SINAC, Costa Rica's National System of Conservation Areas: A Model of Conservation and Biodiversity
SINAC, Costa Rica's National System of Conservation Areas, is a model for conservation efforts worldwide. With its numerous national parks and other protected areas, Costa Rica has dedicated over a quarter of its landmass to conservation, making it one of the most biodiverse countries on Earth.
SINAC, Costa Rica's National System of Conservation Areas
A Model of Conservation and Biodiversity
Costa Rica's National System of Conservation Areas is a model for conservation efforts worldwide. With over 26 national parks and numerous other protected areas, Costa Rica has dedicated over a quarter of its landmass to conservation. This commitment to protecting its natural resources has made Costa Rica one of the most biodiverse countries on Earth, home to over 500,000 species of plants and animals.
SINAC, which stands for Sistema Nacional de Áreas de Conservación in Spanish, is the National System of Conservation Areas in Costa Rica. SINAC is a government agency responsible for managing, conserving, and protecting Costa Rica's vast and diverse natural heritage. Established in 1994, SINAC oversees the country's extensive protected area network, including national parks, wildlife refuges, and other conservation zones.
-
Management of Protected Areas: SINAC is primarily tasked with managing and overseeing Costa Rica's system of protected areas, encompassing many ecosystems, from rainforests and cloud forests to wetlands and marine environments. This involves establishing conservation policies, regulations, and plans for each protected area, ensuring that these areas are adequately protected and maintained.
-
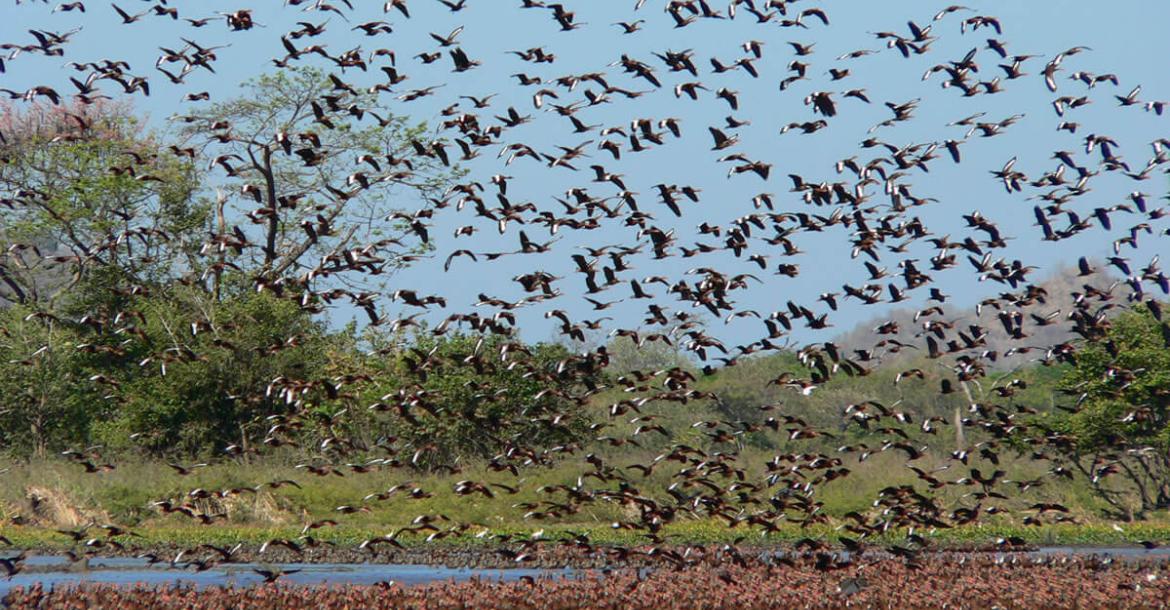
Biodiversity Conservation: SINAC is vital in conserving Costa Rica's rich biodiversity. The agency focuses on protecting the country's diverse flora and fauna by implementing strategies for habitat preservation, wildlife monitoring, and the conservation of endangered species.
