it a regional energy leader. These features define its borders and enable its ambitious hydroelectric projects.
Heart of South America: Paraguay's River-Defined Geography and Hydroelectric Destiny
Paraguay occupies a unique position in the heart of South America as a landlocked nation whose identity and economy are fundamentally shaped by its extensive river systems and strategic water resources. The country's geography is dominated by two of South America's most significant rivers, which not only define its borders but also serve as the foundation for one of the world's most ambitious hydroelectric programs. From the vast wetlands of the Pantanal, which extend into northern Paraguay, to the powerful dams that have transformed the nation into a regional energy powerhouse, Paraguay's water bodies represent a remarkable intersection of natural abundance and human engineering achievement.
The country's hydrological features encompass pristine rivers flowing through diverse ecosystems, artificial lakes created by massive hydroelectric projects, extensive floodplains that support exceptional biodiversity, and one of the world's largest underground freshwater reserves. This combination of surface and subsurface water resources provides the essential foundation for agricultural and industrial development while establishing Paraguay as a critical player in regional water security.
The Great River Systems
The Paraguay River: National Lifeline
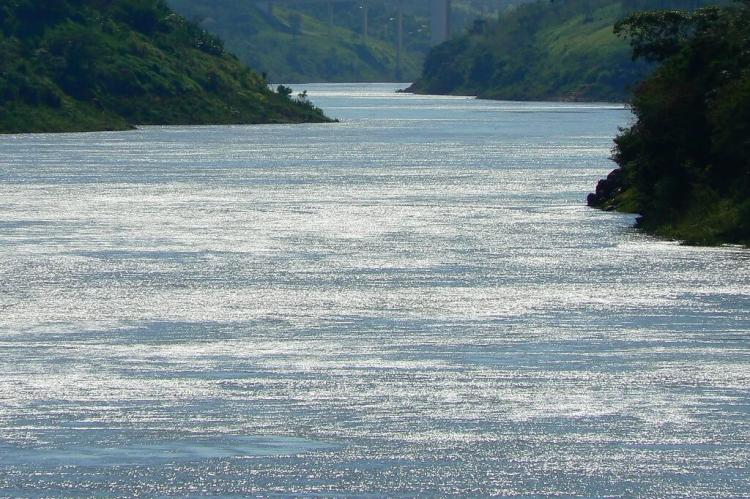
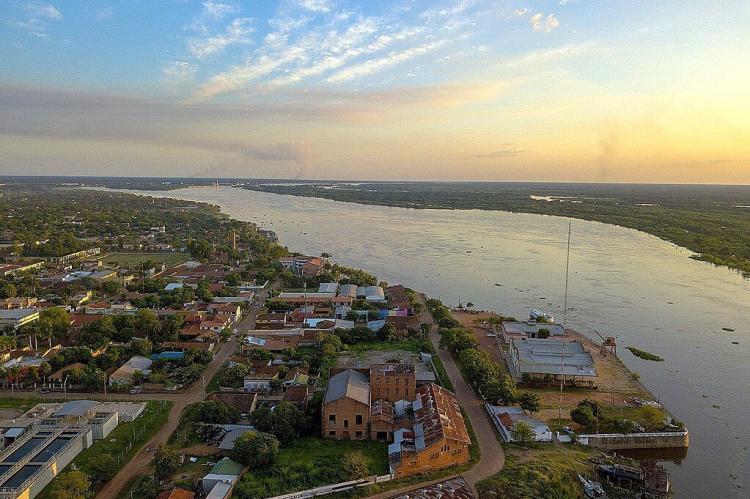
The Paraguay River is the fifth-largest in South America and the main tributary of the Paraná River. It begins in the Mato Grosso region of Brazil at an elevation of 300 meters (980 feet) above sea level and flows through Paraguay to join the Paraná near the Argentine border. Stretching 2,550 kilometers (1,585 miles), it is the largest tributary of the Paraná and the fifth-largest river in the continent. The Paraguay River is the country's most vital waterway, separating Paraguay into two main regions: the eastern part, known as the Región Oriental, and the western part, referred to as the Chaco.
