Colombia: Natural Landscape
Nestled in northwestern South America, Colombia shares its borders with Panama to the northwest, Venezuela and Brazil to the east, and Ecuador and Peru to the south. Colombia spans diverse ecosystems, climates, and topographies as the fourth-largest country in South America.
The Natural Landscape of Colombia
Nestled in northwestern South America, Colombia shares its borders with Panama to the northwest, Venezuela and Brazil to the east, and Ecuador and Peru to the south. Colombia spans diverse ecosystems, climates, and topographies as the fourth-largest country in South America. From the snow-capped peaks of the Andes to the pristine beaches along the Caribbean and Pacific coasts, Colombia’s landscape is a tapestry of geographical extremes that form an impressive panorama of natural beauty.
Geographic Diversity and Major Landforms
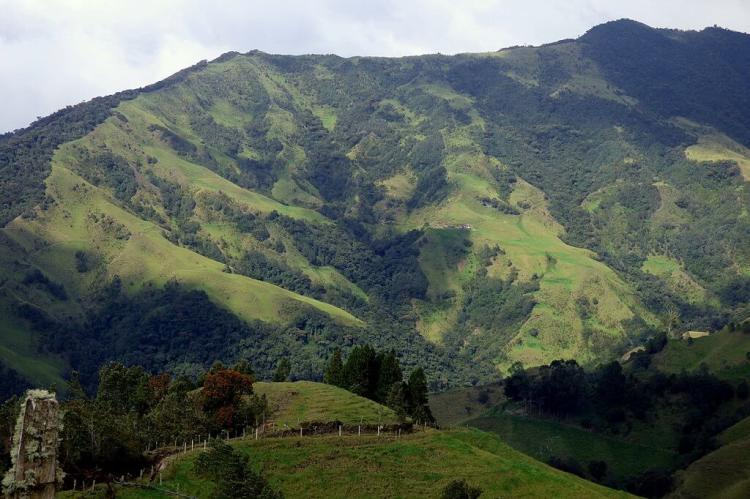
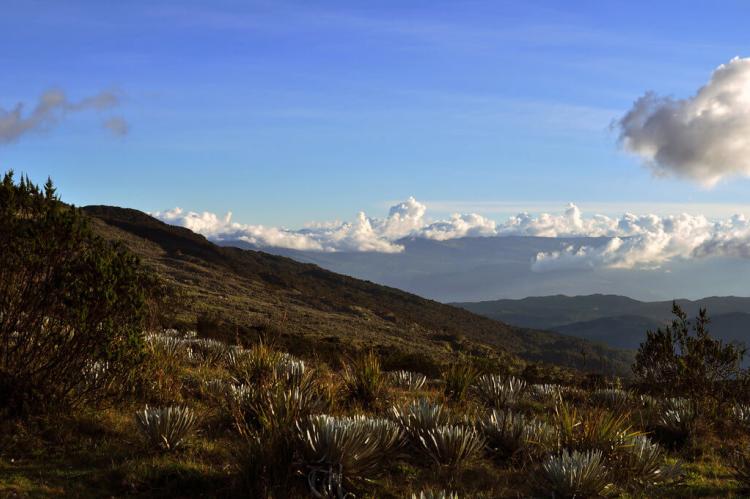
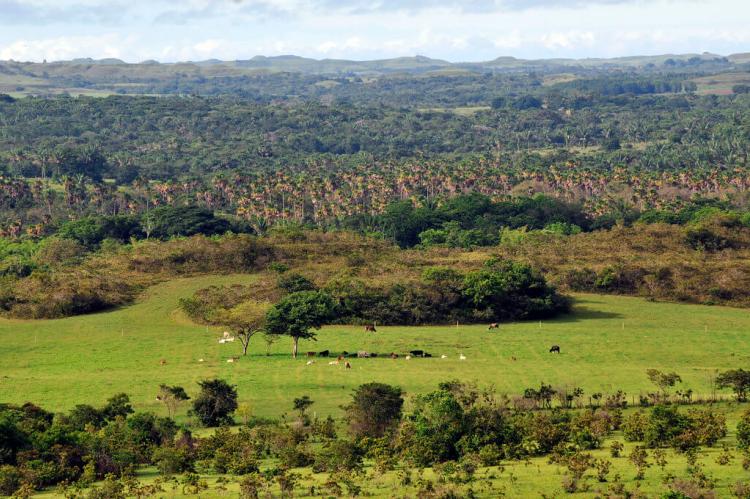
Colombia’s geographic diversity is one of its most striking features. Three main Andean mountain ranges traverse the country, providing snow-draped peaks, fertile valleys, and high-altitude plateaus. These rugged elevations give way to tropical rainforests, particularly in the Amazon basin and Pacific/Chocó regions, which are blanketed with lush vegetation and unique wildlife. Colombia’s eastern plains, known as the Llanos, are extensive grasslands supporting agricultural development and vast ecosystems, offering a distinctive contrast to the mountainous and coastal areas.
