Ecuador: Cultural Landscape
Ecuador, located in the northwestern part of South America, boasts a rich and diverse cultural landscape shaped by its history, geography, and vibrant mix of indigenous, European, and African influences. The cultural landscape is a rich combination of heritage, tradition, and a profound appreciation for nature.
The Cultural Landscape of Ecuador: Tradition, Influence, and Modernity
Ecuador, a vibrant country in northwestern South America, boasts a diverse cultural landscape forged by its historical heritage, unique geography, and dynamic blend of Indigenous, Spanish, African, and modern global influences. Ecuador's culture reflects a profound connection to its natural environment, a rich tapestry of traditions, and a growing array of contemporary elements. The following exploration highlights Ecuador's cultural heritage, the modern influences shaping society, and the challenges facing the country today.
Indigenous Heritage
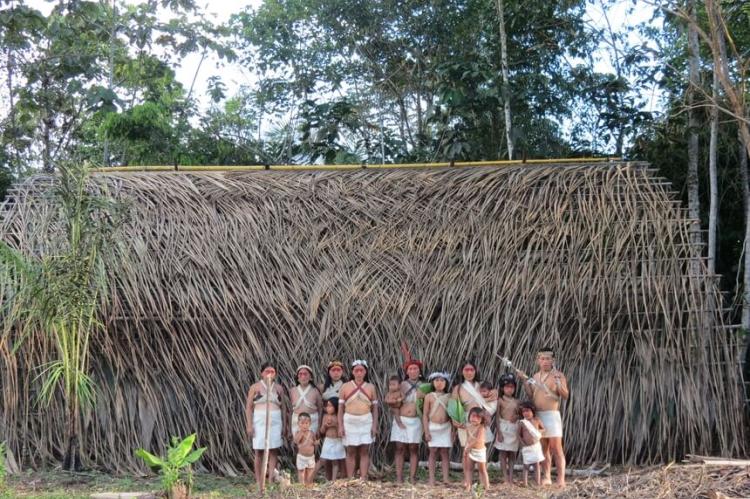
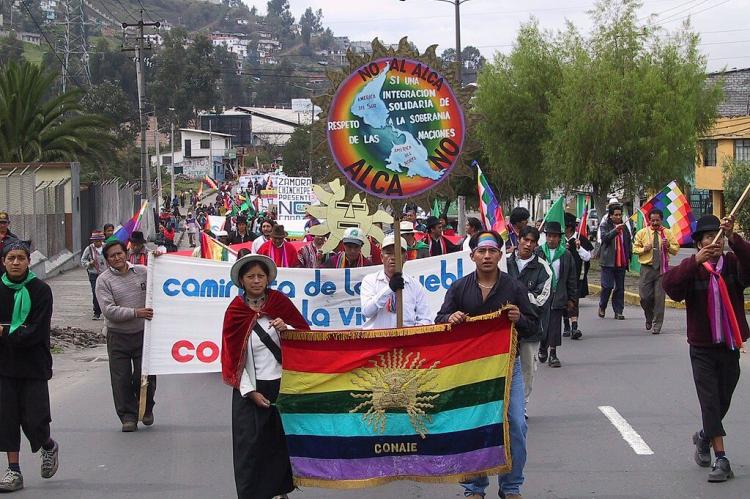
Indigenous communities play a foundational role in Ecuadorian culture, with groups such as the Kichwa, Shuar, Huaorani, and Achuar preserving unique traditions and languages. These groups contribute to Ecuador's cultural identity through their music, festivals, clothing, and rituals, many of which have remained unchanged for centuries. For example, Indigenous art forms like traditional weaving, pottery, and beadwork are artistic expressions and convey spiritual and ancestral significance. Festivals such as the "Inti Raymi" (Festival of the Sun) celebrate the Andean solstice, bringing together music, dance, and rituals to honor nature and ancestral heritage.
Colonial Legacy and Architectural Heritage
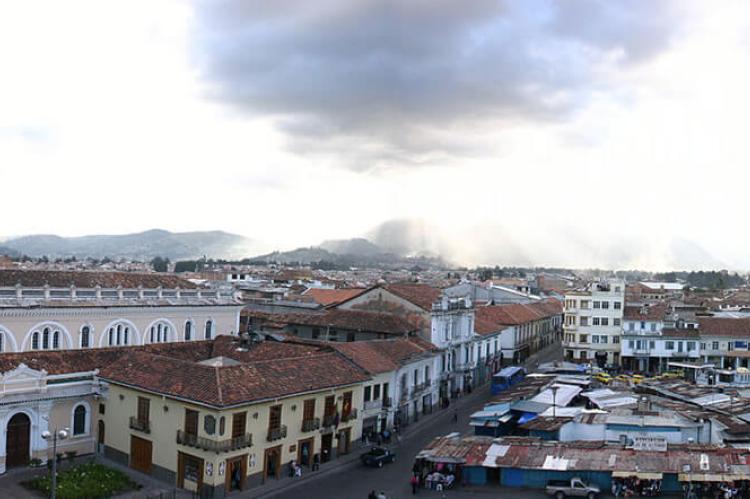
Centuries of Spanish colonization have left a lasting mark on Ecuador, particularly its architecture, religion, and language. The capital, Quito, contains one of South America's most extensive and well-preserved historic centers, recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. This area features baroque and Gothic-style churches, monasteries, and plazas dating back to the 16th century, including iconic structures like the Church of San Francisco and the Compania de Jesús. Ecuadorian cuisine reflects Spanish influence, as seen in traditional dishes such as ceviche, empanadas, and tamales. This legacy is a constant reminder of the country's colonial past and the blend of European and Indigenous cultures that define modern Ecuador.