-
Sustainable Tourism: SINAC promotes and regulates sustainable tourism within protected areas. By collaborating with local communities and tour operators, the agency helps ensure that tourism activities do not harm the environment but contribute to conservation efforts. The revenue generated from ecotourism often goes back into supporting the protected areas.
-
Research and Monitoring: SINAC conducts or supports scientific research and monitoring activities to better understand the ecosystems within the protected areas. This research helps make informed decisions about conservation strategies, managing resources, and adapting to environmental changes.
-
Community Involvement: SINAC recognizes the importance of involving local communities in managing protected areas. Collaboration with local stakeholders is crucial for achieving successful conservation outcomes. By working together, communities and SINAC can find sustainable solutions that benefit conservation and livelihoods.
-
Environmental Education: SINAC is involved in environmental education programs to raise awareness among Costa Ricans and visitors about the importance of conservation. These initiatives aim to instill a sense of responsibility and environmental stewardship in the population.
-
Climate Change Mitigation: Given the global challenges posed by climate change, SINAC is actively involved in projects to mitigate and adapt to climate change impacts. This includes reforestation and other activities designed to sequester carbon and protect vulnerable ecosystems.
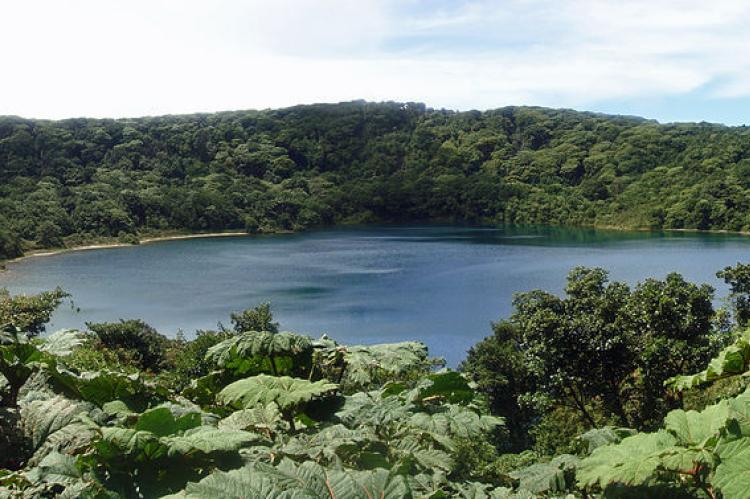
A Diverse Range of Ecosystems
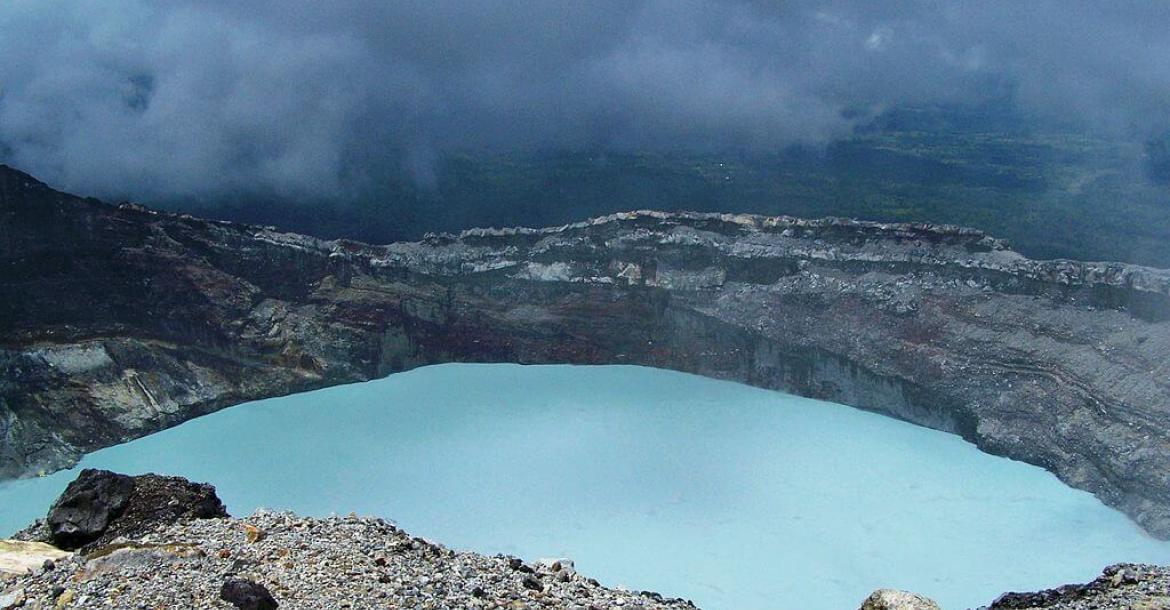
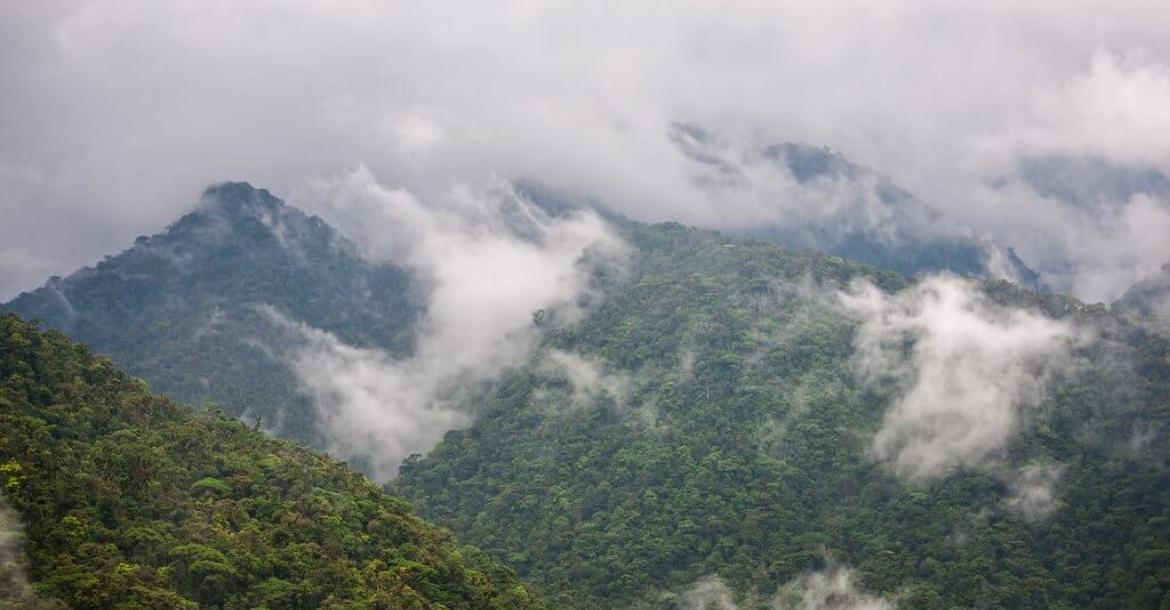
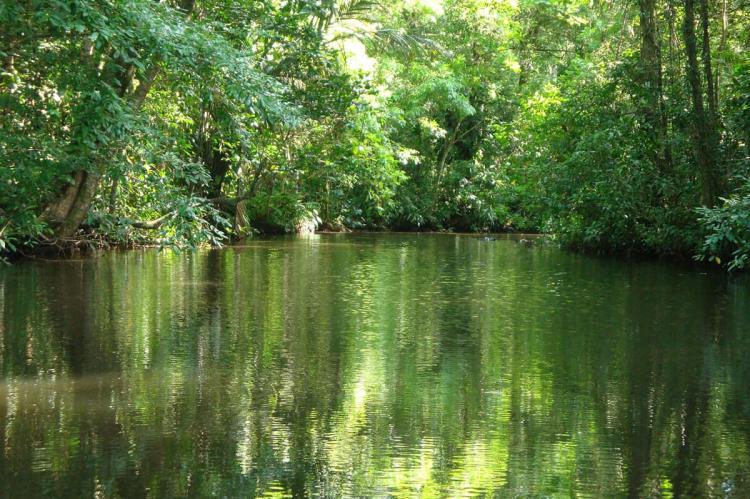
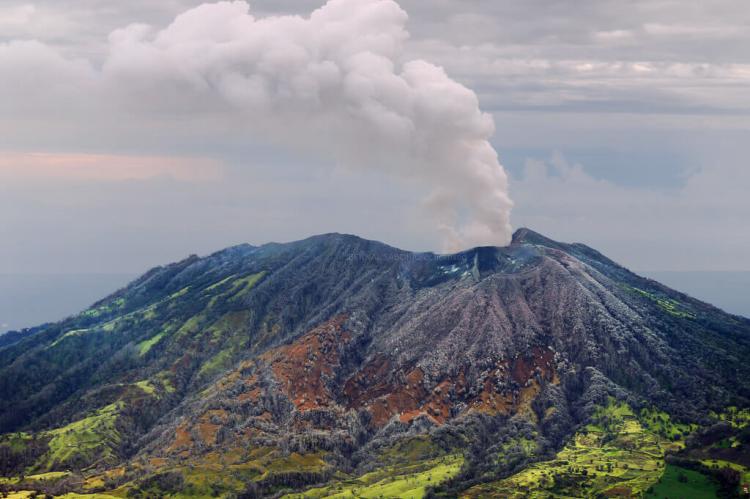