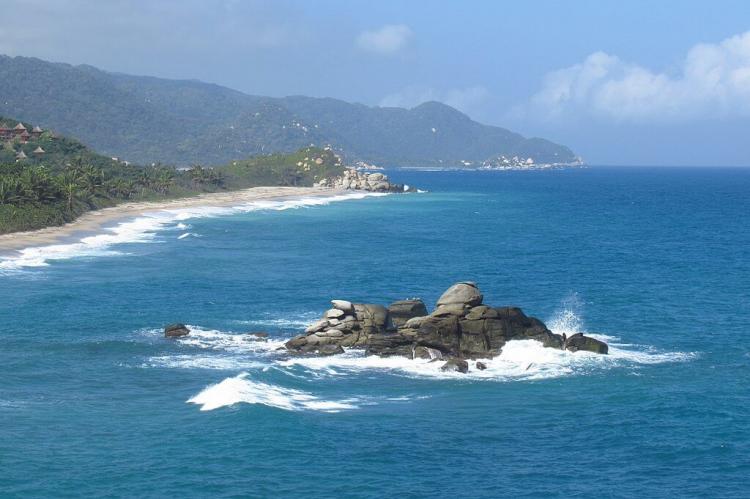
The country's coastal regions, including the Caribbean and Pacific coasts, are characterized by idyllic beaches, mangroves, and vibrant coral reefs. These coastlines support rich marine biodiversity, making Colombia a favored ecotourism and marine research destination. Colombia’s diverse ecosystems range from dense rainforests to high mountain páramos and sprawling savannas, each with a distinct array of plant and animal life.
Biodiversity: A Megadiverse Nation
Colombia ranks among the most biodiverse countries on Earth, distinguished as one of only 17 megadiverse countries globally. According to the Global Biodiversity Index, Colombia is home to an astonishing variety of species across its ecosystems, including 1,863 bird species, 812 amphibian species, 2,105 fish species, 477 mammal species, 634 reptile species, and approximately 24,025 plant species. This exceptional biodiversity is attributed to Colombia's varied landscapes and microclimates, which create a rich array of habitats.
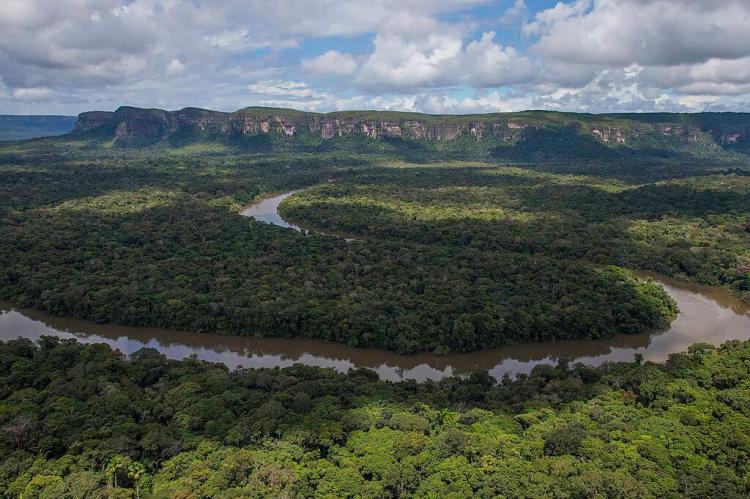
In the Amazon Basin, Colombia boasts one of the largest areas of tropical rainforest, where jaguars, capybaras, and vibrant macaws reside among countless other species. The Andes Mountains are home to species like the Andean condor and spectacled bear, while the coastal and oceanic regions offer thriving habitats for species such as sea turtles, dolphins, and tropical fish. The páramos, high-altitude ecosystems above 3,500 m (11,480 ft), support unique flora and fauna adapted to extreme conditions, including frailejones, large-leaved plants uniquely suited to the cold, wet climates.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Colombia’s commitment to conservation is evident in its extensive network of national parks and protected areas, which cover approximately 14% of the country. Protected areas like Chiribiquete National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, safeguard vast stretches of tropical rainforest and unique archaeological sites. The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta National Park is another critical conservation area, home to a diverse range of species and the Indigenous Kogi people, who maintain a deep spiritual connection to the land.
However, Colombia faces significant challenges in conservation due to pressures from illegal armed groups, deforestation linked to agriculture and cattle grazing, and land conflicts. These issues are compounded by illegal mining and illicit crop cultivation, which contribute to environmental degradation. Despite these challenges, Colombia is committed to advancing sustainable conservation practices, incorporating strategies to balance ecological preservation with sustainable development.