Afro-Ecuadorian Culture
The African diaspora has deeply influenced Ecuadorian culture, particularly in coastal regions like Esmeraldas and the Chota Valley. Afro-Ecuadorian communities have contributed distinct musical styles, including marimba, bomba, and bambuco, as well as dances like the "bomba del chota." These cultural expressions celebrate Afro-Ecuadorian identity and are often performed during local festivals and events. Afro-Ecuadorian cuisine, which features ingredients like coconut, plantains, and seafood, is another testament to the influence of African heritage on the Ecuadorian coast.
Ecuadorian Art, Handicrafts, and Market Culture
Ecuador's reputation for exceptional craftsmanship is showcased in its markets, particularly the Otavalo Market, one of the largest Indigenous markets in South America. Artisans from around the region gather here to sell handmade textiles, jewelry, pottery, and carvings that reflect Indigenous design and techniques. Communities such as the Saraguro and Salasaca are known for intricate weaving, while cities like Cuenca and Guayaquil have established themselves as pottery and ceramic art centers. These art forms and handicrafts reflect cultural pride and serve as economic drivers, supporting local communities and preserving traditional practices.
Festivals and Celebrations
Ecuadorians are known for their enthusiasm for festivals, which blend Indigenous, Spanish, and African traditions. The "Inti Raymi" festival celebrates the summer solstice with rituals honoring Pachamama (Mother Earth), while the "Diablada de Pillaro" in January involves dancers wearing devil masks, a practice that dates back to colonial resistance against Spanish rule. The "Mama Negra" festival in Latacunga, held in honor of the Virgin of Mercy, is another significant event that combines Indigenous, African, and Catholic elements. These celebrations are social gatherings and expressions of Ecuadorian identity, resilience, and faith.
Connection to Nature and Biodiversity
Ecuador's cultural identity is closely intertwined with its natural landscapes, from the Galapagos Islands and Amazon Rainforest to the Andean highlands. Indigenous communities in these areas maintain a profound respect for nature, viewing it as a living entity with its spirit and rights. Sustainable farming, herbal medicine, and forest conservation reflect a deep cultural connection to Ecuador's environment. These ecological values are mirrored in Ecuador's legal recognition of nature's rights within its constitution, making it one of the few countries worldwide to take this step.
Contemporary Influences on Ecuadorian Culture
Modern influences have reshaped Ecuadorian culture in recent decades, adding new layers to its rich heritage.
Globalization: The spread of global media, technology, and ideas has brought new cultural elements into Ecuadorian society. This influence is evident in Ecuador's evolving cuisine, incorporating diverse European, Asian, and American flavors. Ecuadorian music, too, reflects a fusion of traditional rhythms with global genres, resulting in an array of modern styles that appeal to younger generations.
Immigration: Ecuador has long been a destination for immigrants from neighboring Colombia, Peru, Venezuela, and distant countries. These communities contribute to Ecuador's cultural diversity, enriching the country's traditions, foods, and languages.
Technology: Access to the internet and mobile technology has proliferated in Ecuador, shaping how people communicate, learn, and access information. Social media and digital platforms have enabled Ecuadorians to share and preserve their culture globally, allowing artists, musicians, and writers to reach broader audiences.
The Arts: Ecuador's contemporary art scene is thriving, with an expanding theater presence, music festivals, and art galleries. Many artists draw on Ecuador's cultural heritage, environmental themes, and social issues, using their work to explore questions of identity, modernity, and tradition.
Challenges Facing Ecuadorian Culture
Despite its vibrant culture, Ecuador faces significant challenges that threaten the integrity and continuity of its cultural landscape.
Economic Inequality: Ecuador experiences high levels of economic disparity, which can hinder cultural development and access to resources. Rural communities, particularly those of Indigenous and Afro-Ecuadorian heritage, often lack the infrastructure and economic opportunities available in urban areas. This inequality can limit cultural preservation efforts and fuel social tensions.
Environmental Degradation: Ecuador's natural resources face pressures from deforestation, mining, and pollution, harming the environment and the communities that rely on it. The destruction of natural landscapes can lead to the erosion of cultural practices tied to these areas, such as sustainable farming and medicinal plant knowledge.
Political Instability: Ecuador has a history of political instability that has periodically disrupted cultural and economic development. Changes in leadership and policies can impact funding for cultural programs, conservation efforts, and education, making preserving Ecuador's cultural heritage challenging.
