Guatemala: Cultural Landscape
Guatemala's cultural landscape is shaped by its Indigenous heritage, Spanish colonial history, and contemporary culture. At the crossroads of ancient and modern influences, Guatemala has many traditions, artistic expressions, festivals, and historical sites that reflect its diverse and evolving identity.
The Cultural Landscape of Guatemala
Guatemala's cultural landscape is a vibrant mosaic, intricately woven from its rich Indigenous heritage, enduring Spanish colonial legacy, and evolving contemporary influences. Situated at the intersection of ancient civilizations and modern globalization, Guatemala boasts a wealth of traditions, artistic expressions, festivals, and historical landmarks that collectively showcase the depth and diversity of its cultural identity. This dynamic fusion of past and present continues to shape the nation's evolving character, making Guatemala a unique cultural hub in Central America.
Indigenous Heritage
Guatemala is home to over 20 distinct Mayan ethnic groups, making it one of Central America's most culturally diverse nations. These Indigenous communities have preserved their ancestral languages, traditional clothing, artisanal crafts, and spiritual practices for centuries. Each group, from the K'iche' to the Mam, contributes unique customs and perspectives to the nation's cultural fabric. The influence of the Mayan civilization is visible in the country's ancient ruins, such as the monumental Tikal and Quiriguá, both UNESCO World Heritage Sites. These sites are enduring testaments to the Mayan people's advanced urban and architectural achievements, drawing global attention to Guatemala's pre-Columbian heritage.
Spanish Colonial Legacy
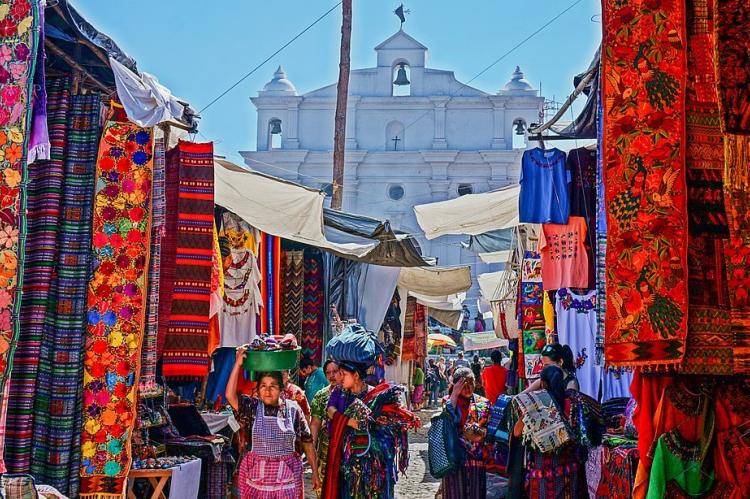
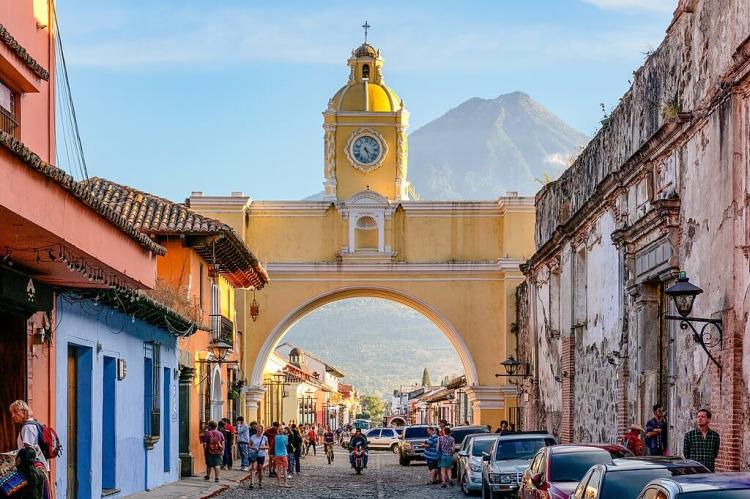
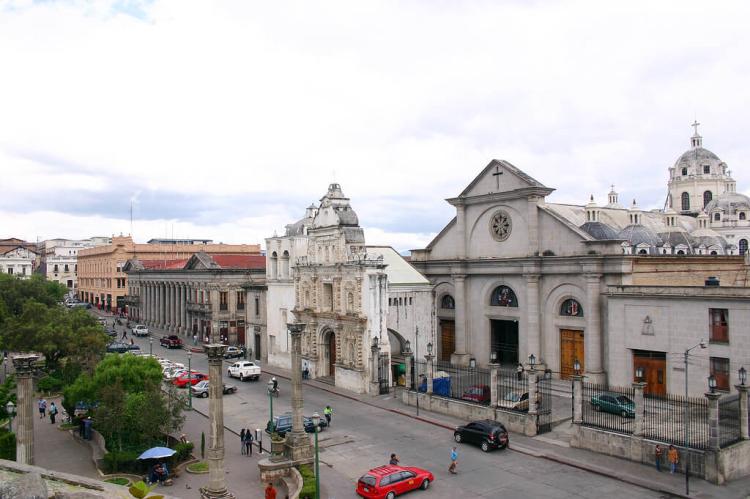
The Spanish colonial period significantly influenced Guatemala's culture, particularly its architecture, religion, and language. Cities like Antigua Guatemala, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, exemplify the splendor of Spanish colonial architecture with their cobblestone streets, baroque churches, and colonial-era homes. The Catholic Church, introduced by the Spanish, remains a dominant influence in Guatemalan society, with many religious practices blending Indigenous beliefs and Catholic traditions in a unique form of syncretism. Catholic festivals, especially Semana Santa (Holy Week), are celebrated with vibrant processions, intricate alfombras (carpets made of colored sawdust), and other elaborate rituals.