Costa Rica's diverse geography, featuring Pacific and Caribbean coasts, towering mountains, active volcanoes, and lush rainforests, has resulted in various ecosystems. These ecosystems support an astonishing array of flora and fauna, from colorful toucans and elusive jaguars to unique amphibians and many plant species.
Tourists worldwide flock to Costa Rica to experience its pristine natural beauty, and the National Parks provide an ideal platform for this. Eco-conscious visitors can explore these protected areas through various activities, including hiking, birdwatching, wildlife photography, and guided nature tours. Moreover, the revenue generated from tourism is reinvested into park management and conservation efforts, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the parks.
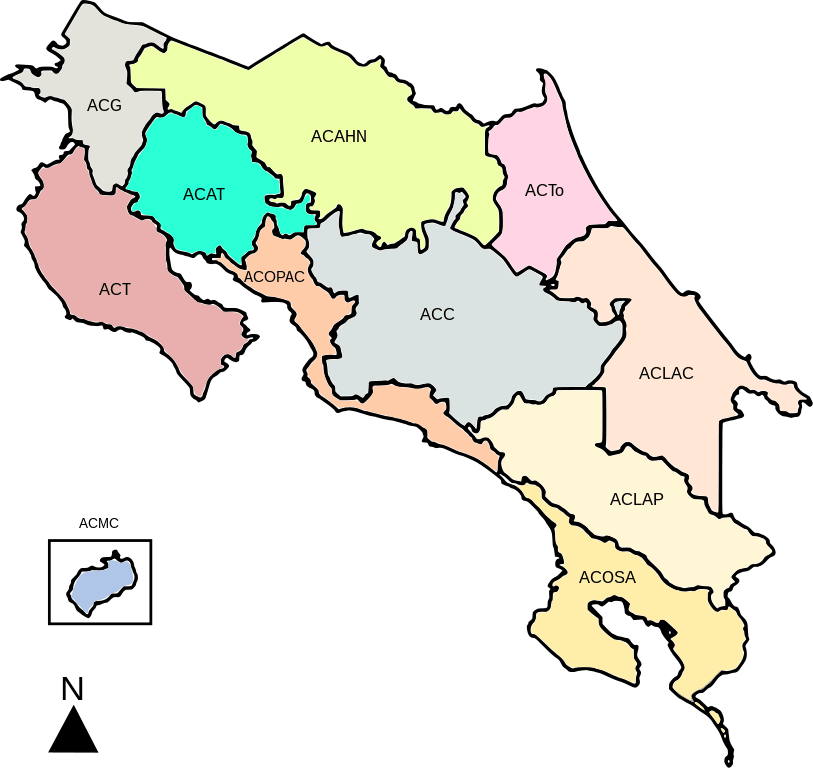
SINAC Areas Map
Conservation Areas
