The Hidden Wonders of Corcovado National Park
Corcovado National Park, located in the Los Lagos Region of southern Chile, stands as a testament to the country's dedication to preserving its natural heritage. It is Chile's fourth-largest national park and one of the world's most remote and untouched landscapes.
Corcovado National Park: A Sanctuary of Wilderness in Southern Chile
Corcovado National Park, located in the Los Lagos Region of southern Chile, stands as a testament to the country's dedication to preserving its natural heritage. Covering 400,011 hectares (988,450 acres), it is Chile's fourth-largest national park and one of the most remote and untouched landscapes in the world. Established in 2005, the park owes much of its existence to the generous land donation by Tompkins Conservation, which contributed over 84,000 hectares (207,570 acres). The park's isolation, challenging terrain, and lack of public access make it a pristine sanctuary for diverse flora and fauna.
Geography and Geology
Coastal and Volcanic Landscapes
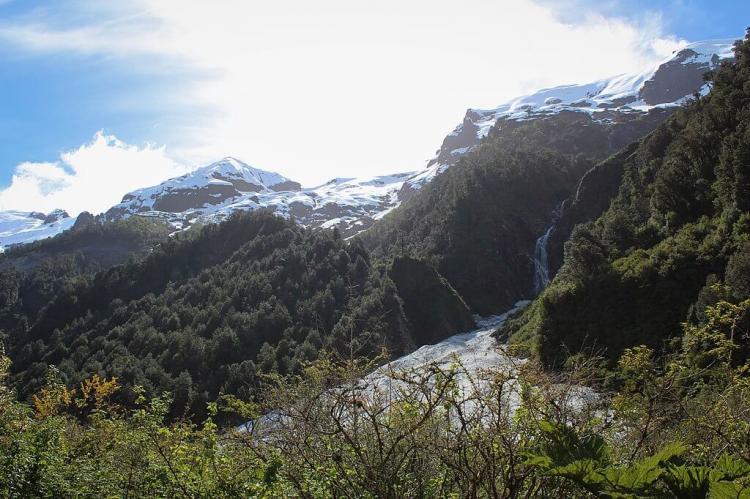
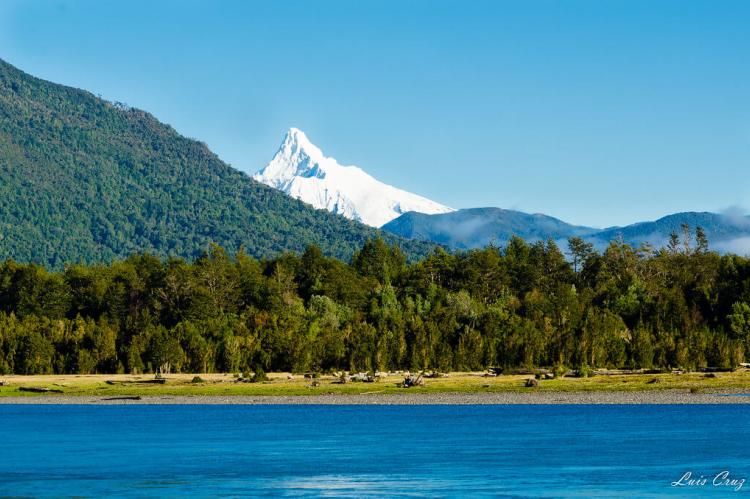
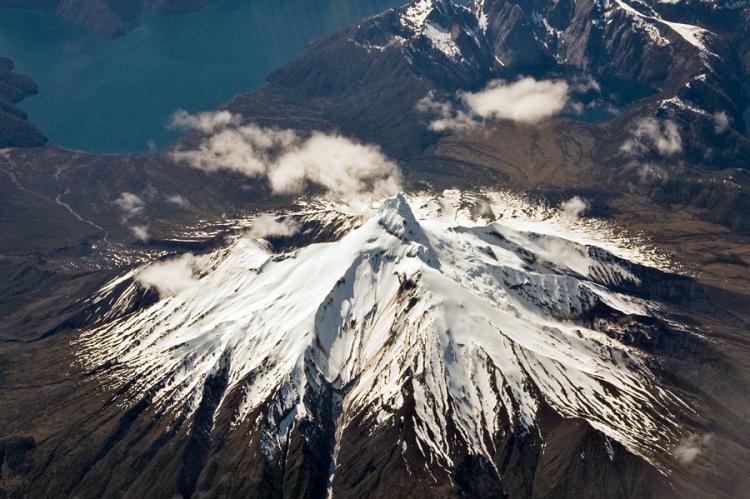
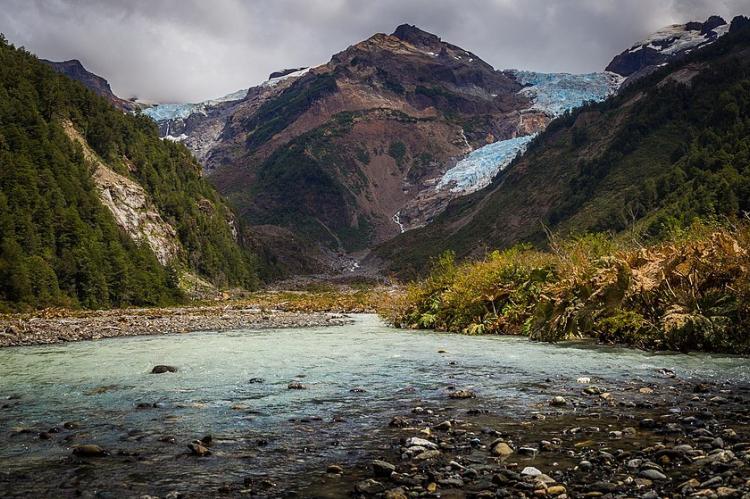
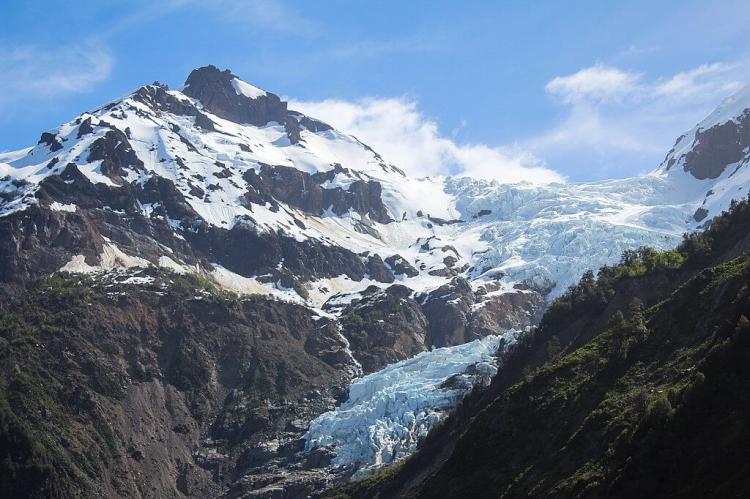
