The Sierra Madre: Mexico's Magnificent Mountain Kingdom
The Sierra Madre mountain system forms a backbone that encloses the central Mexican Plateau. This vast and intricate network of ranges extends in a broad northwest-southeast arc, encompassing a kaleidoscope of landscapes, ecosystems, and cultural heritage that have shaped Mexico's essence.
The Sierra Madre: Mexico's Magnificent Mountain Kingdom
Stretching majestically across Mexico, the Sierra Madre mountain system forms an awe-inspiring backbone that encloses the central Mexican Plateau. This vast and intricate network of ranges, part of the mighty American Cordillera, extends in a broad northwest-southeast arc, encompassing a kaleidoscope of landscapes, ecosystems, and cultural heritage that have shaped the essence of Mexico.
The Imposing Sierra Madre Ranges
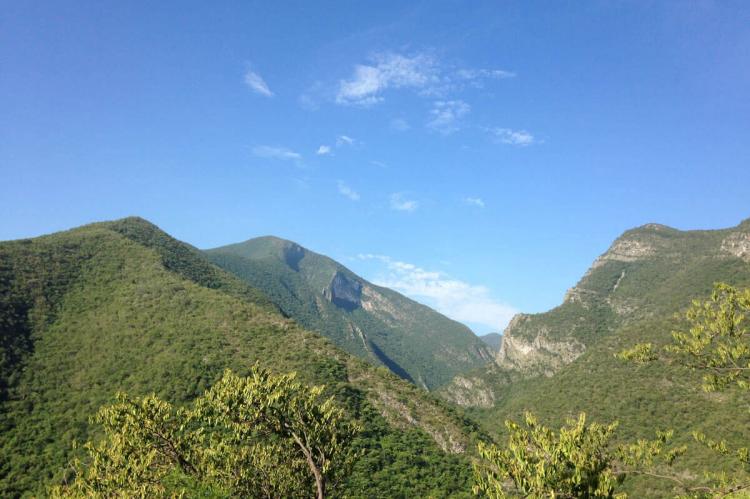
Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental, a primarily volcanic range, runs parallel to Mexico's Pacific coast for a staggering 1,250 kilometers (780 miles). Forming the western rampart of the Mexican Plateau, this formidable range is renowned for its deep, labyrinthine river valleys, or barrancas, the most spectacular of which is the Copper Canyon (Barranca del Cobre) in southwestern Chihuahua. This intricate network of canyons, more profound and vaster than the Grand Canyon, is a true geological marvel carved by the relentless forces of nature over millennia.
The uplift of the Sierra Madre Occidental has profoundly influenced the region's weather patterns, creating pockets of increased rainfall that have given rise to unique ecosystems within the surrounding arid landscapes. These verdant oases, such as the oak forests extending into the lowland deserts, are true islands of biodiversity, differing significantly from the desert vistas that would otherwise dominate the terrain.
The Continental Divide
The Continental Divide is intricately woven into the fabric of the Sierra Madre Occidental. This geological feature plays a pivotal role in shaping the flow of water and defining the watersheds of Mexico. This natural boundary serves as a crucial hydrological linchpin, separating the Pacific and Atlantic watersheds and influencing the distribution of water resources across the nation.
On the western side of the Sierra Madre Occidental, rivers and streams flow westward, descending the mountain slopes and eventually draining into the Pacific Ocean. This vast watershed encompasses a significant portion of western Mexico, nourishing the arid regions with the precious water that sustains life and enables agriculture.
Conversely, on the eastern side of the Sierra Madre Occidental, waterways flow eastward, following the contours of the land and ultimately contributing to the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, which are part of the vast Atlantic Ocean basin. This eastern watershed encompasses the central Mexican Plateau and the eastern states, providing vital water resources to the population centers and agricultural regions that dot this region.
The Continental Divide, therefore, serves as a natural boundary, separating these two distinct watersheds and influencing the distribution of water resources across the nation. Its integration with the Sierra Madre Occidental is a testament to the intricate interplay between the geological formations and the hydrological cycles that shape Mexico's landscape.