Climate: Diversity Across Altitudes
Due to its position near the equator, Colombia experiences relatively consistent temperatures year-round, with variations determined primarily by altitude rather than latitude. The country’s climate can be categorized into five main zones:
- Tierra Caliente (Hot Zone): This region, which includes the coastal areas and Amazon lowlands, experiences warm, humid weather with temperatures ranging from 24 to 32 °C (75 to 90 °F). Its elevation ranges from sea level to 1,000 m (3,280 ft).
- Tierra Templada (Temperate Zone): Located at 1,000 to 2,000 m (3,280 to 6,560 ft), the temperate zone has mild weather, with temperatures between 18 and 24 °C (64 to 75 °F). This region supports coffee production, as the cooler temperatures are ideal for coffee plants.
- Tierra Fría (Cold Zone): This zone, which spans altitudes of 2,000 to 3,000 m (6,560 to 9,840 ft), has cooler weather with temperatures from 13 to 18 °C (55 to 64 °F). It includes highland cities like Bogotá, where the climate supports crops like potatoes and barley.
- Tierra Helada (Frozen Zone): Above 3,000 m (9,840 ft), the frozen zone is characterized by cold weather with temperatures below 13 °C (55 °F), often experiencing frost.
- Páramos: These are unique high-altitude grasslands above 3,500 m (11,480 ft), with cold weather, strong winds, and high humidity. Páramos are vital for water regulation and biodiversity and are found only in a few regions of the world.
Colombia also has two primary seasons: a wet season from April to May and October to November, a dry season from December to January and July to August. The seasonal variation and diverse climate zones contribute to Colombia’s agricultural diversity, from coffee in the highlands to sugarcane and tropical fruits in the lowlands.
Volcanic Activity and the Pacific Ring of Fire
Positioned along the Pacific Ring of Fire, Colombia is home to numerous active and dormant volcanoes. This seismic region results from the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate, which creates intense volcanic activity. Over 20 active volcanoes, including Nevado del Ruiz, Galeras, and Puracé, are located in the Andes, forming part of Colombia's volatile yet beautiful volcanic landscapes.
Volcanic activity shapes the country’s physical geography and impacts local communities and ecosystems. Nevado del Ruiz, Colombia’s most notorious volcano, erupted catastrophically in 1985, claiming thousands of lives in the town of Armero. Despite the risks, Colombia's volcanoes enrich the soil and support diverse ecosystems, making them vital components of the country's natural landscape.
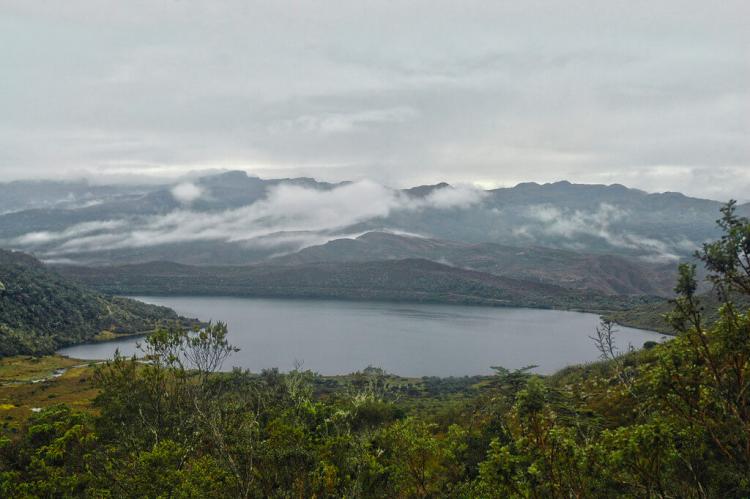
River Systems and Wetlands
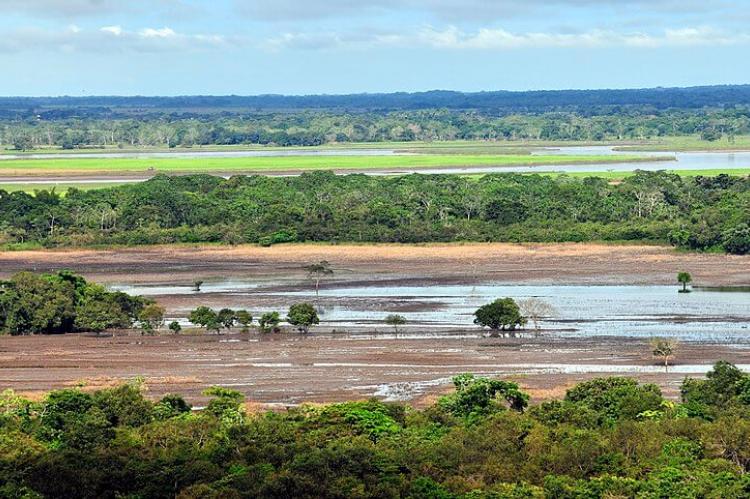
Colombia’s river systems are essential to its geography, with major rivers such as the Magdalena, Cauca, and Amazon flowing through the country. These rivers provide vital resources for transportation, agriculture, and freshwater supply. The Magdalena River, Colombia's principal river, runs the country's entire length, supporting numerous communities and industries.