Corcovado National Park boasts a dramatic landscape with towering volcanoes and rugged coastlines. The park borders the Gulf of Corcovado to the west, creating a striking coastal boundary that separates mainland Chile from Chiloé Island. The Corcovado Volcano is the park's most prominent feature, standing at 2,300 meters (7,546 feet) above sea level. This stratovolcano, eroded by glaciers and flanked by Holocene cinder cones, is notable for its stepped top and densely vegetated base, which includes a series of lakes. Another significant volcanic feature is the Yanteles Volcano, an isolated stratovolcano with five glacier-capped peaks, the highest reaching 2,042 meters (6,699 feet).
Hidden Corners and Isolation
The park's remote and rugged terrain includes hidden corners of the Gulf of Corcovado and Tic Toc Bay in Chaitén. This isolation has preserved vast areas of unexplored land, maintaining their pristine condition and ensuring the protection of various ecosystems within the park.
Flora and Fauna
Rich and Diverse Vegetation
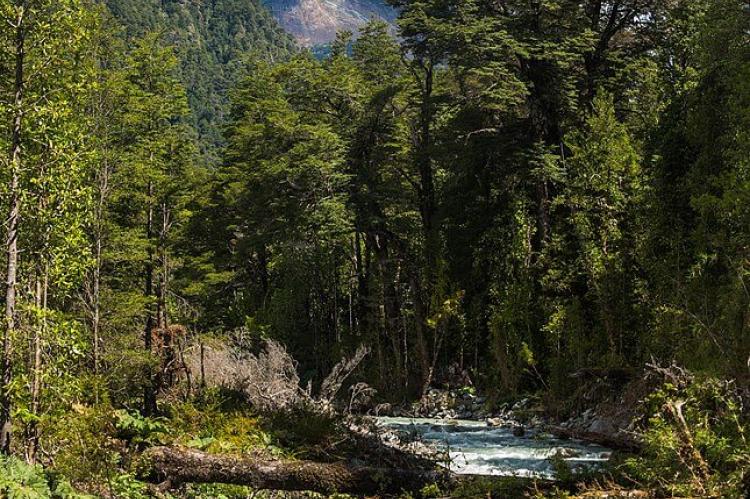
Corcovado National Park is home to a rich temperate rainforest ecosystem and deciduous high-mountain shrubland. The park receives an average annual rainfall of 2,800 mm (110 inches) and enjoys a mild climate, fostering thick forests of diverse tree species such as Canelo, Mañío, Lenga, Coigue, Ñirre, and Ciprés de las Guaitecas (Pilgerodendron).