Globalization: While globalization has brought many benefits, it also poses a risk to traditional Ecuadorian culture. Exposure to foreign media, consumerism, and lifestyle trends can sometimes overshadow local traditions, particularly among younger generations who may feel disconnected from their cultural roots.
Conclusion
Ecuador's cultural landscape is a dynamic fusion of Indigenous heritage, colonial influences, African traditions, artistic expressions, and a growing array of global elements. The country's vibrant festivals, traditional crafts, and connection to nature showcase a cultural identity rooted in history and place. At the same time, modern influences and challenges continue to reshape Ecuadorian society, creating both opportunities and obstacles. As Ecuador navigates these complexities, its cultural resilience and adaptability will likely continue to define and enrich its unique place in the world.

The official flag of Ecuador.
Cultural Geography of Ecuador
Largest Cities / Metro Areas
Ranked by population estimate (2022):
Guayaquil (2,834,000): Guayaquil is Ecuador's largest city and main port on the Pacific coast. It is located on the Guayas River, about 60 km (37 mi) north of the Gulf of Guayaquil, near the Equator. It's known for its economic importance, bustling port, modern infrastructure, and vibrant culture. The city has undergone urban development and is home to attractions like the Malecón 2000 waterfront promenade and historical landmarks.
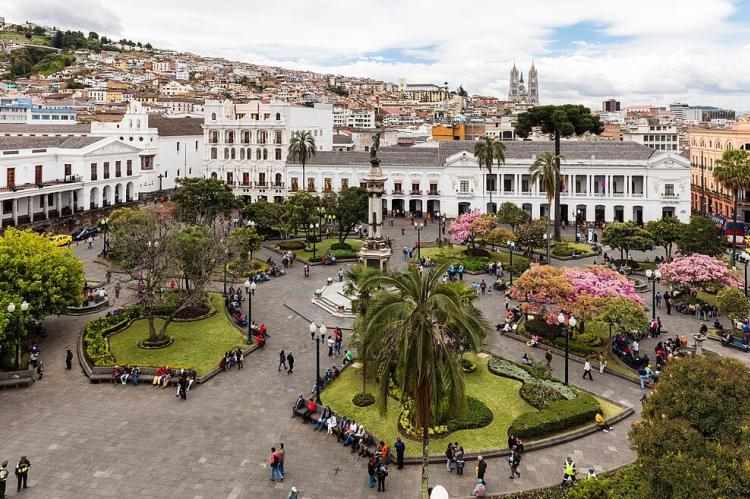
Quito (2,743,000): Quito is the capital city of Ecuador, located in the Andes mountains. It's known for its well-preserved colonial architecture, including the historic center, a UNESCO World Heritage site. At an elevation of 2,850 m (9,350 ft), Quito is the second-highest capital city in the world. The city offers a mix of modern amenities and cultural richness, making it a popular tourist destination and a significant political and economic hub in the country.
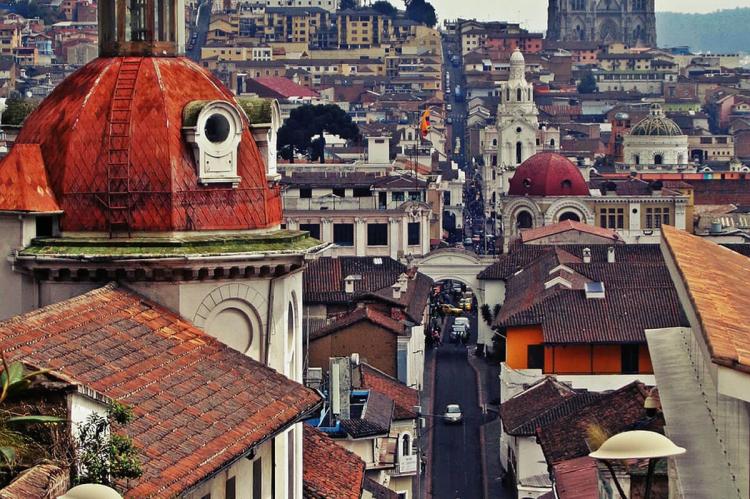
Cuenca (635,000): Cuenca is a city in southern Ecuador, famed for its charming colonial architecture, cobblestone streets, and historical significance. It's nestled in the Andes mountains at an elevation of 2,560 m (8,400 ft), and its historic center is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site. Cuenca is known for its well-preserved colonial architecture, many churches and cathedrals, and vibrant artisan culture.
Loja (327,000): Loja is a city in southern Ecuador known for its rich cultural heritage, historic architecture, and natural beauty. Situated in the Cuxibamba Valley, at an elevation of 2,060 m (6,758 ft), it is the capital of the Loja Province. Due to its historical significance in the arts and music, it is often called the "Cuna de Artistas" (Cradle of Artists). Picturesque landscapes surround the city, a center for education, culture, and regional commerce.
Portoviejo (295,000): Portoviejo is a city in western Ecuador, serving as the capital of the Manabí Province. It's an important commercial and administrative center in the region. The city has a mix of modern infrastructure and historical sites, rebuilt after a significant earthquake in the early 20th century. Portoviejo is known for its vibrant culture and local crafts, and as a gateway to nearby coastal attractions.