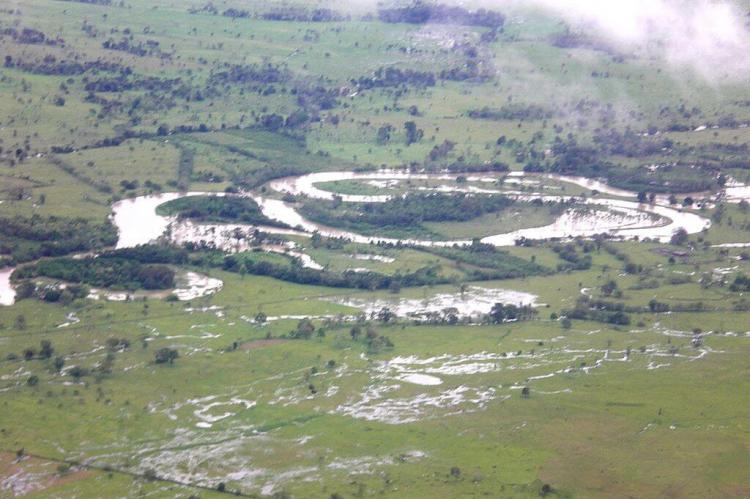
The Amazon and Orinoco river basins create expansive wetland ecosystems in Colombia's eastern plains. These wetlands are critical for water regulation, flood control, biodiversity, and housing species like giant otters, anacondas, and a range of migratory bird species. The Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta, a large marshland near the Caribbean coast, is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve recognized for its importance to migratory birds and its unique ecosystem.
Ecotourism and Sustainable Development
Colombia’s natural beauty and biodiversity attract ecotourists from around the world. The country offers sustainable tourism opportunities that benefit local communities and conservation efforts. Popular destinations include the Amazon rainforest, the Sierra Nevada mountains, and the vibrant coral reefs of the Caribbean. National parks and protected areas such as Tayrona and Los Nevados offer hiking, bird-watching, and educational tours that promote a deeper understanding of Colombia's natural heritage.
Ecotourism initiatives support sustainable development by providing alternative income sources for communities and raising awareness about the importance of environmental conservation. Many regions that once relied on deforestation or hunting have embraced ecotourism, allowing local economies to flourish in harmony with nature.
Conclusion
Colombia’s natural landscape is a remarkable fusion of mountains, forests, coastlines, and rivers, creating an unparalleled ecological diversity tapestry. Its unique position within the Pacific Ring of Fire contributes to the nation’s distinctive volcanic landscapes, while its varied altitude zones foster a wide range of climates and ecosystems. As one of the world’s most biodiverse countries, Colombia serves as a sanctuary for thousands of species and a source of natural resources that sustain its people.
Despite facing challenges such as deforestation, land conflicts, and the impacts of climate change, Colombia continues to prioritize conservation and sustainable development. Through its commitment to protecting its national parks and promoting ecotourism, Colombia offers a model of ecological preservation that acknowledges its people's needs and the importance of its natural heritage. As the world increasingly recognizes the value of preserving diverse ecosystems, Colombia stands as a testament to the beauty and resilience of nature.
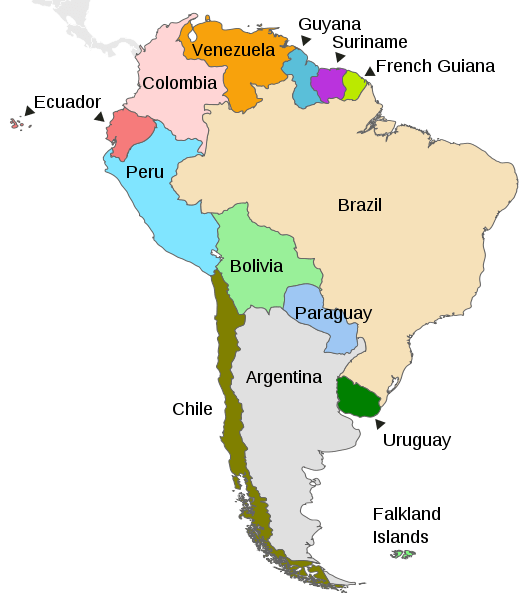
Map depicting the countries on the continent of South America
Colombia's Diverse Natural Regions: A Tapestry of Landscapes
Colombia's remarkable biodiversity and varied ecosystems are best understood through its classification into six distinct natural regions, each shaped by unique geographical and climatic factors. These regions, recognized for their characteristic landscapes, flora, fauna, and human influences, paint a vivid picture of the country's natural wealth:
- The Caribbean Region: in the north
- The Pacific/Chocó Region: in the west
- The Andean Region: at the center
- The Orinoco Region: in the east
- The Amazon Region: in the south
- The Insular Region: in the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean
The Caribbean Region: Where Tropics Meet History
The Caribbean Natural Region, stretching along Colombia's northern coast from the Gulf of Uraba in the west to the Guajira Peninsula in the east, is a land where tropical warmth embraces historical significance. As the first areas settled by Europeans, it cradles the historic port cities of Cartagena and Santa Marta.