The Paraguay River's significance extends far beyond its role as a geographic boundary. The Paraguay River is crucial to the country's economy and culture, providing essential transportation routes, supporting fishing communities, and serving as a vital source of fresh water for irrigation and urban consumption. The river's seasonal flooding patterns have shaped human settlement patterns for centuries, with seasonal flooding of the river's banks sometimes forcing many thousands of displaced residents to seek temporary shelter until the waters recede from their homes.
The river's ecological importance cannot be overstated, as it connects the vast wetlands of the Pantanal in the north with the temperate grasslands of the south. Its headwaters originate in the Chapada dos Parecis and flow into the Pantanal, the largest wetland complex in the world, spanning 140,000 square kilometers across Brazil, Bolivia, and Paraguay. This connection makes the Paraguay River a critical corridor for wildlife migration and a vital component of South America's freshwater ecosystems.
The Paraná River: Border and Energy Source
The Paraná River is an extraordinary natural feature, the second-longest river in South America after the Amazon, spanning approximately 4,880 kilometers (3,030 miles) through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina. The Paraná River forms part of Paraguay's southern border with Argentina and is one of the major rivers in South America, serving as a significant waterway for trade and navigation. The river's importance to Paraguay has been significantly enhanced by the construction of two major hydroelectric dams, which have transformed the nation's energy landscape.
The Paraná River's flow and seasonal variations have a significant impact on Paraguay's economy and energy security. Both the Parana and Paraguay Rivers are loaded with sediment; the Paraguay contains tan sediment, and the Parana contains reddish-brown muddy sediment, reflecting the diverse geological regions they drain. This sediment load, while creating fertile floodplains, also presents challenges for dam operations and navigation.
The Guaraní Aquifer: Hidden Water Treasure
Beneath Paraguay's surface lies one of the world's most significant underground water resources: the Guaraní Aquifer System. This massive transboundary aquifer, shared among Paraguay, Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay, represents the second-largest known aquifer system globally, covering approximately 1.2 million square kilometers with an estimated volume of 40,000 cubic kilometers. The aquifer contains approximately 37,000 cubic kilometers of freshwater, making it a strategic resource that sustains over 30 million people across the four countries, including Paraguay's entire population.
The Guaraní Aquifer provides Paraguay with exceptional water security and serves as a critical backup to the country's extensive surface water systems. Water from the aquifer is accessible at depths ranging from 50 to 1,500 meters, with a natural recharge rate of approximately 166 cubic kilometers per year. The aquifer's water temperatures range from 33°C to 65°C, offering potential for both drinking water supply and geothermal energy applications. This underground reservoir complements Paraguay's abundant surface water, providing a reliable source during periods of drought or seasonal variations in river flow that could impact hydroelectric generation.
The management of the Guaraní Aquifer presents both opportunities and challenges for Paraguay's long-term water strategy. While the aquifer's substantial capacity provides resilience against water scarcity, its transboundary nature requires careful coordination with neighboring countries to ensure sustainable extraction and prevent overexploitation. The absence of a comprehensive binding legal framework governing the aquifer's use underscores the importance of regional cooperation in managing this shared resource. For Paraguay, the Guaraní Aquifer serves as a cornerstone of national water security, offering a critical foundation for future development while requiring responsible stewardship to preserve this invaluable resource for future generations.