Furthermore, the Continental Divide has played a significant role in shaping the ecosystems and biodiversity of the Sierra Madre mountain system. The varying precipitation patterns and water availability on either side of the divide have given rise to distinct ecological communities, each adapted to the specific environmental conditions dictated by the water flow.
Lush forests and riparian habitats thrive on the wetter western slopes, sustained by the abundant water resources flowing towards the Pacific. In contrast, the eastern slopes and central plateau regions are characterized by a more arid climate, where hardy desert and semi-arid ecosystems have evolved to use the limited water resources available efficiently.
The presence of the Continental Divide, intricately woven into the fabric of the Sierra Madre Occidental, adds another layer of complexity and diversity to this remarkable mountain system. It underscores the intricate relationships between geology, hydrology, and biology that have shaped Mexico's natural wonders over millennia.
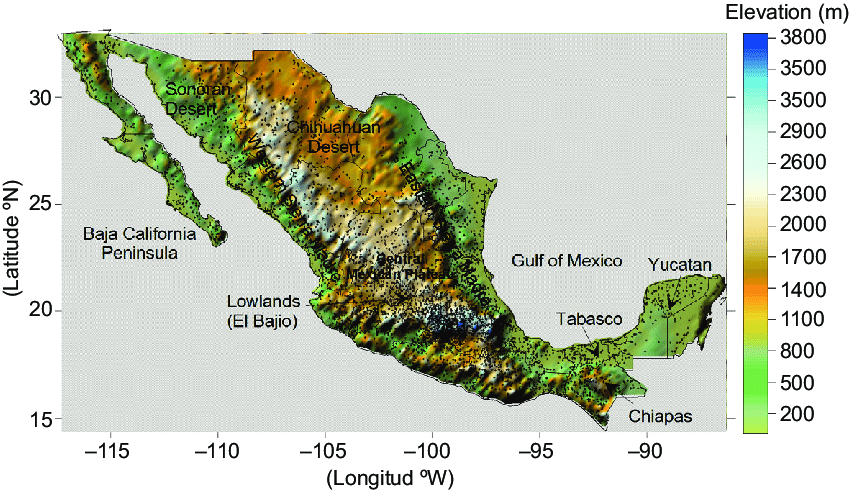
Elevation map of Mexico, including its main topography features.
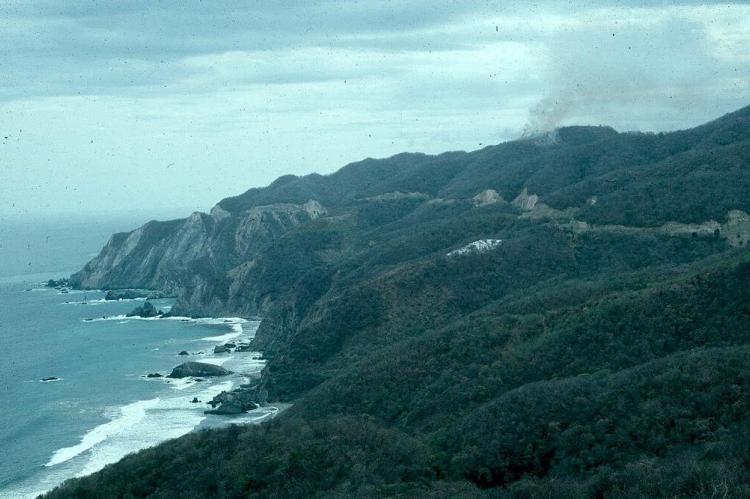
Sierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental extends an impressive 1,000 kilometers (620 miles) from the Rio Grande on the border with Texas southward through the Mexican states of Nuevo León, Tamaulipas, San Luis Potosí, Querétaro, Hidalgo, and northern Puebla. This range is a true repository of biodiversity, harboring an abundance of endemic plant and wildlife species from the arid northern regions to the lush, moisture-rich southern areas.