Arts and Crafts
Guatemala's artistic heritage is deeply rooted in its Indigenous traditions, particularly in the creation of textiles. The vibrant Mayan textiles, woven on backstrap looms using techniques passed down for generations, are highly valued for their intricate designs and vivid colors. Each region has its distinct patterns and motifs, reflecting the identity of the weaver's community. In addition to textiles, Guatemalan artisans are renowned for their pottery, woodcarvings, and jade jewelry, which have historical significance dating back to the Mayan civilization. Markets like Chichicastenango, famous for its bustling stalls, are treasure troves of handcrafted goods that showcase the nation's artistic legacy.
Music and Dance
Music and dance play integral roles in Guatemalan cultural expression. The marimba, a large wooden xylophone, is the national instrument and a symbol of Guatemalan musical identity. It is often featured at important celebrations and cultural events. Indigenous dances, such as the Baile de la Conquista and the Danza del Venado, are performed during festivals and religious ceremonies, each telling stories rooted in Guatemala's history and spiritual traditions. These performances, accompanied by traditional music, provide a living connection to the past while new genres and influences continue to evolve within the country's contemporary music scene.
Cuisine
Guatemalan cuisine is a fusion of Indigenous Mayan ingredients and Spanish colonial influences, offering diverse flavors and dishes. Staples like maize (corn), beans, and chili peppers are central to many traditional meals. Dishes such as tamales, made from steamed corn dough and filled with meats or vegetables, and pepián, a rich meat stew seasoned with roasted spices, are widely enjoyed. Guatemala is also known for its coffee, which is considered some of the best in the world due to the country's ideal growing conditions. The cuisine reflects the agricultural bounty of the land and the blend of Indigenous and European culinary traditions.
Festivals and Celebrations
Guatemala is known for its colorful festivals, blending Mayan and Catholic traditions. Semana Santa (Holy Week) is the most important religious celebration, marked by elaborate processions, street decorations, and deep communal participation. Other significant events include the K'iche' Maya New Year, celebrated with ancient rituals, and the Giant Kite Festival in Sumpango, where enormous handmade kites are flown to honor deceased loved ones on the Day of the Dead. These festivals serve as cultural expressions, strengthen community bonds, and keep ancient traditions alive.