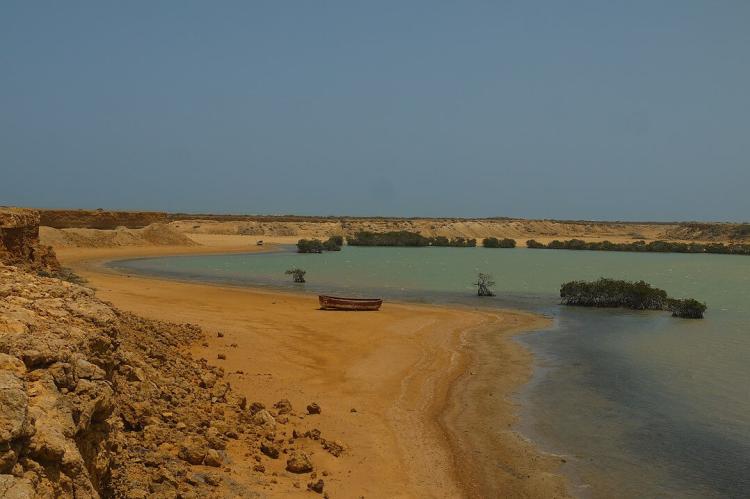
This region is traversed by vital rivers originating in the Andean highlands, most notably the Magdalena River, Colombia's principal waterway, which empties into the Caribbean Sea. The diverse ecosystems here range from humid and dry forests to expansive savannas and crucial wetlands, punctuated by the dramatic Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta mountain range, rising sharply from the coast, and the arid landscapes of the Guajira Desert.
Characterized by a hot and humid climate year-round, the Caribbean coast experiences an average temperature of 27 °C (81 °F) and high humidity of around 80%. Its seasonal rhythms include a wet period from May to November and a drier phase from December to April.
The Pacific/Chocó Region: A Biodiversity Hotspot
The Pacific/Chocó Natural Region, often simply referred to as the "Colombian Chocó," occupies approximately 75,000 square kilometers (29,000 sq mi) along Colombia's western coast. This region is largely defined by its flat terrain, blanketed by dense, humid rainforests, intricate river networks, extensive swamps, and vital mangrove ecosystems bordering the Pacific Ocean.
To the east, the imposing Cordillera Occidental of the Colombian Andes forms a natural boundary, while the border with Peru lies to the south, and the Darién Gap and Panama mark its northern extent.
Ecologically, the Chocó belongs entirely to the globally significant Chocó Biogeographic Region, a key part of the Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena biodiversity hotspot. A unique combination of evolutionary history, ecological factors, climate patterns, and geological processes has resulted in this region boasting the highest concentration of biodiversity per unit area on the planet.
Astonishingly, between 7,000 and 8,000 of the 45,000 species registered in Colombia are found within the Chocó. Endemic plant species number over 2,000, and endemic birds exceed 100 species, representing the highest levels of endemism globally.
The Pacific coast shares a warm and humid climate year-round with the Caribbean, averaging 26 °C (79 °F) and 85% humidity. The wet season typically spans from May to November, followed by a dry season from December to April, with some areas experiencing rainfall among the highest recorded worldwide.
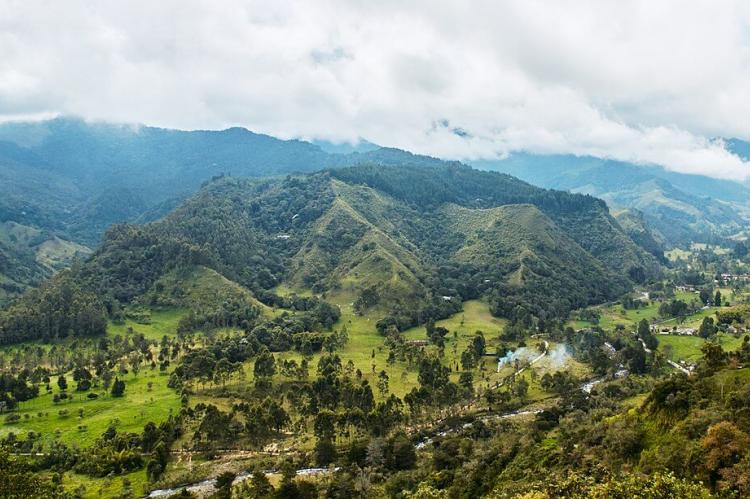
The Andean Region: The Populous Heart
Colombia's most populous natural region is the Andean Natural Region, characterized by its complex and varied mountainous terrain. Beyond its numerous peaks and valleys, this region is home to the majority of the country's urban centers, many of which originated as significant pre-Columbian Indigenous settlements.