Costa Rica's Conservation Areas are vital to the country's natural heritage. They protect many ecosystems and wildlife and play an essential role in promoting sustainable development. The eleven conservation areas in Costa Rica that are part of SINAC are as follows:
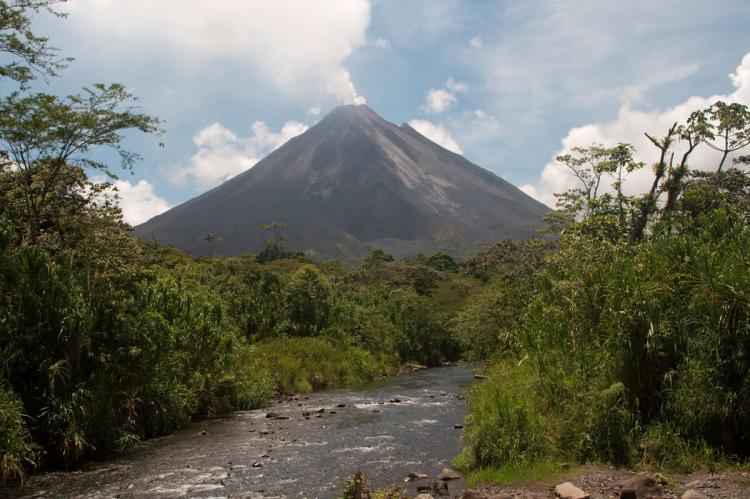
Arenal Huetar Norte Conservation Area (ACAHN)
This conservation area is located in the northern part of the country and encompasses a region characterized by its striking volcanic landscapes, including the iconic Arenal Volcano. This area is known for its lush rainforests, abundant wildlife, and scenic beauty.
Tortuguero Conservation Area (ACTo)
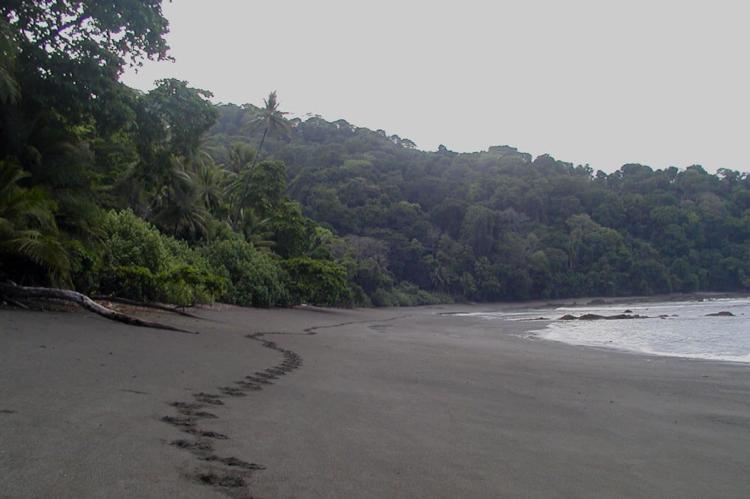
This conservation area is situated on the Caribbean coast and is renowned for its extensive network of canals and waterways. It is a critical nesting site for sea turtles and features lush rainforests, wildlife, and beautiful beaches.
