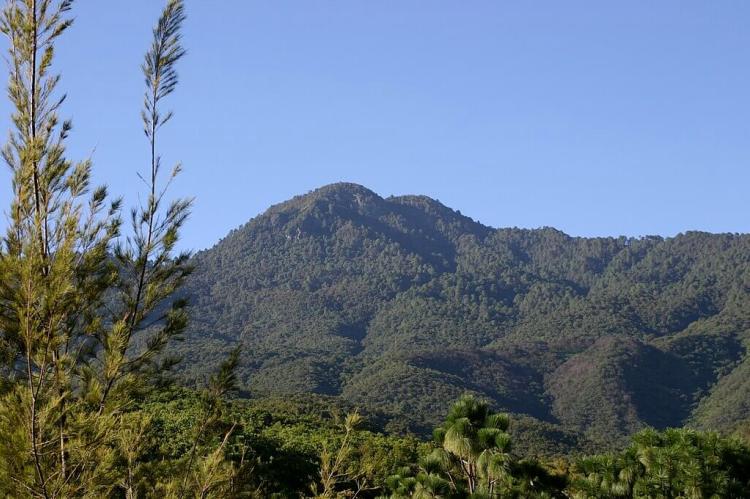
The Heart of Southern Mexico: The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is one of Mexico's most biologically and culturally rich mountain ranges, spanning parts of Oaxaca, Puebla, and Veracruz. This range forms a crucial component of the Sierra Madre mountain system, linking the Sierra Madre Oriental to the east and the Sierra Madre del Sur to the south.
Exploring the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca: A Biodiversity Haven in Southern Mexico
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is one of Mexico's most biologically and culturally rich mountain ranges, spanning parts of Oaxaca, Puebla, and Veracruz. This range forms a crucial component of the Sierra Madre mountain system, linking the Sierra Madre Oriental to the east and the Sierra Madre del Sur to the south. Known for its rugged terrain and diverse ecosystems, the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca has played a pivotal role in shaping the environment, history, and cultures of southern Mexico.
Geographic Overview
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca, which stretches approximately 300 km (186 mi), is defined by a series of high ridges and deep valleys. Peaks within the range often exceed 3,000 m (9,840 ft), with Zempoaltépetl at 3,396 m (11,142 ft), one of the tallest. The Gulf Coastal Plain flanks the range to the north and the Central Valleys of Oaxaca to the south, creating a dramatic and ecologically significant landscape.
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca also acts as a key geographical divide, influencing weather patterns and river systems. Several important rivers, including the Papaloapan and Tehuantepec, originate within the range, supporting both human settlements and ecological systems. The range's proximity to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec enhances its ecological and cultural importance as a transition zone between the Pacific and Gulf regions.
Within the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca lies the Sierra Mazateca, a distinct subregion known for its steep terrain and rich biodiversity. This area is especially notable for its cloud forests and the cultural traditions of the Mazatec people, who have inhabited the region for centuries.
Ecological Significance
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is part of the Sierra Madre pine–oak forests ecoregion, which is recognized for its extraordinary biodiversity. These forests are characterized by a mix of pine and oak species, along with a variety of shrubs, ferns, and grasses. The composition of the vegetation shifts with altitude, from tropical dry forests at lower elevations to pine–oak woodlands and cloud forests at higher elevations.
This ecoregion provides habitat for numerous endemic species, including the Oaxaca hummingbird and the dwarf jay. It also hosts mammals such as the jaguar and white-tailed deer, as well as a wide array of reptiles and amphibians. The cloud forests, in particular, are known for their rich plant diversity, including bromeliads, orchids, and mosses, which thrive in humid environments.
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca's ecosystems play an essential role in regulating the regional climate, maintaining water cycles, and preventing soil erosion. They also support human livelihoods through agriculture, forestry, and ecotourism.
Cultural and Historical Importance
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca has long been a center of human activity. Indigenous groups, including the Zapotec, Mixtec, Chinantec, and Mazatec peoples, have lived in the region for thousands of years, cultivating the land and developing unique cultural traditions. The Sierra Mazateca, in particular, is renowned for its spiritual and cultural significance. Practices such as the use of medicinal plants and sacred rituals are deeply rooted in the local way of life.
The range is dotted with ancient archaeological sites, such as Monte Albán and Mitla, which testify to the ingenuity of these civilizations in adapting to the mountainous terrain. The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca also played a role in more recent history, serving as a refuge for communities during times of conflict, including the Mexican War of Independence. Today, the region continues to be a hub of cultural expression, with traditional crafts, music, and cuisine reflecting its rich heritage.
Economic Contributions
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is vital to the economy of southern Mexico. Agriculture remains a cornerstone of local livelihoods, with farmers growing crops such as maize, beans, and coffee. The region's forests provide timber, medicinal plants, and other resources, contributing to both local and national economies.
Ecotourism is an increasingly important economic activity, drawing visitors to the area's natural beauty and cultural landmarks. Hiking, birdwatching, and visits to Indigenous communities offer opportunities for sustainable tourism that benefits local populations while preserving the environment.
Environmental Challenges
Despite its ecological and cultural value, the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca faces numerous environmental threats. Logging and agricultural expansion drive deforestation and habitat loss, which pose significant risks to the region's biodiversity. Climate change exacerbates these issues, with rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns affecting ecosystems and water availability.
Mining and infrastructure development further threaten the region, often destroying habitats and polluting the water. Balancing economic development with environmental preservation is a critical challenge for the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts to protect the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca focus on preserving its unique ecosystems and supporting sustainable development. Protected areas like the Tehuacán-Cuicatlán Biosphere Reserve aim to safeguard critical habitats while promoting ecological research and ecotourism.
Community-led conservation initiatives are also making a difference. Indigenous groups and local communities play a key role in managing forests, restoring degraded lands, and protecting wildlife. Programs that encourage sustainable agriculture, reforestation, and renewable energy use are helping to mitigate environmental pressures.
International partnerships and funding mechanisms, such as those provided by the Global Environment Facility (GEF), further support conservation efforts in the region. Education and outreach initiatives are fostering greater awareness of the importance of preserving the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca's natural and cultural heritage.
Summary
The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is a testament to the interconnectedness of natural and human systems. As part of the Sierra Madre pine–oak forests ecoregion, it is a biodiversity hotspot with ecosystems that sustain both wildlife and human communities. Its cultural significance, economic contributions, and natural beauty make it a cornerstone of Mexico's heritage. However, the range faces pressing environmental challenges that require coordinated conservation and sustainable development efforts. By valuing and protecting this unique region, future generations can continue to benefit from its ecological, cultural, and economic riches.
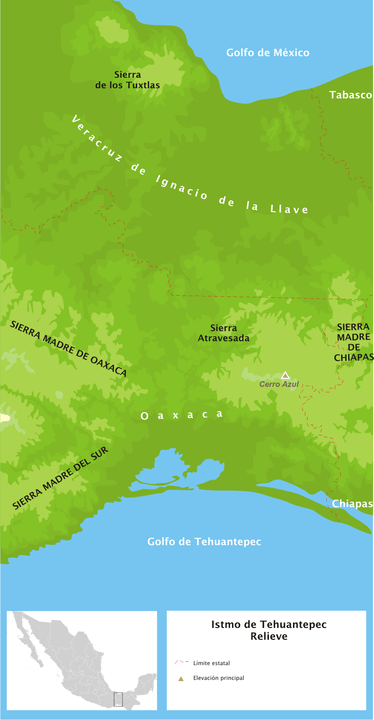
Relief map depicting the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in southeastern Mexico.