Machala (275,000): Machala is a city in southwestern Ecuador, known as a major commercial and agricultural center. It's the capital of the El Oro Province and is renowned for its significant banana production and export. Located near the Gulf of Guayaquil on fertile lowlands, the city's economy is closely tied to agriculture and trade, and it offers a mix of urban amenities and local culture.
Ambato (265,000): Ambato is a city in central Ecuador known for its cultural events, natural beauty, and agricultural significance. It's the capital of the Tungurahua Province and is often called the "City of Flowers and Fruits" due to its agricultural production. Located in the Andes Mountains, at an elevation of 2,577 m (8,458 ft), it is surrounded by picturesque landscapes, including the Tungurahua volcano.
Esmeraldas (250,000): Esmeraldas is a coastal port city in northwestern Ecuador, known for its beautiful beaches, cultural diversity, and natural resources. It's the capital of the Esmeraldas Province and is situated on the shores of the Pacific Ocean. The city has a significant Afro-Ecuadorian population, contributing to its rich cultural heritage and traditions. Esmeraldas is a hub for the fishing industry and offers a mix of cultural attractions and coastal tourism.
Ibarra (230,000): Ibarra is a city in northern Ecuador, known for its pleasant climate, colonial architecture, and surrounding natural beauty. It's the capital of the Imbabura Province and is nestled in the Andes mountains at the foot of the Imbabura Volcano. Ibarra is recognized for its historic churches, plazas, and colonial whitewashed houses. The city is a gateway to exploring the surrounding highland landscapes and Indigenous communities.
Manta (220,000): Manta is a coastal city in western Ecuador, known for its bustling port, beautiful beaches, and fishing industry. It's one of the country's largest and busiest ports, facilitating trade and commerce. Due to its large tuna fishing industry, Manta is known as the "Tuna Capital of the World." The city offers maritime activities, tourism, and cultural attractions.
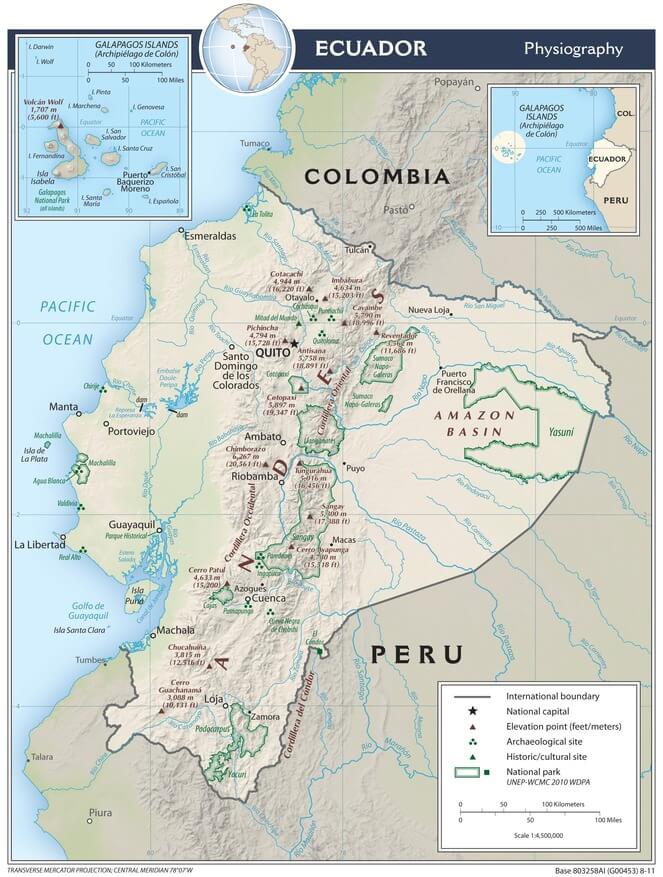
Ecuador physiographic map.
Administrative Divisions
Administratively, Ecuador is divided into 24 provinces, each with its capital, and each province into cantons.
Provinces
The provinces of Ecuador, their capitals, and a brief description are as follows:
Azuay (Capital: Cuenca): Azuay is known for its well-preserved colonial architecture and rich cultural heritage. Its capital, Cuenca, features cobblestone streets and ornate churches, reflecting its historical significance.
Bolívar (Capital: Guaranda): Bolívar is recognized for its annual Carnival celebrations and artisanal crafts. Its capital, Guaranda, serves as a center for these festivities and cultural traditions.
Cañar (Capital: Azogues): Cañar's capital, Azogues, is a historic city with colonial architecture. The province showcases Indigenous culture, traditional markets, and highland landscapes.
Carchi (Capital: Tulcán): Carchi, located near the Colombian border, is characterized by its cross-border trade. Its capital, Tulcán, is known for its elaborate cemetery and border proximity.
Chimborazo (Capital: Riobamba): Chimborazo province is named after the iconic Chimborazo volcano. Its capital, Riobamba, offers access to the surrounding Andean landscapes and Indigenous markets.