Natural and Historical Sites
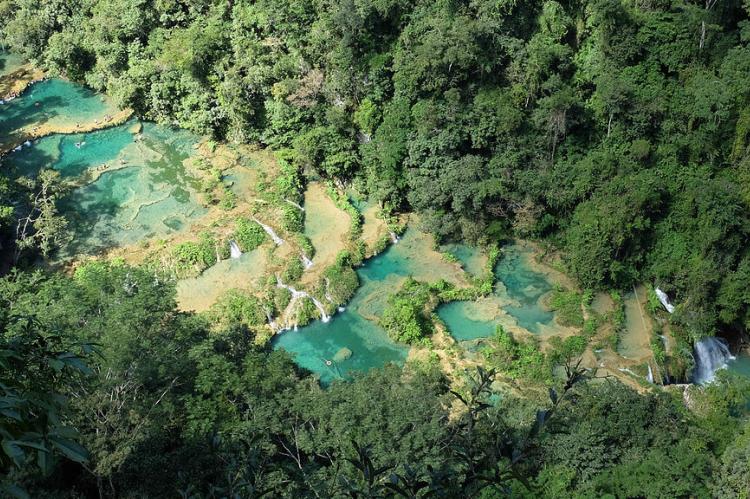
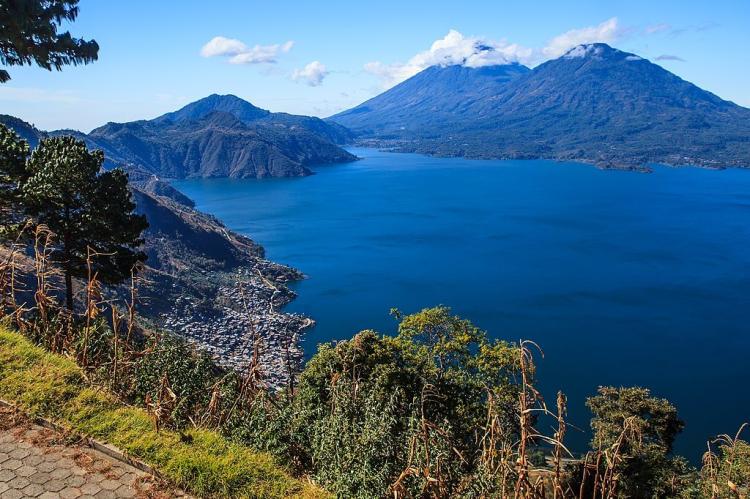
Guatemala's cultural identity is closely intertwined with its breathtaking natural and historical landmarks. Lake Atitlán, surrounded by towering volcanoes and Indigenous villages, is often described as one of the most beautiful lakes in the world. It has long been a spiritual and cultural center for the local Maya. The country's rich history is further reflected in its well-preserved colonial cities, ancient Mayan ruins like those in Tikal National Park, and natural wonders such as the limestone pools of Semuc Champey. Each of these sites adds to the tapestry of Guatemala's cultural landscape, offering visitors and locals alike a profound sense of connection to both history and nature.
Contemporary Influences on Guatemalan Culture
While rooted in ancient traditions, Guatemalan culture continues to evolve under the influence of modern forces such as globalization, technology, economic development, and migration. These influences are reshaping the cultural landscape, introducing new ideas and trends, and presenting challenges to preserving traditional customs.
Globalization
Globalization has increasingly exposed Guatemala to foreign cultures and influences, particularly through media, travel, and trade. While this has brought greater cultural exchange and new opportunities, it has also contributed to the erosion of some traditional practices. Younger generations, especially in urban areas, are adopting global trends, which sometimes conflict with the preservation of Indigenous traditions and local customs.
Technology
The rise of technology has transformed daily life in Guatemala, particularly in terms of communication, education, and entertainment. Social media platforms and the Internet have connected Guatemalans to global conversations and ideas, facilitating cultural exchange. However, the rapid adoption of technology is also altering some traditional ways of life, creating a tension between modernity and tradition.
Economic Development
As Guatemala's economy grows, so does access to education, healthcare, and modern amenities. This economic progress is leading to shifts in values and lifestyles, particularly among urban populations. While increased affluence has improved living standards for many, it also risks widening the gap between rural and urban areas, where traditional ways of life are more closely preserved.
Migration
Migration, especially to the United States, has significantly impacted Guatemalan culture. Many Guatemalans living abroad maintain strong connections to their home country, sending remittances and sharing aspects of Guatemalan culture with the global diaspora. At the same time, the influence of other cultures on returned migrants and their families contributes to the gradual blending of traditions.
Challenges Facing Guatemalan Culture
While Guatemalan culture remains vibrant, it faces significant challenges threatening its preservation and growth.
Poverty
With over half of its population living in poverty, Guatemala struggles with limited access to education, healthcare, and basic services. This economic hardship affects the daily lives of many Guatemalans and puts cultural preservation at risk, as younger generations may lack the resources to maintain traditional practices.
Violence
Guatemala has one of the highest rates of violence in Latin America, driven by poverty, gang activity, and drug trafficking. This violence destabilizes communities and threatens cultural gatherings, festivals, and the safety of public spaces where culture thrives.
Corruption
Corruption remains a pervasive issue in Guatemala. It undermines the country's ability to provide essential services and protect cultural heritage sites. Corruption also hampers development, leading to a lack of infrastructure and support for preserving historical landmarks and traditional practices.
Climate Change
Guatemala is particularly vulnerable to climate change, which threatens its natural environment and agricultural heritage. Rising temperatures, unpredictable rainfall, and extreme weather events pose risks to rural communities and their way of life, which is often closely tied to the land.
Conclusion
Guatemala's cultural landscape is a testament to its rich and complex history, shaped by ancient civilizations, colonial legacies, and modern influences. Its Indigenous heritage, vibrant arts, traditional music, and breathtaking natural sites offer a unique window into the country's soul. However, contemporary challenges such as globalization, poverty, and climate change threaten the preservation of this cultural wealth. Efforts to address these issues while embracing the positive aspects of modernity will ensure that Guatemala's cultural legacy endures for generations to come.