Hydroelectric Reservoirs and Artificial Lakes
Itaipu Reservoir: Engineering Marvel
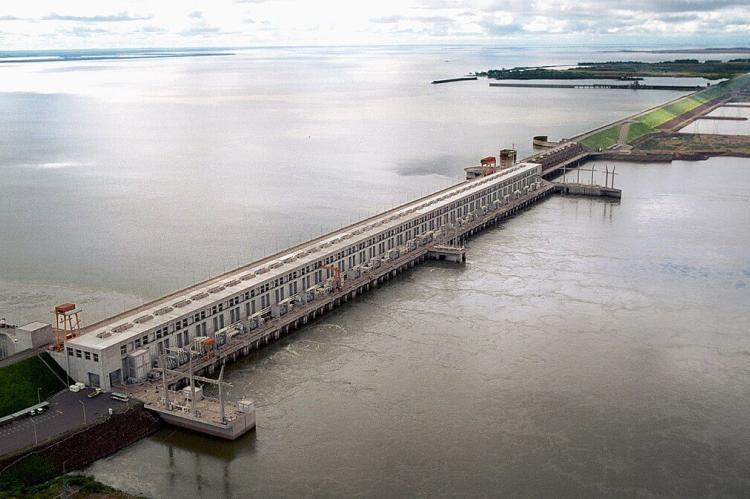
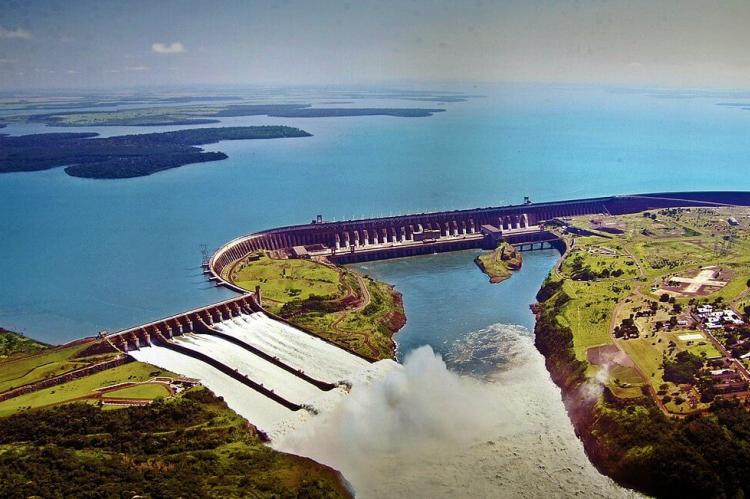
The Itaipu Dam, constructed on the Paraná River between Paraguay and Brazil, has created one of the world's largest artificial lakes and represents one of the most significant hydroelectric projects in human history. This dam creates a reservoir (artificial lake) of about 29,000 cubic hectometers of water, with approximately 200 kilometers of straight-line extension and an approximate area of 1,400 square kilometers. The Itaipu project involved the construction of a 7,919-meter-long and 196-meter-high dam designed to form an artificial lake that accumulates water.
The creation of the Itaipu Reservoir came at significant environmental and social costs. Approximately 65,000 people were displaced – 40,000 on the Brazilian side and 25,000 on the Paraguayan side - with resettlement occurring in coordination between the governments and Itaipu Binacional. The company paid compensation of USD 190 million to the displaced populations. When it was built, it made the Guairá Falls extinct, but when the water level drops, part of these waterfalls, which were once among South America's most spectacular natural features, can still be glimpsed beneath the reservoir's surface.
The economic importance of Itaipu to Paraguay cannot be overstated. The dam is a major source of electricity for both countries, particularly Paraguay, which relies heavily on the dam as a structural element of its economy, with around 10% of the country's public revenues derived from the dam's operations. This massive infrastructure project has fundamentally altered Paraguay's economic landscape, transforming it from an agricultural economy to one increasingly dependent on energy exports.
Yacyretá Reservoir: Binational Cooperation
The Yacyretá Dam or Jasyretâ-Apipé Hydroelectric Power Station (from Guaraní jasy retã, "land of the moon") is a dam and hydroelectric power plant built over the waterfalls of Jasyretâ-Apipé in the Paraná River, between the Paraguayan City of Ayolas and the Argentine Province of Corrientes. The Yacyretá Dam is a significant hydroelectric power plant located on the Paraná River, jointly operated by Paraguay and Argentina. The reservoir created by the dam spans both countries and serves as an essential source of hydroelectric power.
The Yacyretá hydroelectric project, a joint Paraguayan-Argentine effort in the Yacyretá-Apipé islands zone of the Paraná River, was established by a 1973 treaty. However, delays hindered its construction, and the plant operated below capacity for many years due to a lack of financing. Despite these challenges, the project represents an important example of international cooperation in water resource management and energy development.