The Andean region also encompasses a substantial portion of the Magdalena River and its basin, a waterway of immense economic and environmental importance to Colombia.
North of the Colombian Massif in the extreme southwest, the Andes Mountains in Colombia diverge into three parallel ranges: the Cordillera Occidental, running adjacent to the Pacific coast and home to Cali; the Cordillera Central, traversing the country's center between the Cauca and Magdalena river valleys; and the Cordillera Oriental, extending northeast towards the Guajira Peninsula and encompassing the major cities of Bogotá, Bucaramanga, and Cúcuta.
The climate in the Andes is notably cooler than the coastal regions, with temperatures varying significantly with altitude. The temperate zone averages around 18 °C (64 °F), while the colder higher elevations average 13 °C (55 °F). The Andean region experiences a bimodal rainfall pattern, with wet seasons typically occurring from April to May and October to November, and drier periods from December to January and July to August.
The Orinoco Region: The Eastern Plains
The Orinoco Natural Region, also known as the Orinoquía or Eastern Plains, forms part of the vast Llanos, a sprawling tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes Mountains. This region lies entirely within the Orinoco River watershed.
Sparsely populated, the Orinoquía is rich in oil reserves and offers extensive lands suitable for cattle ranching. Its characteristic ecosystems are tropical savannas, interspersed with gallery forests lining the rivers and significant wetlands that play a crucial ecological role.
The Amazon Region: The Southern Rainforest
The Amazon Natural Region covers about 35% of Colombia's total territory, making it the largest. Located in southern Colombia and encompassing a significant portion of the Amazon Basin, this region is characterized by dense tropical rainforest and is bordered to the west by the Cordillera Oriental of the Colombian Andes, extending eastward to the borders with Venezuela and Brazil.
As the most heavily forested and least populated of Colombia's natural regions, it boasts unparalleled biodiversity. Major rivers, including the Amazon, Caquetá, and Putumayo, meander through its vast expanse.
The Amazon Rainforest here experiences a hot and humid climate year-round, with an average temperature of 27 °C (81 °F) and very high humidity of around 90%. The wet season typically runs from October to May, followed by a drier period from June to September.
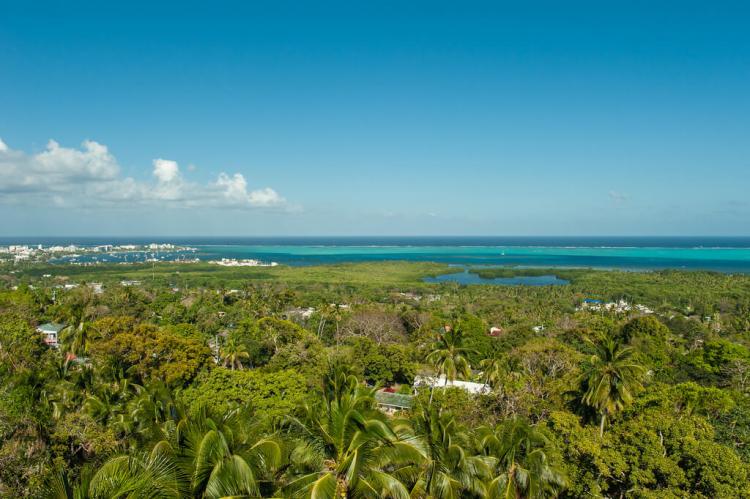
The Insular Region: Outlying Territories
The Insular Region comprises Colombia's territories located outside the continental landmass, situated in both the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean. While some classifications might include parts of the Caribbean islands within the Caribbean Natural Region, the Insular Region is often considered a distinct geopolitical entity.
Its most significant components are the Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina in the Caribbean Sea, and the Pacific islands of Malpelo and Gorgona. This region also includes other groups of Caribbean islands such as the Archipiélago de San Bernardo, Islas del Rosario, Isla Fuerte, Isla Barú, Isla Tortuguilla, and Isla Tierra Bomba, each with its own unique island ecosystems and cultural influences.