The northernmost reaches of the Sierra Madre Oriental, including the Sierra del Burro and the Sierra del Carmen, extend into the United States, where they continue as the Davis and Guadalupe Ranges in Texas. This seamless integration of mountain systems across international borders underscores the interconnectedness of the Earth's geological tapestry.
Sierra Madre de Oaxaca
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is a rugged mountain range in southern Mexico, primarily in the state of Oaxaca. Its peaks average an impressive 2,500 meters (8,200 feet) in elevation, with some towering giants exceeding 3,000 meters (9,800 feet). This range is characterized by its wetter eastern slopes, which intercept moisture-laden winds from the Gulf of Mexico. These slopes sharply contrast with the drier valleys to the west, sheltered in the range's rain shadow.
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is home to the Sierra Madre pine–oak forests ecoregion, which thrives above 1,600 meters (5,200 feet) in elevation. On the eastern slopes, the humid Oaxacan montane forests ecoregion flourishes below this altitude, cascading towards the Veracruz lowlands.
Sierra Madre del Sur
The Sierra Madre del Sur extends for an impressive 1,000 kilometers (620 miles) from south Michoacán through Guerrero to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca. It is a renowned biodiversity hotspot. Its highest point, a towering 3,703 meters (12,149 feet), stands sentinel in central Guerrero, offering breathtaking vistas to those who brave its lofty heights.
This range is particularly noteworthy for its remarkable diversity of ecosystems, from the Sierra Madre del Sur pine–oak forests that cloak its higher reaches to the tropical dry forests and subtropical dry broadleaf forests that blanket its lower elevations, creating a tapestry of natural wonders.
Sierra Madre de Chiapas
The southernmost extension of the Sierra Madre system, the Sierra Madre de Chiapas, extends beyond Mexico's borders into Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras. This range is not only a testament to the region's geological interconnectedness but also a repository of rich cultural heritage. Indigenous communities such as the Maya have called these mountains home for centuries.
The Sierra Madre de Chiapas is renowned for its lush cloud forests and tropical rainforests, which harbor an extraordinary array of plant and animal life, many species of which are found nowhere else on Earth.
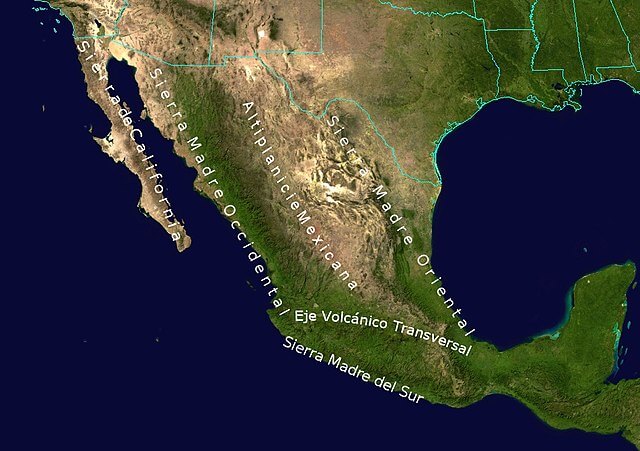
Topographic map of Mexico: Sierra Madre System.
Ecological Treasures
The Sierra Madre mountain system is an ecological marvel, harboring unparalleled biodiversity in North America. From the wetter regions in the south, where lush rainforests and cloud forests thrive, to the drier northern reaches, where resilient desert ecosystems cling to life, the Sierra Madre ranges support an astounding array of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to the region.
For instance, the uplift of the Sierra Madre Occidental has created distinct microclimates and ecosystems, with increased mountain rainfall providing verdant oases amidst the surrounding arid landscapes. These pockets of biodiversity, such as the oak forests extending into the lowland deserts, are true ecological treasures, harboring an incredible diversity of life that has adapted to these unique conditions over countless generations.