Cotopaxi (Capital: Latacunga): Cotopaxi province is home to the Cotopaxi volcano. Its capital, Latacunga, hosts festivals and is a gateway to natural wonders and cultural experiences.
El Oro (Capital: Machala): El Oro is a coastal province known for its agricultural and commercial activities. Its capital, Machala, is a significant banana production and trade center.
Esmeraldas (Capital: Esmeraldas): Along the northern coast, Esmeraldas province features Afro-Ecuadorian culture and beautiful beaches. Its capital, Esmeraldas, is a fishing industry hub.
Galápagos (Puerto Baquerizo Moreno, San Cristóbal Island): The Galápagos Islands are a unique province with remarkable biodiversity. Its capital, Puerto Baquerizo Moreno, serves as a gateway to exploring this natural wonder.
Guayas (Capital: Guayaquil): Guayas is Ecuador's most populous province, centered around the bustling city of Guayaquil. It's an economic powerhouse with a significant industrial and commercial presence.
Imbabura (Capital: Ibarra): Imbabura is known for its Indigenous culture and picturesque landscapes. Its capital, Ibarra, is a hub for exploring the province's highland attractions.
Loja (Capital: Loja): Loja province boasts a pleasant climate and Indigenous traditions. Its capital, Loja, is known for its historical charm and as a center for arts and education.
Los Ríos (Capital: Babahoyo): Los Ríos province is characterized by its riverine landscape. Its capital, Babahoyo, is central to the province's agriculture and commerce.
Manabí (Capital: Portoviejo): Manabí is a coastal province with a vibrant culture. Its capital, Portoviejo, is a major city known for its historical significance and local traditions.
Morona Santiago (Capital: Macas): This province offers diverse terrain and Indigenous communities. Its capital, Macas, is a gateway to exploring the Amazon Rainforest.
Napo (Capital: Tena): Napo province is part of the Amazon rainforest region. Its capital, Tena, provides access to ecotourism and experiences in the jungle.
Orellana (Capital: Puerto Francisco de Orellana / Coca): Orellana province is named after the Amazon explorer Francisco de Orellana. Its capital, Coca, is a gateway to the Amazon Rainforest and Indigenous communities.
Pastaza (Capital: Puyo): Pastaza is known for its Amazonian landscapes and diverse cultures. Its capital, Puyo, offers access to rainforest adventures and Indigenous heritage.
Pichincha (Capital: Quito): Pichincha province encompasses Quito, Ecuador's capital. It's a center of politics, culture, and commerce surrounded by scenic landscapes.
Santa Elena (Capital: Santa Elena): Santa Elena is a coastal province with beautiful beaches. Its capital, Santa Elena, is a popular destination for sun and sea activities.
Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas (Capital: Santo Domingo): Santo Domingo province is known for its Tsáchila Indigenous culture. Its capital, Santo Domingo, showcases cultural diversity and natural attractions.
Sucumbíos (Capital: Nueva Loja): Sucumbíos province is in the northeastern Amazon region. Its capital, Nueva Loja, provides access to the Amazon Rainforest and its biodiversity.
Tungurahua (Capital: Ambato): Tungurahua is named after the Tungurahua volcano. Its capital, Ambato, is known for its festivals and as a gateway to the surrounding Andean landscapes.
Zamora-Chinchipe (Capital: Zamora): This Amazonian province has rich biodiversity. Its capital, Zamora, offers access to rainforest exploration and Indigenous communities.
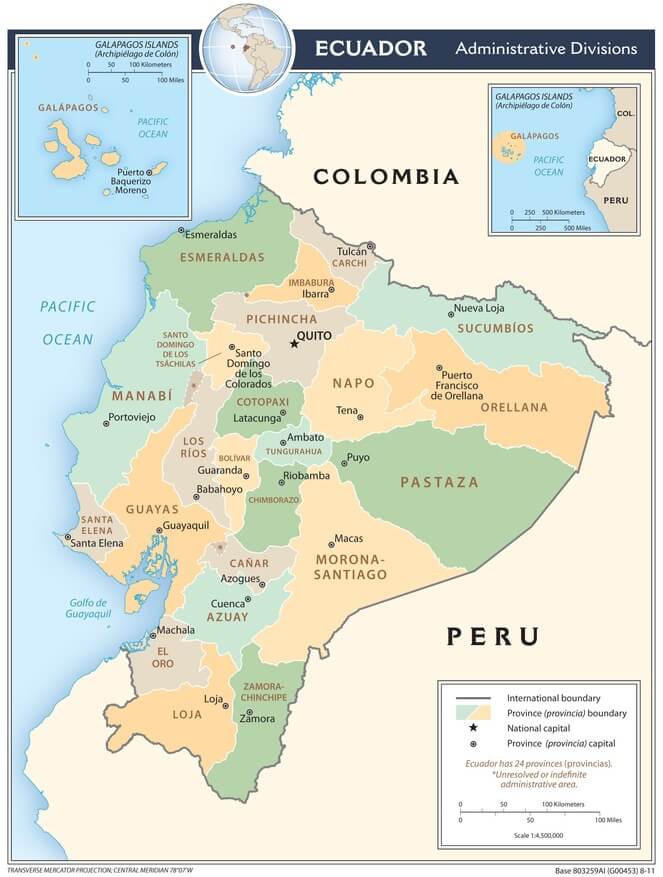
Ecuador administrative map.