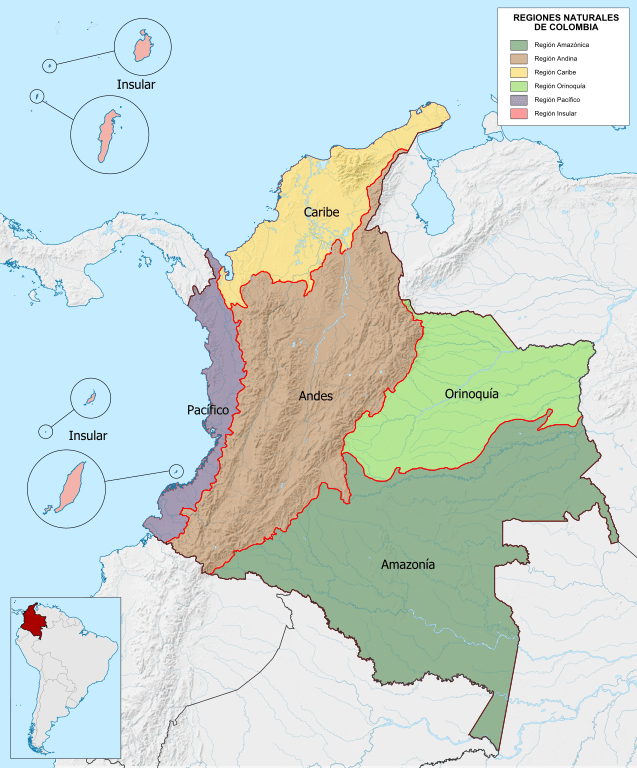
Map depicting the natural regions of Colombia.
Mountain Ranges
Colombia's mountain ranges contribute to the country's diverse landscapes and ecological importance and offer outdoor activities, research, and exploration opportunities. They showcase the remarkable geographical features and natural beauty that make Colombia a unique and fascinating country.
See more: Mountain Ranges of Colombia
Islands and Archipelagos
Colombia has many islands and archipelagos in the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean. These islands vary in size, culture, and natural beauty. Each destination has its unique charm, from pristine beaches and vibrant marine life to historical sites and cultural experiences.
See more: Islands and Archipelagos of Colombia
Bodies of Water
Colombia's bodies of water contribute to the country's diverse natural beauty, provide vital resources, and support a variety of ecosystems and human activities. They also offer opportunities for tourism, recreation, and exploring the country's rich aquatic environments.
See more: Water Bodies of Colombia
Administrative Divisions
Colombia is comprised of 32 departments and a capital district. A grouping of municipalities forms departments. Each department has a capital, a Governor, and an Assembly.
See more: Cultural Landscape of Colombia
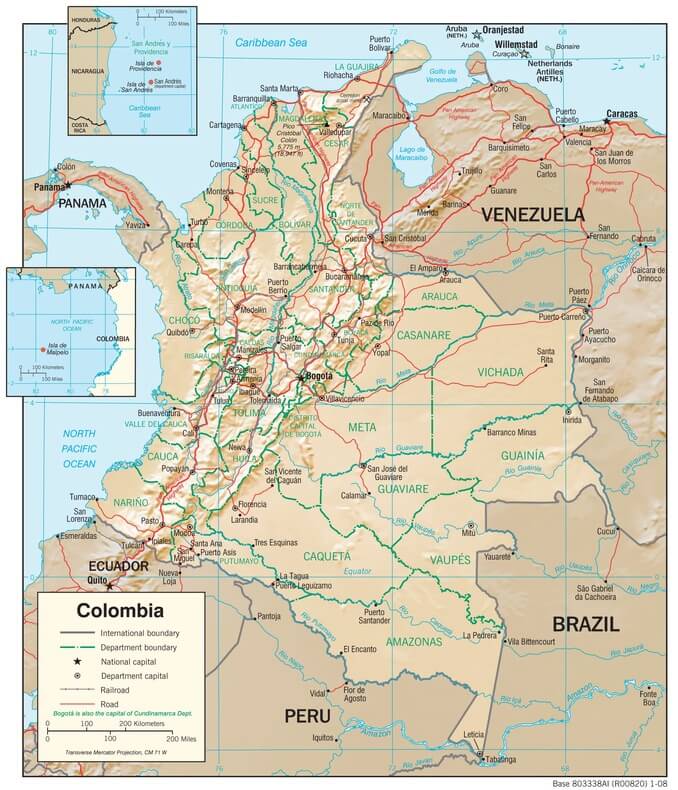
Colombia physiographic map
Biomes
Colombia's complex climate, soil, and topography have produced an extraordinary range of plants and plant communities. These range from the mangrove swamps of the coasts, the desert scrub of La Guajira, the savanna grasslands and gallery ecosystems of the Atlantic lowlands and the Llanos, the rainforests of the Amazon and Chocó natural regions, to the widely diverse and complex montane ecosystems of the Andean slopes.