Similarly, the Sierra Madre Oriental and Sierra Madre de Oaxaca are renowned for their abundant biodiversity. Their various ecoregions, which include pine–oak forests, tropical moist forests, and dry scrublands, each support distinctive flora and fauna.
Cultural Tapestry
In addition to its natural wonders, the Sierra Madre mountain system holds immense cultural significance for Mexico, serving as a tapestry upon which the rich tapestry of the nation's heritage has been woven over millennia. Indigenous communities, such as the Tarahumara in the Sierra Madre Occidental and the Zapotec and Mixtec in the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca, have called these mountains home for centuries, preserving their rich traditions, languages, and ways of life in harmony with the rugged landscapes that have nurtured them.
The Sierra Madre ranges have also played a pivotal role in shaping Mexico's history and cultural identity. They have served as refuges for rebel movements and preserved ancient customs and practices that might otherwise have been lost to the tides of time. These mountains' rugged terrain and remote locations have afforded a degree of isolation and protection, allowing indigenous cultures to flourish and maintain their unique identities in the face of external influences.
Moreover, the Sierra Madre has left an indelible mark on Mexico's arts and literature. Its towering peaks, plunging canyons, and diverse ecosystems have inspired countless writers, poets, and artists throughout the centuries, capturing the imagination of those who have witnessed its grandeur firsthand or through the pages of evocative prose.
Adventure and Exploration
The Sierra Madre mountain system offers many opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts and adventure seekers, beckoning those daring to explore its vast and varied landscapes. From the challenging hikes and treks that wind through the rugged terrain to the adrenaline-fueled pursuits of rock climbing and canyoning, the diverse topography of these ranges provides ample opportunities for exploration and adventure.
Popular destinations like the Copper Canyon in the Sierra Madre Occidental and the Sierra Gorda Biosphere Reserve in the Sierra Madre Oriental attract visitors worldwide. They offer breathtaking scenery, opportunities for cultural immersion, and a chance to experience the majesty of nature firsthand. Guided tours, eco-lodges, and adventure outfitters cater to those seeking to uncover the secrets of these ancient mountains, providing a gateway to exhilarating and enlightening experiences.
For those with a more contemplative spirit, the Sierra Madre offers a sanctuary for quiet reflection and rejuvenation. Remote hiking trails wind through pristine wilderness, and secluded campsites provide front-row seats to the natural grandeur that unfolds with each passing day.
Conservation and Sustainability
Recognizing the ecological and cultural significance of the Sierra Madre mountain system, various conservation efforts are underway to protect and preserve these natural wonders for future generations. Several national parks, biosphere reserves, and protected areas have been established throughout the ranges to safeguard the region's biodiversity and ensure the sustainable use of its resources.
Organizations such as the National Commission for Protected Natural Areas (CONANP) in Mexico work tirelessly to promote conservation efforts, engage local communities, and raise awareness about preserving these invaluable ecosystems. Through initiatives such as reforestation programs, wildlife monitoring, and sustainable tourism practices, these organizations strive to balance maintaining the Sierra Madre's natural heritage and promoting economic development for local communities.
One key challenge in conserving the Sierra Madre lies in harmonizing the needs of indigenous and rural communities, who have depended on these mountain ranges for their livelihoods and cultural practices for generations, with modern conservation efforts. By involving local stakeholders in decision-making processes and developing sustainable economic alternatives, such as ecotourism ventures and sustainable forestry practices, conservation initiatives aim to create a symbiotic relationship between people and nature.
Furthermore, establishing biosphere reserves, such as the Monarch Butterfly Biosphere Reserve in the Sierra Madre Oriental, is a model for integrating conservation, sustainable development, and research efforts. These reserves protect critical habitats for endangered species and provide opportunities for scientific exploration, environmental education, and the preservation of traditional ecological knowledge.
Another vital aspect of conservation efforts in the Sierra Madre is the promotion of connectivity and biological corridors. As human activities continue to fragment habitats, maintaining ecological connectivity between protected areas becomes crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of species and the resilience of ecosystems. Initiatives such as the Mesoamerican Biological Corridor, which spans from Mexico to Colombia, aim to create a network of protected areas and sustainable land-use practices, allowing for the free movement of wildlife and the exchange of genetic material.