Geographic Regions (Zones)
The Ecuadorian mainland is divided into three main physical regions:
Coastal Lowlands (La Costa): The coastal lowlands of Ecuador (La Costa) extend eastward from the Pacific Ocean to the western edge of the Ecuadorian Andes.
Central Highlands (La Sierra): Ecuador's central highlands or Sierra natural region (La Sierra).
Eastern Lowlands (El Oriente): Beyond the eastern ranges of the central highlands are the eastern lowlands of Ecuador (El Oriente).
The Galápagos Islands make up the fourth geographic region.
See more: Natural Landscape of Ecuador
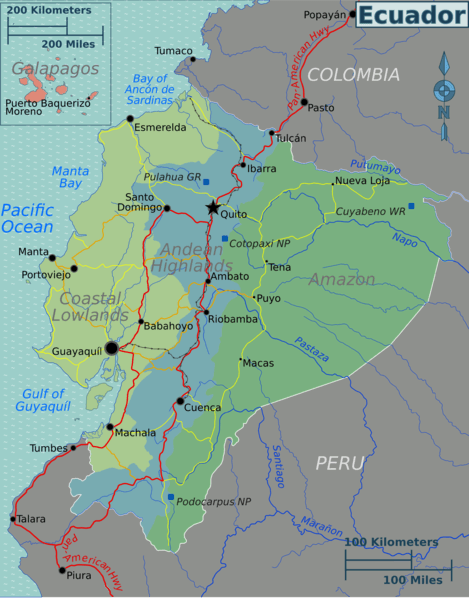
Map depicting the geographic regions of Ecuador.
Historical, Cultural, and Natural Landmarks
Ecuador has remarkable diversity, featuring many historical, cultural, and natural landmarks. Here are some notable examples in each category, separated by region:
Coastal Lowlands (La Costa)
The coastal lowlands region of Ecuador, also known as "La Costa," offers diverse attractions, including beautiful beaches, vibrant cities, and unique cultural experiences. Here are some popular attractions in this region:
Guayaquil: As Ecuador's largest city, Guayaquil is a bustling metropolis on the coast. It offers a mix of modern and historical attractions, including the Malecón 2000 boardwalk along the Guayas River, the colorful Las Peñas neighborhood, and the Parque Histórico Guayaquil, which showcases Ecuadorian history and wildlife.
Montañita: Montañita is a renowned beach town and surfing destination known for its lively atmosphere and vibrant nightlife. Its consistent waves, beachfront bars, and energetic parties attract locals and international tourists.
Salinas: Salinas is a famous beach resort town that attracts visitors with its long sandy beaches and crystal-clear waters. It offers a variety of water sports activities, such as surfing, jet skiing, and sailing. Salinas also has a bustling malecón (boardwalk) lined with restaurants, shops, and entertainment options.
Puerto López: Puerto López is a charming fishing village and a gateway to the Machalilla National Park. It is mainly known for whale-watching tours, as humpback whales migrate to the area from June to September. Visitors can also explore nearby Isla de la Plata, often called the "poor man's Galápagos," home to diverse bird species.
Isla Puná: Isla Puná is an island near Guayaquil known for its rich biodiversity and Indigenous communities. Visitors can explore the island's mangroves, observe wildlife, and experience the culture and traditions of the local communities.
Ayangue: Ayangue is a small fishing village with a picturesque bay known for its calm waters, making it ideal for swimming and snorkeling. The town offers a relaxed atmosphere and fresh seafood options.
Santa Elena Peninsula: The Santa Elena Peninsula is a scenic region with beautiful beaches, charming towns, and natural attractions. Notable places to visit include the beach town of Ballenita, the vibrant city of La Libertad, and Punta Carnero Beach, known for its excellent surfing conditions.
Manglares Churute Ecological Reserve: Located near Guayaquil, the Manglares Churute Ecological Reserve is a protected area comprising mangrove forests, wetlands, and tropical dry forests. It is home to diverse bird species, monkeys, and other wildlife. Visitors can take boat tours to explore the mangroves and observe the abundant flora and fauna.
Machalilla National Park: Machalilla National Park is a vast protected area along the coast encompassing diverse ecosystems, including dry forests, beaches, and the offshore Isla de la Plata. The park offers opportunities for hiking, wildlife viewing, and exploring the fascinating cultural heritage of the Manteño civilization.
Central Highlands (La Sierra)
The central highlands region of Ecuador, known as "La Sierra," is characterized by its stunning mountain landscapes, colonial cities, Indigenous markets, and a wealth of cultural heritage. Here are some popular attractions in this region:
Quito: Ecuador's capital is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and offers a fascinating mix of history, culture, and natural beauty. The historic center, known as "Old Town," is renowned for its well-preserved colonial architecture, cobblestone streets, and beautiful churches, including the iconic Basilica del Voto Nacional and the Compañía de Jesús. Visitors can also enjoy panoramic views from the TelefériQo cable car and explore the lively neighborhoods and markets.