Moist Forest: tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests
Dry Forest: tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests
Grasslands: tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
Montane Grasslands: montane grasslands and shrublands
Desert: deserts and Xeric shrublands
Mangroves: salt-tolerant trees, shrubs, and other vegetation
Ecosystems
Páramo: tussock grasses and frailejones
Upper Montane Forest: diverse vegetation at slightly lower elevations
Lower Montane Forest: mix of evergreen and deciduous trees at lower altitudes
Dry Forest of the inter-Andean Valleys: drought-resistant vegetation adapted to seasonal water variations
Savanna of the Llanos Oriental: tropical grassland
Amazonian Rainforest and other lowlands: lush and biodiverse lowland ecosystems
Ecological Regions
The following is a list of terrestrial ecoregions in Colombia, as defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). Colombia is in the neotropical realm. Ecoregions are classified by biome type—the major global plant communities determined by rainfall and climate.
Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests
Caquetá moist forests
Cayos Miskitos - San Andrés and Providencia moist forests
Cordillera Oriental montane forests
Eastern Cordillera Real montane forests
Eastern Panamanian montane forests
Guayanan Highlands moist forests
Japurá-Solimões-Negro moist forests
Magdalena Valley montane forests
Negro-Branco moist forests
Northwestern Andean montane forests
Rio Negro campinarana
Solimões-Japurá moist forests
Venezuelan Andes montane forests
Western Ecuador moist forests
Tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests
Apure-Villavicencio dry forests
Sinú Valley dry forests
Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
Montane grasslands and shrublands
Deserts and xeric shrublands
Guajira-Barranquilla xeric scrub
Malpelo Island xeric scrub
Mangroves
Esmeraldas-Pacific Colombia mangroves
Magdalena-Santa Marta mangroves
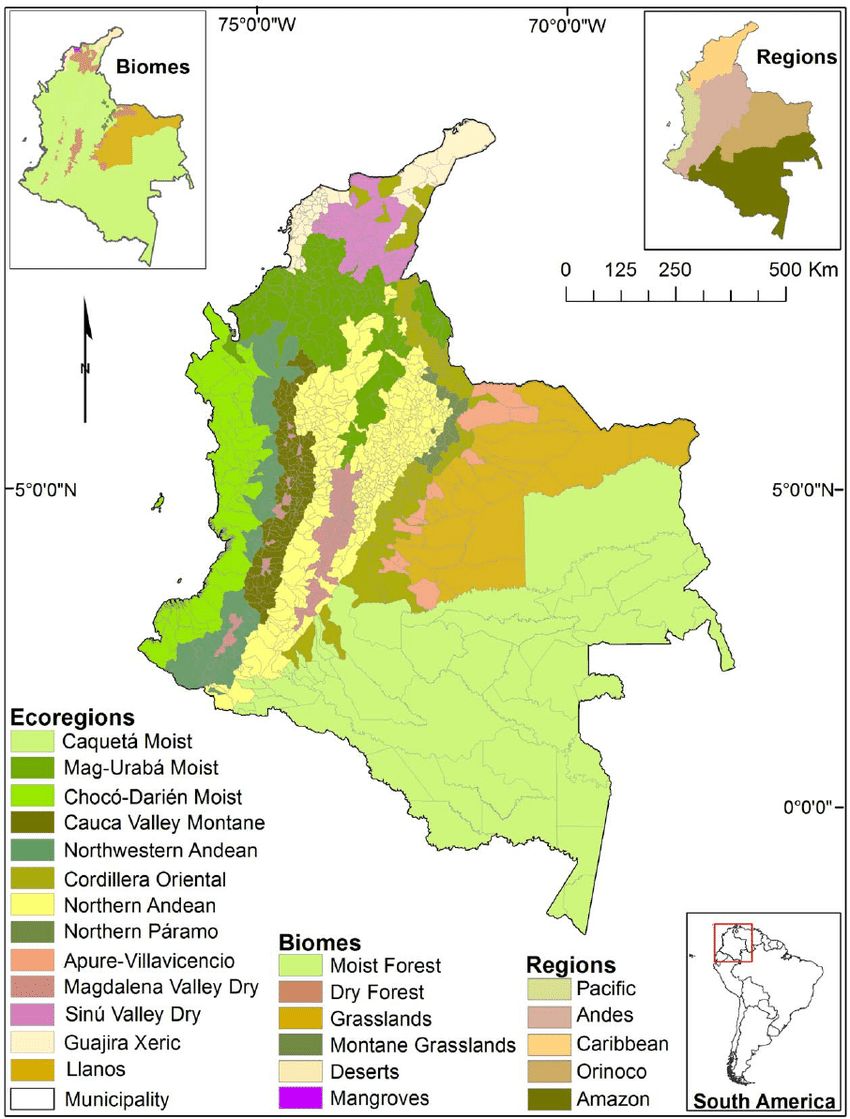
Colombia ecoregions and biomes map.