Endangered and Unique Species
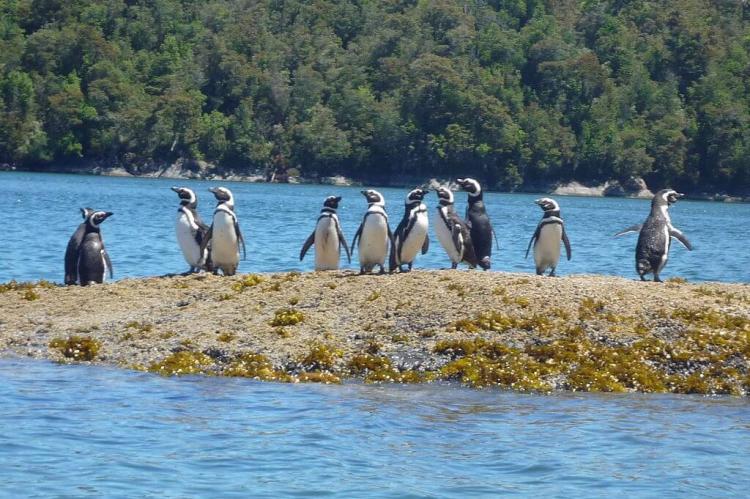
The park provides critical habitat for various endangered species. Notable mammals include the Pudú Deer, Chiloé Fox, Güiña (Kodkod), Huillín (southern river otter), monito del Monte (Colocolo Opossum), and Puma. The park's coastal areas and estuaries are vital for large colonies of marine birds, including the Magellanic penguin (Spheniscus magellanicus).
Marine Mammals and Blue Whales
Corcovado's coastal waters are rich in marine life, including seals, sea lions, and various whale species such as blue, humpback, pilot, and sperm whales. The Gulf of Corcovado serves as a critical nesting sanctuary for migratory blue whales, the largest mammals on earth, which are currently classified as endangered on the IUCN Red List.
Conservation and Management
Creation and Protection
The establishment of Corcovado National Park in 2005 marked a significant achievement in Chilean conservation. The park's creation resulted from a collaboration between Tompkins Conservation and the Chilean government, incorporating donated lands and national parklands into a single protected area.
Route of Parks
Corcovado National Park is a key component of Chile's scenic "Route of Parks," a 2,800 km (1,700 mi) trail that stretches from Puerto Montt in the north to Cape Horn in the south. This route encompasses 17 national parks, protecting over 11.8 million hectares (28 million acres) and highlighting the natural beauty and biodiversity of Patagonia.
Future Prospects
Conservation Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its remote location and current lack of public access, Corcovado National Park faces challenges in maintaining its pristine condition. Continued efforts are needed to protect its diverse ecosystems and endangered species. Future initiatives may include developing sustainable tourism infrastructure to allow public access while preserving the park's natural integrity.
Research and Education
Corcovado National Park offers valuable opportunities for scientific research and environmental education. Studying its unique ecosystems and species can provide insights into conservation strategies and contribute to global biodiversity knowledge.
Conclusion
Corcovado National Park is a hidden gem in southern Chile. It offers a unique blend of dramatic landscapes, rich biodiversity, and significant conservation efforts. Its volcanic peaks, pristine forests, and coastal waters make it a critical sanctuary for endangered species and a vital part of Chile's natural heritage.
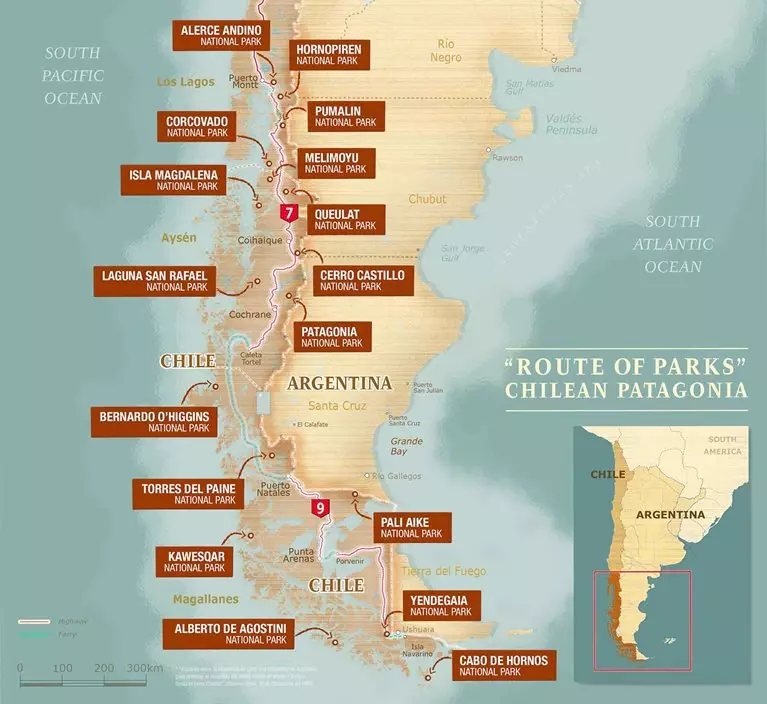
Chile's Route of Parks map - Thompson Conservation