Otavalo: Otavalo is famous for its Indigenous market, the Otavalo Market, one of South America's largest and most vibrant Indigenous markets. Visitors can browse various handmade crafts, textiles, and traditional artwork. In addition, the nearby town of Cotacachi is known for its leather goods, and the picturesque Cuicocha Lake offers opportunities for hiking and boating.
Baños: Baños is a small town nestled in the Andean highlands and is a popular destination for adventure activities and relaxation. The village is known for its hot springs, waterfalls, and outdoor adventures such as zip-lining, canyoning, and biking. Visitors can also enjoy the breathtaking views of the Tungurahua volcano.
Cuenca: Cuenca is a UNESCO World Heritage city known for its well-preserved colonial architecture, narrow streets, and rich cultural heritage. The town boasts numerous churches, museums, and plazas, including the impressive Cuenca Cathedral and the Pumapungo Archaeological Park. Cuenca is also famous for its arts and crafts, particularly Panama hats and ceramics.
Quilotoa: The Quilotoa Crater Lake is a mesmerizing natural attraction in the central highlands. The lake, located inside the collapsed caldera of a volcano, displays stunning turquoise waters surrounded by cliffs. Visitors can hike around the rim, descend to the lake's shore, or admire the breathtaking views.
Riobamba and the Chimborazo Volcano: Riobamba is near the majestic Chimborazo Volcano, Ecuador's highest peak. Visitors can take a train ride known as the "Devil's Nose" for a thrilling and scenic journey through the Andes. The area is also known for its Indigenous communities and traditional handicrafts.
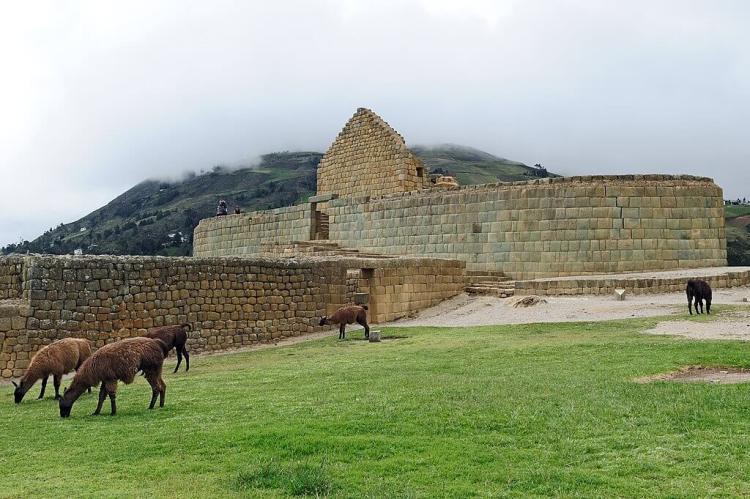
Ingapirca: Ingapirca is an archaeological site and Ecuador's most extensive Inca ruins. The site features ancient stone structures, including the Temple of the Sun and the elliptical Plaza of Pilaloma. Visitors can explore the ruins and learn about the influence of the Inca civilization in the region.
Mindo Cloud Forest: Located on the western slopes of the Andes, the Mindo Cloud Forest is a biodiverse paradise. It offers opportunities for birdwatching, hiking, and exploring the lush vegetation. In addition, the region is home to numerous hummingbirds, orchids, and other unique species.
Eastern Lowlands (El Oriente)
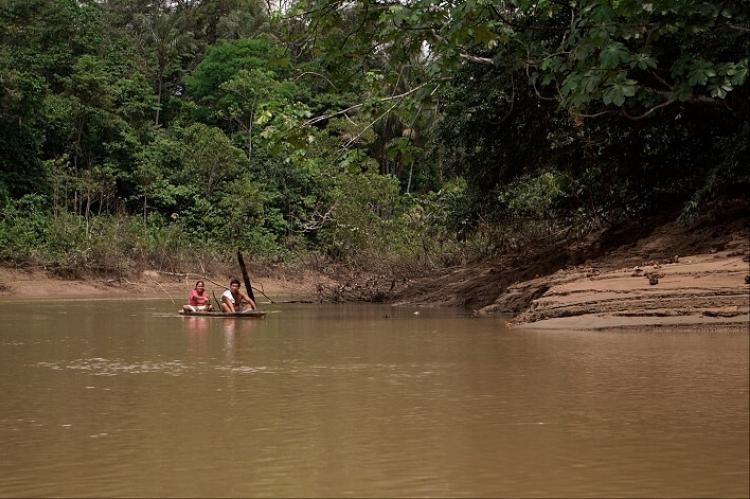
The eastern lowlands region of Ecuador, known as "El Oriente" or the Amazon Rainforest, is a biodiverse and captivating area with a wealth of natural attractions and Indigenous cultures. Here are some popular attractions in this region:
Yasuní National Park: Yasuní National Park is one of the most biodiverse areas in the world and a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. It is home to an incredible array of plant and animal species, including jaguars, tapirs, monkeys, and various bird species. Visitors can explore the rainforest through guided hikes, canoe excursions, and visits to Indigenous communities.