Despite these efforts, the Sierra Madre mountain system continues to face numerous threats, including deforestation, illegal mining, and the impacts of climate change. Ongoing collaboration between government agencies, non-governmental organizations, academic institutions, and local communities is essential to address these challenges and develop comprehensive strategies to preserve this invaluable natural and cultural heritage long-term.
As we look to the future, the conservation and sustainable management of the Sierra Madre mountain system will play a pivotal role in ensuring the resilience of Mexico's ecosystems, the preservation of its rich biodiversity, and the continued well-being of the communities that call these mountains home. By embracing a holistic approach that recognizes the intricate connections between human societies and the natural world, we can safeguard the Sierra Madre's majesty for future generations.
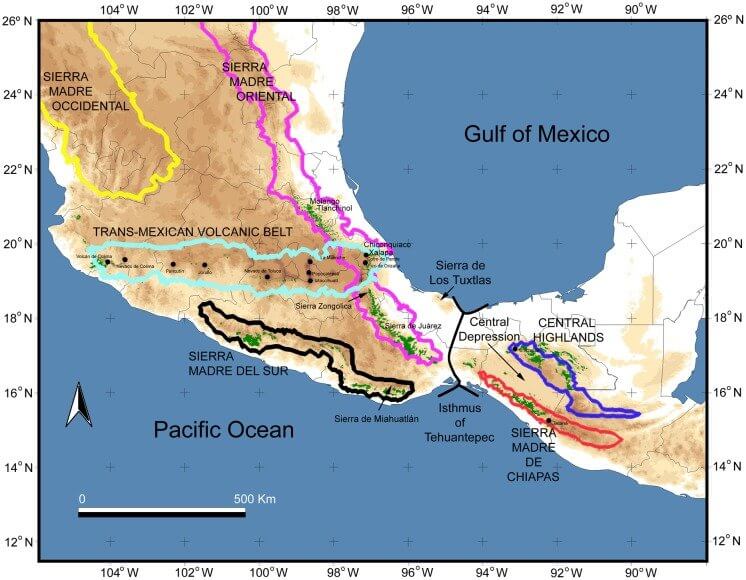
Topographic map of Mexico / Central America.
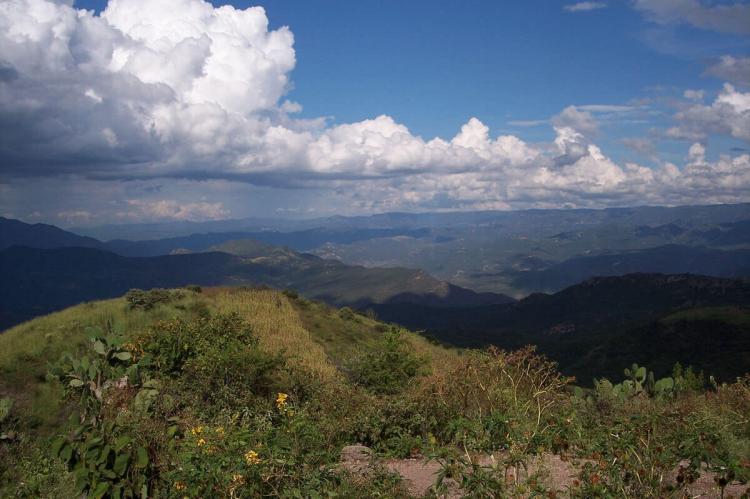

![Sierra Madre Occidental, looking across Rio San Ignacio from near the village of Guajurana - via Wikimedia Commons by Cataclasite [CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)] Sierra Madre Occidental, looking across Rio San Ignacio from near the village of Guajurana](/sites/default/files/styles/large/public/sierra_madre_occidental_volcanics_opt%20%281%29.jpg?itok=_vHyQan-)