The official flag of Guatemala
Cultural Geography of Guatemala
Largest Cities / Metro Areas
Ranked by population estimate (2023):
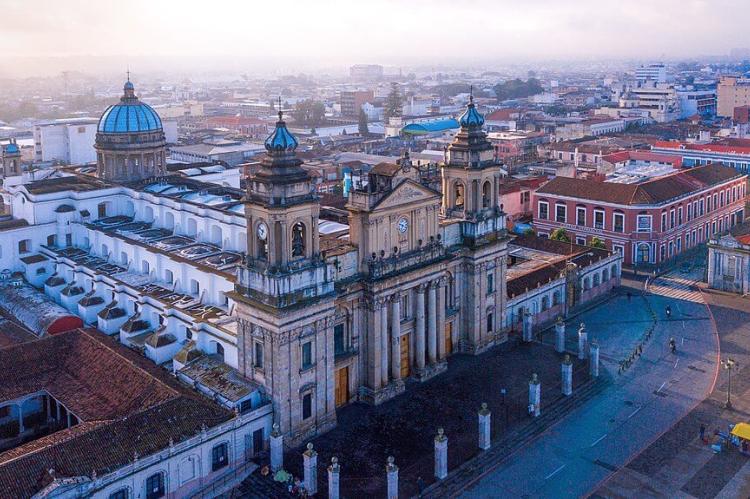
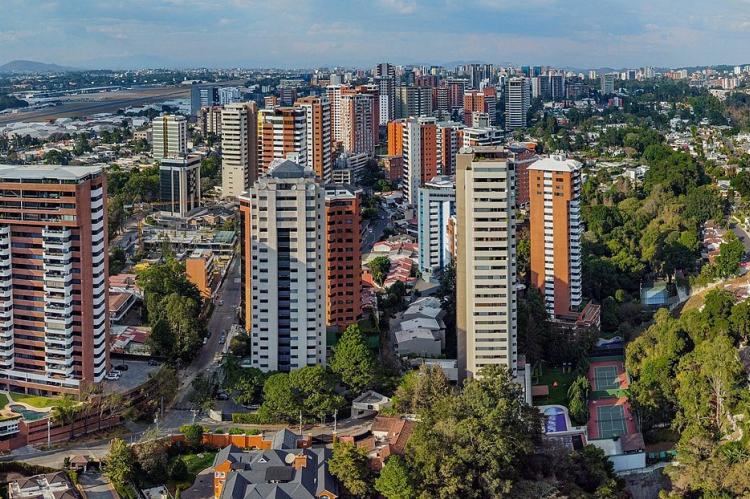
Guatemala City (995,000): Guatemala City is the capital of Guatemala, the Municipality of Guatemala, and the Guatemala Department. It is located in the south-central part of the country, nestled in a mountain valley called Valle de la Ermita (Hermitage Valley). Guatemala City is a significant business, government, and education center that is home to diverse cultures, including Maya, Spanish, and European. The city is also a popular tourist destination with many historical and cultural attractions.
The Guatemala City metropolitan area (AMG) is a collection of densely populated municipalities surrounding Guatemala City. The area includes the municipalities of Amatitlán, Chinautla, Guatemala City, Mixco, San Miguel Petapa, Santa Catarina Pinula, Villa Canales, and Villa Nueva. The metro area's population was estimated to be nearly 4 million in 2023.
Mixco (473,000): Mixco is a city and municipality in the Guatemala Department of Guatemala. It is next to the central Guatemala City municipality and has become part of the Guatemala City Metropolitan Area. Most of Mixco is separated from the city by canyons, for which many bridges have been created.
Villa Nueva (407,000): Villa Nueva is a city and municipality in the Guatemala department of Guatemala. It is located 16 km (10 mi) south of Guatemala City. It was founded on April 17, 1763, before Guatemala declared independence from the Spanish Empire. The local economy largely depends on industrial production, including textiles, metallurgical goods, and plastics. The area's agricultural products include rice, dairy, fruits, and vegetables.
Petapa (141,000): Petapa is a city and municipality in the Guatemala department of Guatemala. It is located south of Guatemala City and is a central transportation hub. Petapa is known for its pottery and ceramics and is home to the IRTRA Mundo Petapa amusement park as well as several educational institutions, including the Universidad Mariano Gálvez de Guatemala and the Instituto Tecnológico de Petapa.