Tempisque Conservation Area (ACT)
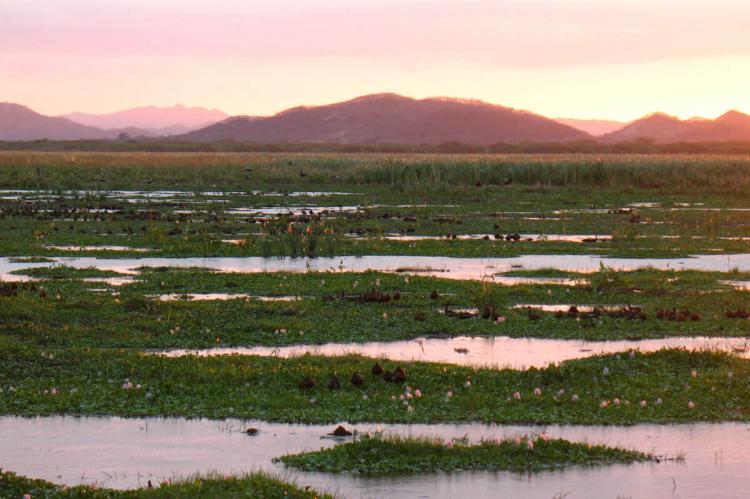
This conservation area, located in the country's northwestern part, is characterized by its extensive wetlands, mangroves, and river systems. It is home to diverse bird species and serves as a vital habitat for wildlife.
Pacífico Central Conservation Area (ACOPAC)
Situated along the central Pacific coast of the country, this conservation area encompasses a wide range of ecosystems, including rainforests, mangroves, and marine environments.
-
Carara National Park
Osa Conservation Area (ACOSA)
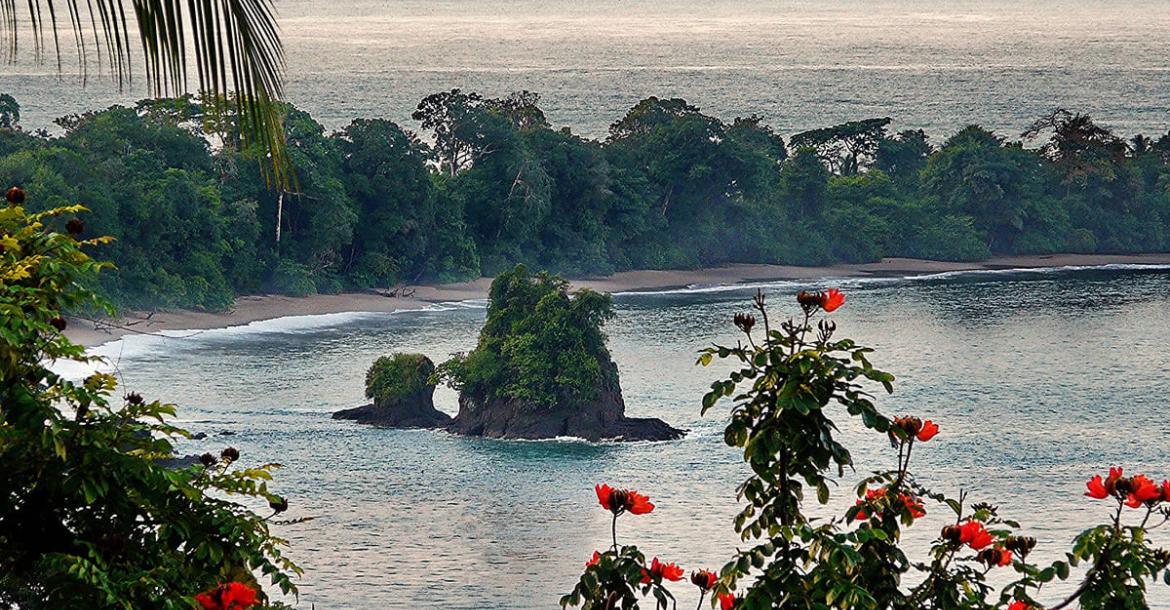
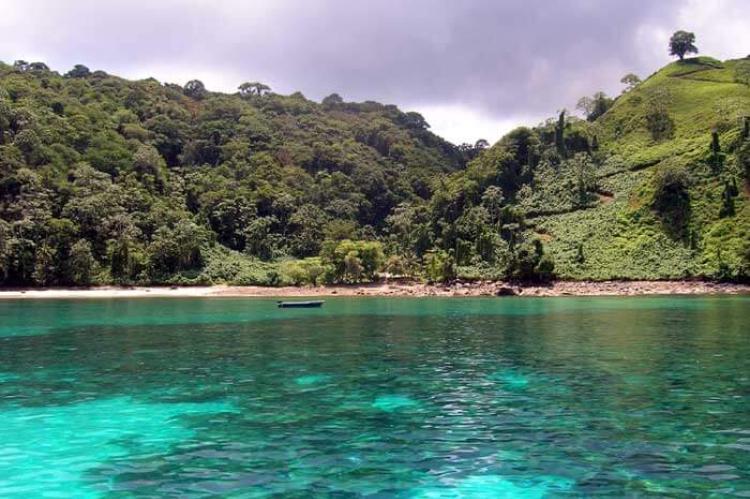
Located on the Osa Peninsula in the southern part of the country, this conservation area is celebrated for its pristine tropical rainforests, abundant wildlife, and remote, unspoiled beaches. Within this area lies one of the most biodiverse places on Earth.
