Guardians of the Drylands: The Cauca Valley Dry Forests of Colombia's Tropical Andes
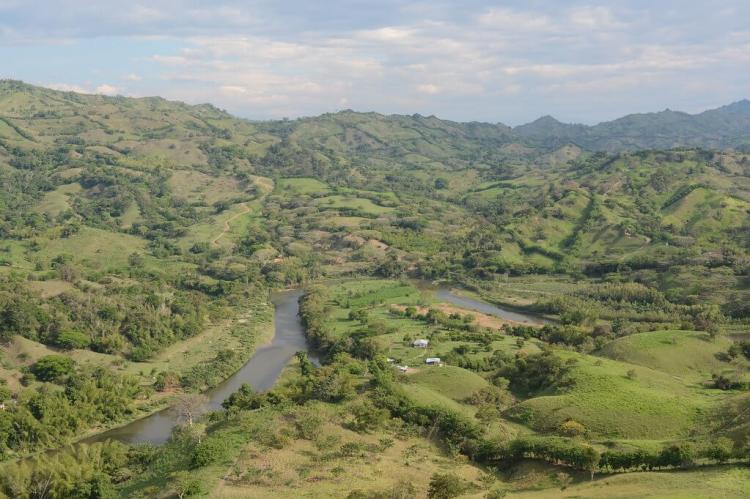
Colombia's Cauca Valley dry forests are part of the Tropical Andes Biodiversity Hotspot, one of Earth's most biologically diverse regions. This ecoregion is characterized by its distinct dry climate, varied topography, and remarkable array of flora and fauna.
The Cauca Valley Dry Forests: An Ecological Treasure in Colombia's Tropical Andes
Colombia's Cauca Valley dry forests are part of the Tropical Andes Biodiversity Hotspot, one of Earth's most biologically diverse regions. This ecoregion is characterized by its distinct dry climate, varied topography, and a remarkable array of flora and fauna. Despite its ecological importance, the Cauca Valley dry forests face significant threats from human activities and environmental changes. Understanding and conserving these forests are crucial for maintaining biodiversity and ensuring the sustainability of the region's natural resources.
Geographical Scope and Climate
Location and Topography
The Cauca Valley dry forests are situated in the inter-Andean valley of the Cauca River, extending across Valle del Cauca, Cauca, and Quindío departments. The ecoregion is flanked by the Western and Central Cordilleras of the Andes, creating a distinctive topographical setting. The terrain includes rolling hills, alluvial plains, and low-lying mountains, providing a variety of habitats for diverse species.
Climate
The climate of the Cauca Valley dry forests is characterized by a pronounced dry season, with annual rainfall ranging from 800 to 1,500 millimeters (30 to 60 inches). Temperatures vary between 20°C and 30°C (68°F and 86°F), with significant seasonal fluctuations. The dry season, which can last several months, is a defining feature of the ecoregion, influencing the types of vegetation and animal life that can thrive in this environment.
Biodiversity and Endemism
Flora
The vegetation in the Cauca Valley dry forests is adapted to the arid conditions, featuring a mix of deciduous trees, shrubs, and grasses. Prominent plant species include the ceiba (Ceiba pentandra), the cactus (Cactaceae family), and various species of Acacia. These plants have evolved to conserve water and withstand prolonged dry periods. The forests also support numerous endemic plant species, adding to the ecoregion's botanical significance.
Fauna
The animal life in the Cauca Valley dry forests is equally diverse, with many species adapted to the dry conditions. Mammals such as the white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) and the collared peccary (Pecari tajacu) are commonly found in these forests. Bird species like the Cauca guan (Penelope perspicax), which is endemic to the region, highlight the avian diversity. Reptiles and amphibians, including several species of lizards and frogs, also inhabit this ecoregion.
Conservation Significance and Threats
Importance of Conservation
The Cauca Valley dry forests are crucial for their biodiversity, serving as habitats for numerous species, including many that are endemic or threatened. As part of the Tropical Andes Biodiversity Hotspot, these forests are integral to the region's overall ecological health. They also provide essential ecosystem services, such as soil stabilization, water regulation, and carbon sequestration. Additionally, the area holds cultural and economic significance for local communities who depend on the forests for resources and livelihoods.
Human Impacts
Human activities have significantly impacted the Cauca Valley dry forests. Agricultural expansion, especially for sugarcane and coffee plantations, has led to extensive deforestation. Urbanization and infrastructure development have further encroached on natural habitats. Additionally, logging and extracting non-timber forest products contribute to habitat degradation.
Climate Change
Climate change significantly threatens the Cauca Valley dry forests, exacerbating environmental challenges. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can alter the delicate balance of these ecosystems, potentially leading to shifts in species distributions and the loss of specialized habitats. Increased frequency and intensity of droughts can further stress the vegetation and wildlife, making conservation efforts more urgent.
Conservation Efforts and Strategies
Protected Areas and Reserves
Protected areas and reserves are crucial for conserving the Cauca Valley dry forests. Notable protected areas include the Los Katíos National Natural Park and the Farallones de Cali National Natural Park, which aim to preserve critical habitats and protect biodiversity. These areas also serve as refuges for threatened species and play a role in maintaining ecological processes.
Community Involvement
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is essential for the sustainable management of the Cauca Valley dry forests. Initiatives that promote sustainable land use practices, agroforestry, and ecotourism can enhance conservation outcomes while supporting local economies. Involving indigenous and rural communities in decision-making processes fosters a sense of ownership and stewardship, ensuring long-term conservation success.
Research and Monitoring
Ongoing research and monitoring are crucial for understanding the ecological dynamics of the Cauca Valley dry forests and addressing conservation challenges. Studies on species populations, ecosystem functions, and the impacts of climate change can inform adaptive management strategies. Collaboration between scientists, conservation organizations, and government agencies is vital for implementing effective conservation measures.
Conclusion
The Cauca Valley dry forests are an ecological treasure within Colombia's Tropical Andes Biodiversity Hotspot, rich in biodiversity and environmental significance. Protecting these forests is imperative for maintaining their unique flora and fauna, supporting ecosystem services, and preserving cultural heritage. Addressing the threats posed by human activities and climate change requires coordinated efforts at multiple levels. By valuing and safeguarding these dry forests, future generations can continue to benefit from their ecological and economic contributions.
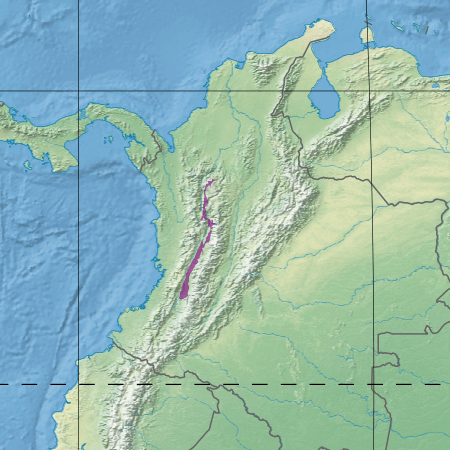
Map depicting the location of the Cauca Valley dry forests (in purple).