San Juan Sacatepéquez (137,000): Sacatepéquez is a city and municipality in the Guatemala Department of Guatemala. It is located 25 km (15 mi) west of Guatemala City. The city is known for its annual kite festival, the San Andrés Apóstol Church, a beautiful example of colonial architecture, and the Sacatepéquez Market, which offers traditional Guatemalan handicrafts.
Quetzaltenango: (132,000): Quetzaltenango, also known as Xela, is located in the western highlands of Guatemala at an altitude of 2,330 m (7,640 ft) above sea level. The city is known for its colonial architecture, Maya culture, and vibrant arts and culture scene. The nearby Santa María Volcano offers views of the city and the surrounding area.
Villa Canales (122,000): Villa Canales is a city and municipality in the Guatemala Department of Guatemala. It is located 22 km (14 mi) south of Guatemala City. The city's economy is based on coffee, sugarcane, and pineapple. The nearby Pacaya Volcano fertilizes the soil, making it the largest pineapple producer in the nation. Due to rapid growth and development, it has become one of the department's principal municipalities.
Escuintla (103,000): Escuintla is a city and municipality in the Escuintla department of Guatemala. It is located 45 km (28 mi) southwest of Guatemala City. Escuintla is an important commercial and industrial center, home to several factories and businesses. The city is also a popular tourist destination for its beaches, surfing, and volcanoes.
Chinautla (97,000): Chinautla is a city and municipality in the Guatemala Department of Guatemala. It is located 10 km (6 mi) north of Guatemala City. Chinautla is a traditional pottery-making town home to several pottery workshops and markets. The city is also known for its annual pottery festival, which is held in February.
Chimaltenango (82,000): Chimaltenango is the capital of the Chimaltenango department and the municipal seat for the surrounding municipality of the same name. It is located approximately 56 km (35 mi) west of Guatemala City on the Pan-American Highway. The municipal capital produces textiles and pottery.
Administrative Divisions
Guatemala is divided into 22 departments. The departments are subdivided into 340 municipalities.
Departments
Alta Verapaz (Capital: Cobán): Alta Verapaz is known for its lush landscapes and Indigenous cultures. It features mountains, forests, and natural attractions like Semuc Champey, making it a destination for eco-tourism.
Baja Verapaz (Capital: Salamá): Baja Verapaz is characterized by its hilly terrain and agricultural activities. It offers scenic views and access to natural wonders.
Chimaltenango (Capital: Chimaltenango): Chimaltenango is located in the central highlands. It has both urban and rural areas. It's known for its Indigenous traditions and handicrafts.
Chiquimula (Capital: Chiquimula): Chiquimula is located in the eastern part of the country and offers a mix of agriculture and commerce. It's known for its fertile valleys and archaeological sites.
El Progreso (Capital: Guastatoya): El Progreso is known for its agricultural activities and rural landscapes. The department offers opportunities for exploring rural life and natural beauty.
Escuintla (Capital: Escuintla): Escuintla is located along the Pacific coast and is known for its beaches and coastal attractions. It's an important agricultural and commercial center.
Guatemala (Capital: Guatemala City): The Department of Guatemala houses the country's capital city, the political, economic, and cultural hub. It offers a blend of historical sites, modern infrastructure, and cultural diversity.
Huehuetenango (Capital: Huehuetenango): This city is known for its diverse Indigenous cultures and mountainous landscapes. It offers opportunities to explore traditional communities and natural attractions.
Izabal (Capital: Puerto Barrios): Izabal is in the country's northeastern part, known for its Caribbean coastline and lake. It offers opportunities for boating, eco-tourism, and relaxation.
Jalapa (Capital: Jalapa): Jalapa is characterized by its agriculture and mountainous terrain. It's known for its rural atmosphere and access to natural landscapes.
Jutiapa (Capital: Jutiapa): Jutiapa is located in the country's southeastern part and features a mix of rural and urban areas. It offers access to both agricultural activities and commercial centers.