-
Marino Ballena National Park
La Amistad Pacífico Conservation Area (ACLAP)
This conservation area is located on the Pacific side of the Cordillera de Talamanca mountain range in the southern part of the country, bordering Panama. It is home to many ecosystems, including rainforests, cloud forests, and páramos. It is also home to various wildlife, including jaguars, tapirs, and macaws.
La Amistad Caribe Conservation Area (ACLAC)
This conservation area is located on the Caribbean side of the Cordillera de Talamanca mountain range in the eastern part of the country, bordering Panama. It is home to many ecosystems, including rainforests, cloud forests, and Caribbean coastlines. It is also home to various wildlife, including jaguars, tapirs, and macaws.
Guanacaste Conservation Area (ACG)
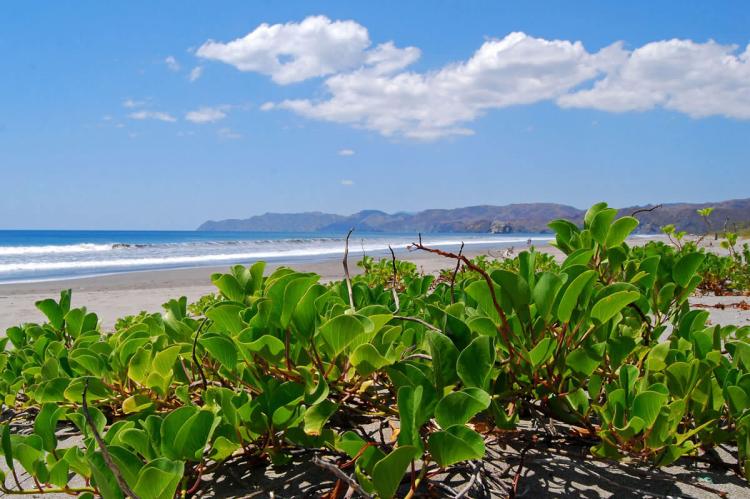
Guanacaste Conservation Area is located in the country's northwestern part and is home to many ecosystems, including dry forests, rainforests, cloud forests, and coastal areas. It is also home to various wildlife, including jaguars, tapirs, and macaws.
-
Murciélago National Park
Coco Marine Conservation Area (ACMC)
Covering over 2.4 million hectares (9,200 square miles) of marine and coastal habitat, this conservation area is located in the Pacific Ocean, about 535 km (332 mi) southwest of the mainland. It is home to various marine life, including sharks, dolphins, whales, turtles, and seabirds. It is also home to various coral reefs, mangroves, and other coastal ecosystems.
Central Conservation Area (ACC)
This conservation area is located in the central part of the country and includes six national parks, several wildlife refuges, and other types of nature reserves. It is home to a wide range of ecosystems, including rainforests, cloud forests, and volcanoes, as well as a variety of wildlife, including jaguars, tapirs, and macaws.
Arenal Tempisque Conservation Area (ACAT)
Located in the country's northwestern part, this conservation area includes the Arenal and Tenorio volcanoes. It is home to a wide range of ecosystems, including rainforests, cloud forests, and dry forests, as well as a variety of wildlife, including jaguars, tapirs, and macaws.






