Natural Lakes and Wetlands
Lake Ypoá and Lake Vera: Paraguay's Natural Water Bodies
Paraguay's natural lake systems are relatively modest compared to its massive river systems and artificial reservoirs. The major bodies of water in Paraguay are Lake Ypoá and Lake Vera, with the largest of the two, Lake Vera, draining into the Ñeembucú plain, a large expanse of marshland. These natural water bodies play important roles in local ecosystems and provide habitat for numerous species of waterfowl, fish, and other aquatic life.
Lake Ypoá, situated in the central region of Paraguay, serves as a vital freshwater resource for local communities and supports traditional fishing practices. The lake's seasonal variations reflect the broader patterns of precipitation and river flow that characterize Paraguay's climate. Lake Vera, located in the southern wetlands, is a critical component of the Ñeembucú wetland complex, serving as a natural flood control system and supporting diverse wildlife populations.
River Tributaries and Drainage Patterns
Eastern Tributaries of the Paraguay River
Important eastern tributaries of the Paraguay River include, from north to south, the Apa, Aquidabán, Ypané, Jejuí Guazú, and Tebicuary. These tributaries drain the eastern highlands of Paraguay and play crucial roles in the country's water resource management. The Apa River forms part of the northern border with Brazil and provides important water resources for agricultural activities in the region.
The Tebicuary River, one of the most significant eastern tributaries, flows through important agricultural regions and supports irrigation systems that are vital for Paraguay's soybean and cattle production. The river's watershed encompasses a diverse range of ecosystems, from subtropical forests in the headwaters to extensive grasslands in the lower reaches.
Western Tributaries and the Pilcomayo River
The only important tributary flowing from the west is the sluggish Pilcomayo, which joins the Paraguay near Asunción and originates in the northwest of Bolivia. The Pilcomayo River represents one of the most challenging waterways in South America due to its high sediment load and constantly changing course. The river's behavior has led to ongoing disputes among Paraguay, Argentina, and Bolivia regarding navigation rights and water allocation.
The Pilcomayo's significance extends beyond its role as a water source, as it provides habitat for numerous species adapted to its unique sediment-rich environment. The river's seasonal flooding creates extensive wetlands that support important wildlife populations and provide crucial ecosystem services.
Paraná River Tributaries
Except for the Acaray and Ytambey rivers, the streams that flow into the Paraná have little economic significance. However, these tributaries play important roles in local water supply and ecosystem function. The Acaray River, in particular, has been developed for hydroelectric generation and provides water for industrial activities in the southeastern region of Paraguay.
The Pantanal Wetlands
The northern region of Paraguay encompasses part of the world's largest tropical wetland complex, the Pantanal. This vast ecosystem, which spans Brazil, Bolivia, and Paraguay, represents one of the most biodiverse regions on the Planet. The Paraguayan portion of the Pantanal covers approximately 15,000 square kilometers (5,792 square miles) and supports exceptional wildlife populations, including jaguars, giant otters, caimans, and over 650 bird species.
The Pantanal's seasonal flooding cycle creates a dynamic landscape that alternates between vast lakes during the wet season and extensive grasslands during the dry season. This natural rhythm has shaped the evolution of unique plant and animal communities, which are adapted to the extreme variations in water levels. The region's importance extends beyond its ecological value, as it serves as a critical source of freshwater for downstream communities and helps regulate regional climate patterns.
The Chaco Region: Arid Landscapes and Scarce Water
The Chaco region is one of the most sparsely populated areas in South America due to its challenging terrain and harsh environment. This vast plain, which covers approximately 60% of Paraguay's territory, presents significant challenges for water resource management due to its arid climate and limited surface water availability. The region's water resources consist primarily of seasonal streams, temporary wetlands, and underground aquifers that support scattered communities and extensive cattle ranching operations.
The Chaco's hydrological challenges have led to innovative water management strategies, including the construction of artificial ponds and the development of deep well systems to access groundwater resources. The region's unique ecosystems have adapted to water scarcity, with many species exhibiting remarkable drought tolerance and specialized water conservation behaviors.
Climate Variability and Water Security
Paraguay's water resources are significantly influenced by climate variability, particularly the El Niño and La Niña phenomena that affect precipitation patterns and river flows throughout the region. The giant Itaipu hydroelectric power plant, wedged between Paraguay and Brazil on the Parana River, is facing an energy crunch amid record-low river and rainfall levels, highlighting the vulnerability of the country's energy system to climate variability.