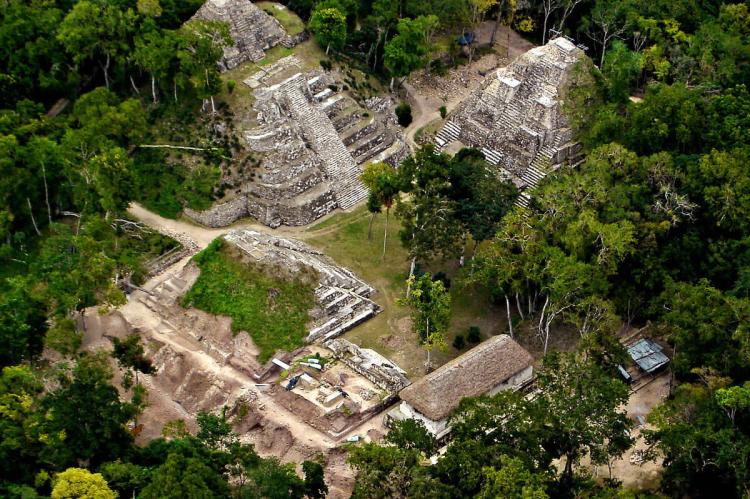
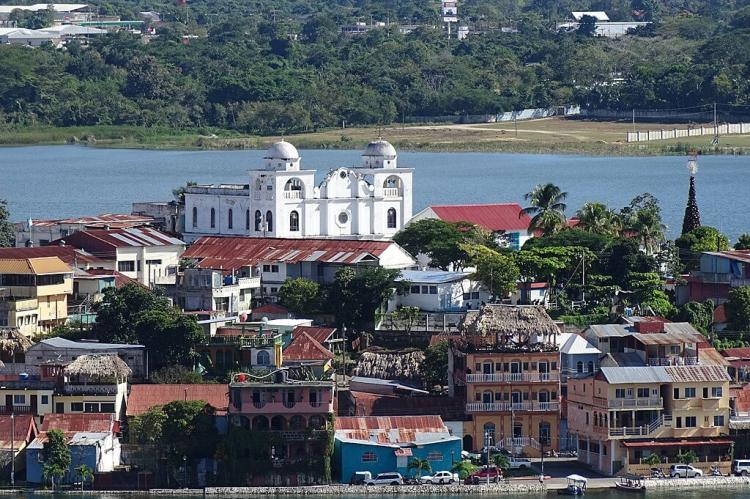
Petén (Capital: Flores): Petén is known for its ancient Maya ruins and dense rainforests. It's a destination for archaeological exploration and wildlife observation.
Quetzaltenango (Capital: Quetzaltenango): Quetzaltenango, also known as Xela, is the second-largest city in Guatemala. It's known for its cultural vibrancy, colonial architecture, and nearby natural attractions.
Quiché (Capital: Santa Cruz del Quiché): Quiché is characterized by its Indigenous culture and mountainous landscapes. It offers archaeological sites, traditional communities, and historical significance.
Retalhuleu (Capital: Retalhuleu): Retalhuleu is known for its Pacific coast beaches and attractions, such as the Xetulul amusement park. It offers a mix of relaxation and entertainment.
Sacatepéquez (Capital: Antigua Guatemala): Sacatepéquez is home to Antigua Guatemala, a UNESCO World Heritage site known for its well-preserved colonial architecture and cultural heritage.
San Marcos (Capital: San Marcos): San Marcos is known for its diverse geography, including volcanoes, lakes, and mountains. It's a destination for outdoor activities and nature exploration.
Santa Rosa (Capital: Cuilapa): Santa Rosa is located along the Pacific coast and offers access to beaches and coastal attractions. It's known for its agriculture and rural landscapes.
Sololá (Capital: Sololá): Sololá is known for its Indigenous culture and picturesque Lake Atitlán. It offers opportunities to explore traditional communities and natural beauty.
Suchitepéquez (Capital: Mazatenango): Suchitepéquez is known for its agricultural activities and coastal attractions. It offers a blend of rural and urban features.
Totonicapán (Capital: Totonicapán): Totonicapán is characterized by its Indigenous communities and mountainous landscapes. It offers opportunities to experience traditional cultures and highland beauty.
Zacapa (Capital: Zacapa): Zacapa is located in the eastern part of the country and is known for its agriculture and hot climate. It offers opportunities for exploring rural life and local traditions.
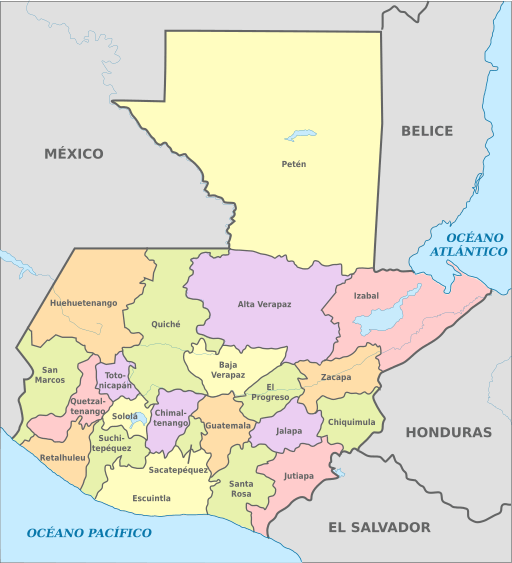
Map depicting the departments of Guatemala
Geographic Regions (Zones)
The surface of Guatemala is characterized by three major topographical features that can also be defined as geographic regions or zones:
The Petén Lowlands, the Guatemalan Highlands, and the Pacific Coast Flatlands. A minor zone, the Caribbean Coast, can also be defined.
