Guaraní Aquifer: Navigating the Depths of South America's Vital Aquifer System
The Guaraní Aquifer System is a colossal underground reservoir beneath Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Named in homage to the Guaraní peoples who once inhabited its expanse, this hydrogeological marvel is known for its sheer size and critical role in sustaining life across the region.
Guaraní Aquifer: Navigating the Depths of South America's Vital Aquifer System
The Guaraní Aquifer System (GAS) is a colossal underground reservoir that weaves beneath the South American territories of Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Named in homage to the Guaraní peoples who once inhabited a significant portion of its expanse, this hydrogeological marvel has garnered global attention for its sheer size and critical role in sustaining life across the region.
The geological foundations of the Guaraní Aquifer are rooted in the Triassic and Jurassic periods, where fluvial and aeolian sandstones of the Piramboia and Botucatu sedimentary formations were deposited. This geological history, spanning millions of years, has endowed the aquifer with a unique composition, making it an invaluable freshwater repository.
Geographical Extent
Encompassing an astounding 1,200,000 square kilometers (463,300 square miles), the GAS sprawls across northeastern Argentina, southern Brazil, southeastern Paraguay, and northern Uruguay. Its thickness ranges from 50 to 600 meters (165 to 2,000 feet), with an average depth of approximately 250 meters (800 feet). Remarkably, it is recognized as one of the largest sandstone aquifers on Earth.
The transboundary nature of the Guaraní Aquifer emphasizes the shared responsibility of the countries it spans. Approximately 70% of the aquifer lies beneath the subsoil of south-central Brazil, while Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay account for the remaining 30%. The interconnectedness of these nations necessitates collaborative efforts to ensure sustainable management and protection of this vital resource.
River Network
The Guaraní Aquifer is intricately interwoven with the hydrological network of six major South American rivers. Stretching beneath the Paraná, Paraguay, Uruguay, Bermejo, Salado, and Pilcomayo rivers, its influence extends across national borders, shaping the aquatic landscapes and ecosystems of Argentina, Brazil, and Paraguay.
Economic Importance
Approximately 24 million people reside within the defined boundaries of the Guaraní Aquifer, relying on its pristine waters for sustenance. Beyond these boundaries, a staggering 70 million individuals are directly or indirectly influenced by its intricate web. The aquifer's significance as a lifeline for human settlements underscores the imperative to balance human needs with sustainable conservation practices.
The Guaraní Aquifer serves as a primary source of drinking water, meeting the daily needs of millions across the four participating nations. Beyond domestic consumption, its waters support industrial processes such as agricultural irrigation and contribute to thermal tourism. In Brazil's São Paulo State, the aquifer's exploitation reaches its zenith, constituting 80% of the total extraction rate.
Challenges and Conservation
The extensive use of the Guaraní Aquifer poses challenges, including the potential for over-extraction and contamination. Sustainable water management practices are crucial to ensure the long-term viability of this vital resource. International collaboration among the participating nations is essential to develop strategies that balance human needs with preserving the aquifer's ecological integrity.
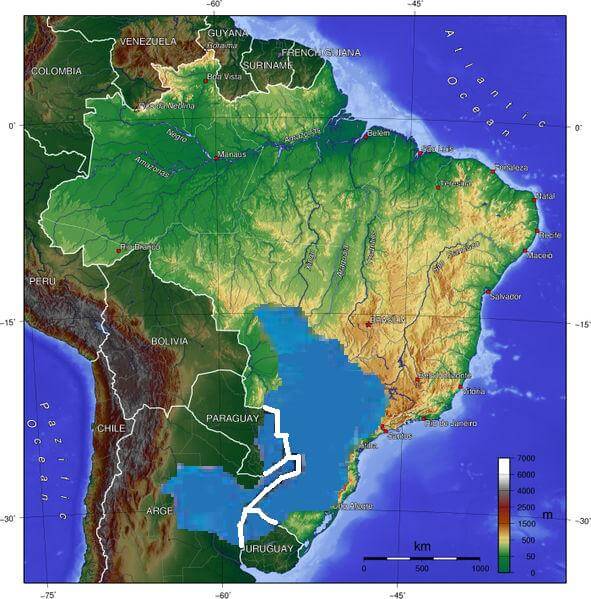
Topographic map depicting the location of the Guaraní Aquifer.