Drought conditions can severely impact both hydroelectric generation and agricultural productivity, while excessive rainfall can lead to devastating floods that affect thousands of residents. The country's water management strategies must strike a balance between the need for reliable energy production, flood control, and the preservation of its ecosystems. In this context, the Guaraní Aquifer provides crucial resilience, offering a stable water supply that is less vulnerable to short-term climate variations than surface water systems.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Paraguay's water bodies support exceptional biodiversity and provide essential ecosystem services that benefit both local communities and the global environment. The country's rivers and wetlands serve as crucial corridors for wildlife migration, connecting diverse habitats across the South American continent. These aquatic ecosystems support numerous endemic species and provide critical habitat for endangered wildlife, including the giant otter, marsh deer, and various species of waterfowl.
The ecosystem services provided by Paraguay's water bodies include flood control, water purification, carbon sequestration, and climate regulation. The extensive wetlands act as natural sponges, absorbing excess water during flood events and releasing it slowly during dry periods. This natural water management system helps protect downstream communities from flooding while maintaining water availability during periods of drought.
Economic Importance and Development Challenges
Paraguay's water resources form the foundation of the country's economy, with hydroelectric exports generating substantial revenue and supporting industrial development. The country's strategic position between Brazil and Argentina has made it a crucial link in regional energy markets, while its rivers provide essential transportation routes for agricultural exports.
However, the concentration of economic activity around major water bodies has created environmental pressures and social challenges. Urban development along riverbanks has led to water pollution and habitat degradation, while the construction of large dams has altered natural river flows and displaced communities. Balancing economic development with environmental protection remains a significant challenge for Paraguay's water resource management.
International Cooperation and Transboundary Issues
Paraguay's major rivers are shared with neighboring countries, requiring extensive international cooperation for effective water resource management. The country participates in several regional agreements and organizations focused on sustainable water use, including the Treaty of the River Plate Basin and various bilateral agreements with Brazil and Argentina.
Transboundary water management involves complex negotiations regarding water allocation, environmental protection, and economic development. The success of projects like Itaipu and Yacyretá demonstrates the potential for international cooperation, while ongoing disputes over navigation rights and environmental impacts highlight the challenges of managing shared water resources. The Guaraní Aquifer presents similar challenges and opportunities for regional cooperation, as its sustainable management requires coordination among all four countries that share this vital underground resource.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
Climate change poses significant challenges to Paraguay's water resources, with projected changes in precipitation patterns potentially affecting river flows and hydroelectric generation. The country's heavy dependence on hydroelectric power makes it particularly vulnerable to climate-related changes in water availability.
However, Paraguay's abundant water resources also present opportunities for sustainable development. The country's potential for additional hydroelectric development, combined with its strategic position in regional energy markets, presents opportunities for continued economic growth through renewable energy exports. The Guaraní Aquifer adds another dimension to these opportunities, providing a foundation for long-term water security that could support expanded agricultural and industrial development. Sustainable management of these resources will require balancing energy development with environmental protection and social equity, while ensuring that both surface and groundwater systems are managed in harmony to maximize benefits.
Summary
Paraguay's water bodies represent a remarkable confluence of natural abundance and human engineering that has fundamentally shaped the nation's identity and economic development. The country's position at the heart of South America, defined by the Paraguay and Paraná rivers and underlain by the vast Guaraní Aquifer, has created unique opportunities for hydroelectric development while presenting ongoing challenges for sustainable water resource management. From the vast wetlands of the Pantanal to the massive reservoirs of Itaipu and Yacyretá, Paraguay's surface and groundwater resources demonstrate both the potential and complexity of water-based development in the 21st century. The transformation from an agricultural economy to a regional energy powerhouse illustrates the profound impact that water resources can have on national development. As climate change and growing energy demands create new challenges, Paraguay's future depends on continued regional cooperation, environmental conservation, and adaptive management strategies that recognize the interconnected nature of surface and groundwater resources, energy security, and ecological sustainability.