See more: Natural Landscape of Guatemala
Historical, Cultural, and Natural Landmarks
Guatemala has a rich history, diverse culture, and stunning natural landscapes. Here are some notable historical, cultural, and natural landmarks in Guatemala, listed by region:
Petén Lowlands
The Petén Lowlands region in Guatemala is a fascinating area known for its rich Mayan history, lush rainforests, and impressive archaeological sites. Here are some of the notable attractions located in Guatemala's Petén Lowlands:
Tikal National Park: Tikal is one of the world's most famous and important Mayan archaeological sites. It was once a thriving city of the ancient Maya civilization known for its towering pyramids, temples, and expansive plazas. Exploring Tikal allows visitors to immerse themselves in the history and grandeur of the Mayan civilization.
Yaxhá: Yaxhá is another important Mayan archaeological site located near Tikal. It features impressive temples, pyramids, and an ancient ball court. Yaxhá offers stunning views over the surrounding jungle and nearby Yaxhá Lake, making it a picturesque destination for history and nature enthusiasts.
El Mirador: This ancient Mayan city is deep in the jungle. It is known for its massive pyramids, including the impressive La Danta temple, one of the world's largest pyramids by volume. Although the site is remote and challenging, the journey rewards with a unique and awe-inspiring archaeological experience.
Lake Petén Itzá: Lake Petén Itzá is a large lake surrounded by lush rainforest. It offers opportunities for swimming, boating, and fishing. The lakeside town of Flores, located on an island in the lake, is a popular base for exploring the Petén Lowlands region.
Ixpanpajul Nature Park: Ixpanpajul is a nature reserve and adventure park near Flores. It features canopy walkways, zip lines, and hiking trails that allow visitors to experience the beauty of the rainforest from different perspectives. The park also has diverse flora and fauna, including howler monkeys and tropical birds.
Ceibal: This archaeological site is known for its well-preserved Mayan ruins and intricate stelae (carved stone monuments). It is located in a remote jungle and offers a more off-the-beaten-path experience than other significant sites. Ceibal is surrounded by lush vegetation and provides insights into the daily lives of the ancient Mayans.
Biotopo Cerro Cahuí: Biotopo Cerro Cahuí is a protected area near Flores that preserves a range of ecosystems, including wetlands and tropical forests. It is home to various wildlife species, including jaguars, monkeys, and colorful bird species. Guided tours allow visitors to explore the region's natural beauty and biodiversity.
Guatemalan Highlands
Guatemala's Highlands region, also known as the Guatemalan Altiplano, is a stunning mountainous area known for its Indigenous culture, colorful markets, and breathtaking landscapes. Here are some of the notable attractions located in Guatemala's Highlands:
Lake Atitlán: Lake Atitlán is a magnificent volcanic lake surrounded by picturesque villages and towering volcanoes. It is considered one of the most beautiful lakes in the world. Visitors can take boat tours or kayaking trips or enjoy the stunning views of the lake and its surroundings.
Antigua Guatemala: Antigua Guatemala, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is a colonial city in the highlands. It is famous for its well-preserved Spanish Baroque-influenced architecture, cobblestone streets, and ruins of colonial churches. Visitors can explore the city's historic center, visit museums, and indulge in local cuisine.
Chichicastenango Market: Chichicastenango, or Chichi, is home to one of Central America's largest and most vibrant Indigenous markets. The market, which takes place on Thursdays and Sundays, offers a colorful display of handicrafts, textiles, fresh produce, and traditional Maya rituals. It is an excellent place to immerse yourself in Indigenous culture and buy unique souvenirs.
Quetzaltenango (Xela): Quetzaltenango, often called Xela, is the second-largest city in Guatemala and a hub of Indigenous culture. It is surrounded by scenic landscapes, including hot springs, volcanoes, and highland valleys. Xela offers opportunities for language study, volunteering, and exploring nearby natural attractions.
Iximché Archaeological Site: Iximché was once the capital of the Kaqchikel Maya civilization and is now an archaeological site. It features ruins of temples, pyramids, and ceremonial structures. Visitors can explore the area, learn about Mayan history, and enjoy panoramic views of the surrounding countryside.
Fuentes Georginas: This natural hot spring is located near the town of Zunil. The thermal pools are surrounded by a lush cloud forest, offering a relaxing and rejuvenating experience. Visitors can soak in the warm waters while enjoying the tranquil beauty of the highland environment.