Cuyabeno Wildlife Reserve: Cuyabeno Wildlife Reserve is another protected area in the Amazon Rainforest known for its rich biodiversity. Visitors can take guided tours through the reserve to observe wildlife, hike through the dense jungle, navigate the tranquil lagoons, and learn about the Indigenous cultures that call this region home.
Tena: Tena is a vibrant town in the Amazon Rainforest and a gateway to the region. Visitors can enjoy outdoor activities such as whitewater rafting in the Napo River, jungle trekking, and exploring waterfalls. Tena is also known for its Indigenous markets and cultural experiences.
Puyo: Puyo is another town in the eastern lowlands that offers access to the Amazon Rainforest. Lush vegetation, rivers, and waterfalls surround it. Visitors can go tubing down the Puyo or Pastaza rivers, visit the Puyo Zoo, or experience the culture of Indigenous communities in the area.
Indigenous Communities: The eastern lowlands are home to numerous Indigenous communities, such as the Waorani, Kichwa, and Shuar. Visitors can engage with these communities, learn about their traditional ways of life, and participate in cultural activities and ceremonies.
Amazon River Cruises: Exploring the Amazon River on a cruise is a popular way to experience the region. Cruises offer opportunities to navigate the river, spot wildlife, visit Indigenous communities, and learn from knowledgeable guides about the Amazon's diverse ecosystems and cultural heritage.
Wildlife Observation: The eastern lowlands of Ecuador are a haven for wildlife enthusiasts. From birdwatching to spotting monkeys, sloths, caimans, and various reptiles, the region provides ample opportunities to observe and appreciate the incredible biodiversity of the Amazon Rainforest.
Canopy Walkways and Observation Towers: Some lodges and ecotourism centers in the region provide canopy walkways and observation towers that allow visitors to explore the forest canopy and observe the ecosystem from different perspectives. These elevated platforms offer unique views and a chance to encounter wildlife inhabiting the rainforest's upper levels.
Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos Islands, located off the coast of Ecuador, are renowned for their unique wildlife, volcanic landscapes, and pristine ecosystems. Here are some of the main attractions of the Galápagos region:
Unique Wildlife: The Galápagos Islands are famous for their incredible wildlife, much of which is found nowhere else on Earth. Visitors can observe iconic species such as giant tortoises, marine iguanas, blue-footed boobies, Galapagos penguins, and Darwin's finches. The islands offer exceptional opportunities for up-close encounters with these remarkable animals.
Snorkeling and Diving: The Galápagos Islands are a paradise for snorkelers and scuba divers. The crystal-clear waters are home to a diverse marine ecosystem, including sea turtles, rays, colorful fish, and even sharks. Snorkelers can swim alongside playful sea lions and see marine life up close.
Charles Darwin Research Station: Located on the island of Santa Cruz, the Charles Darwin Research Station is a significant attraction for learning about the islands' natural history and ongoing conservation efforts. Visitors can see giant tortoises up close and learn about the breeding programs aimed at preserving these magnificent creatures.
Volcanic Landscapes: The Galápagos Islands were formed by volcanic activity, and their unique geology is a sight to behold. Visitors can explore stunning volcanic landscapes, including lava fields, craters, and otherworldly formations. Volcano hikes, such as the Sierra Negra volcano on Isabela Island, offer breathtaking views.
Post Office Bay: Post Office Bay on Floreana Island has a fascinating history dating back to the whaling era. Visitors can participate in a centuries-old tradition of leaving postcards in a barrel and picking up mail destined for their home region. It's an intriguing and interactive way to connect with travelers worldwide.
Tortuga Bay: Located on Santa Cruz Island, Tortuga Bay is a beautiful beach known for its powdery white sand and turquoise waters. It's an ideal spot for swimming, sunbathing, and observing marine iguanas and nesting sea turtles.
Bartolome Island: Bartolome Island is famous for its iconic volcanic landscape and breathtaking panoramic views from its summit. Visitors can climb the wooden staircase to the viewpoint and witness stunning vistas of the surrounding islands and Pinnacle Rock.
Santa Fe Island: Santa Fe Island offers an opportunity to see unique wildlife, including the endemic Santa Fe land iguana and the Galapagos hawk. Snorkeling around the island's rocky coastline allows one to spot sea lions, tropical fish, and perhaps even a passing reef shark.
Isabela Island: Isabela Island is the largest of the Galápagos Islands and offers diverse attractions. Visitors can explore Sierra Negra volcano, the second-largest volcanic crater in the world, and the picturesque Tintoreras Islets, home to marine iguanas, sea turtles, and penguins. Isabela also has stunning beaches, lagoons, and the famous Los Tuneles, a unique rock formation ideal for snorkeling and spotting marine life.