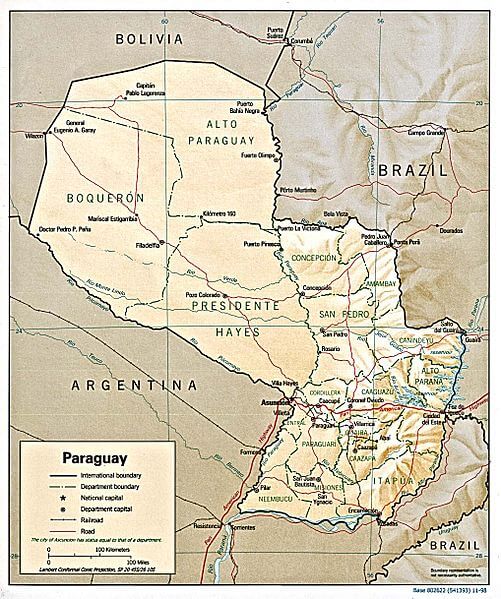
Shaded relief map of Paraguay.
Notable Water Bodies of Paraguay
Major Rivers
- Paraguay River: 2,550 km (1,585 mi), North-south through central Paraguay
- Paraná River: 4,880 km total (3,030 mi), Southern border with Argentina
- Pilcomayo River: 1,100 km (684 mi), Northwestern border and western tributary
- Tebicuary River: 360 km (224 mi), Eastern Paraguay to Paraguay River
- Apa River: 370 km (230 mi), Northern border with Brazil
- Aquidabán River: 200 km (124 mi), Eastern Paraguay to Paraguay River
- Jejuí Guazú River: 220 km (137 mi), Eastern Paraguay to Paraguay River
- Ypané River: 280 km (174 mi), Eastern Paraguay to Paraguay River
- Acaray River: 150 km (93 mi), Eastern Paraguay to Paraná River
- Ytambey River: 120 km (75 mi), Eastern Paraguay to Paraná River
Artificial Lakes and Reservoirs
- Itaipu Reservoir: 1,400 km² (540 sq mi), Eastern Paraguay-Brazil border
- Yacyretá Reservoir: 1,600 km² (618 sq mi), Southern Paraguay-Argentina border
- Republic Lake: 25 km² (9.7 sq mi), Caaguazú Department
- Acaray Reservoir: 15 km² (5.8 sq mi), Alto Paraná Department
Natural Lakes and Wetlands
- Lake Vera: 45 km² (17 sq mi), Ñeembucú Department
- Lake Ypoá: 35 km² (14 sq mi), Central Paraguay
- Pantanal Wetlands (Paraguay portion): 15,000 km² (5,792 sq mi), Northern Paraguay
- Ñeembucú Wetlands: 8,000 km² (3,089 sq mi), Southern Paraguay
- Esteros del Iberá (Paraguay portion): 500 km² (193 sq mi), Southern Paraguay
Hydrographic Regions
- Paraguay River Basin: 410,000 km² (158,301 sq mi), Central and western Paraguay
- Paraná River Basin: 90,000 km² (34,749 sq mi), Eastern Paraguay
- Pilcomayo River Basin: 50,000 km² (19,305 sq mi), Northwestern Paraguay
- Tebicuary River Basin: 12,000 km² (4,633 sq mi), Eastern Paraguay
Transboundary Water Bodies
- Paraná River System: Shared with Brazil and Argentina
- Paraguay River System: Shared with Brazil, Bolivia, and Argentina
- Pilcomayo River System: Shared with Bolivia and Argentina
- Apa River System: Shared with Brazil
- Itaipu Reservoir: Shared with Brazil
- Yacyretá Reservoir: Shared with Argentina
Seasonal Wetlands and Flood Plains
- Central Chaco Wetlands: 25,000 km² (9,653 sq mi), Western Paraguay
- Eastern Pantanal: 15,000 km² (5,792 sq mi), Northern Paraguay
- Paraguay River Floodplains: 5,000 km² (1,931 sq mi), Central Paraguay
- Pilcomayo River Delta: 2,000 km² (772 sq mi), Northwestern Paraguay