Nebaj, Chajul, and Todos Santos: These three towns in the Quiché department are known for their vibrant Indigenous culture. Visitors can witness traditional Maya ceremonies, explore local markets, and learn about the distinctive customs and traditions of the region's Indigenous communities.
Acatenango Volcano: Acatenango is one of Guatemala's most challenging and rewarding hikes. It offers stunning views of nearby Volcán de Fuego and Lake Atitlán. Hiking to the summit allows visitors to witness breathtaking sunrises and experience the power of the volcanic landscape.
Pacific Coast Flatlands
Guatemala's Pacific Coast region offers a range of attractions, including stunning beaches, mangrove forests, charming coastal towns, and cultural sites. Here are some notable attractions located in Guatemala's Pacific Coast region:
Monterrico: Monterrico is a popular beach town known for its volcanic black sand beaches and sea turtle conservation efforts. Visitors can relax on the beach, take boat tours through the mangrove forests, and witness sea turtle nesting (especially during the nesting season).
Hawaii Beach: Located near Champerico, Hawaii Beach is known for its long stretch of pristine sandy beach and clear waters. It is an excellent place for swimming, sunbathing, and enjoying water sports like surfing and kayaking.
Sipacate-Naranjo National Park: This national park encompasses a stretch of coastline with diverse ecosystems, including mangrove forests, wetlands, and beaches. It is an essential habitat for migratory birds and sea turtles. Visitors can explore the park's natural beauty, spot wildlife, and learn about the region's ecological significance.
Tilapa Beach: This secluded beach is located near the town of Tilapa. It is a tranquil spot known for its calm waters and beautiful sunsets. Visitors can enjoy swimming, beachcombing, and peaceful walks along the shore.
Santa Lucia Cotzumalguapa: This town is home to several ancient Mayan archaeological sites, including Takalik Abaj. Takalik Abaj features stone sculptures, pyramids, and altars from the pre-Columbian era. Visitors can explore the archaeological site and learn about the Mayan civilization that once thrived there.
Iztapa: Iztapa is a fishing village known for its excellent sport fishing opportunities. Anglers can enjoy deep-sea fishing for sailfish, marlin, and other species. The town also offers boat tours along the coastline, where visitors can spot dolphins, seabirds, and marine life.
Champerico: Champerico is a small coastal town known for its laid-back atmosphere and picturesque beach. It is a popular destination for surfing and fishing. Visitors can relax on the beach, try local seafood dishes, and explore the nearby mangrove forests.
Escuintla: While not directly on the coast, Escuintla is the gateway to the Pacific Coast region and offers cultural attractions. The city features colonial architecture, a lively central plaza, and a bustling local market where visitors can experience the local culture and sample traditional cuisine.
Caribbean Coast
Guatemala's Caribbean Coast region, also known as the Caribbean Lowlands, is a diverse and vibrant area with a unique blend of Indigenous culture, lush rainforests, and a stunning coastline. Here are some notable attractions located in Guatemala's Caribbean Coast region:
Livingston: Livingston is a lively coastal town known for its Afro-Caribbean culture and laid-back atmosphere. The village is accessible only by boat and offers a distinct blend of Garifuna, Maya, and Caribbean influences. Visitors can explore the colorful streets, taste delicious Creole cuisine, and experience traditional Garifuna drumming and dancing.
Río Dulce: Río Dulce is a scenic river that flows from Lake Izabal to the Caribbean Sea. A lush rainforest and towering cliffs surround the river. Visitors can take boat tours along the river, visit the impressive Castillo de San Felipe fortress, and explore the nearby hot springs and waterfalls.
Livingston Garifuna Cultural Center: This cultural center in Livingston provides insights into the Garifuna community's traditions, music, and dance. Visitors can participate in workshops, watch performances, and learn about the Garifuna people's history and heritage.
Quiriguá Archaeological Site: Although not directly on the coast, Quiriguá is an important Mayan archaeological site near the Caribbean Coast. It is renowned for its intricately carved stelae and zoomorphic sculptures, offering a glimpse into the ancient Maya civilization and its artistic achievements.
Punta de Manabique Wildlife Refuge: This protected area encompasses coastal mangroves, wetlands, and forests along the Caribbean Coast. It is a haven for wildlife, including manatees, crocodiles, monkeys, and various bird species. Visitors can take boat tours to explore the diverse ecosystems and observe the abundant wildlife.
Izabal: Izabal is a department located on the Caribbean Coast and offers various attractions. One highlight is Lake Izabal, Guatemala's largest lake, where visitors can enjoy boating, fishing, and exploring the scenic surroundings. The department is also home to the historic town of Izabal and the impressive Finca Paraíso hot waterfall.
Ak'tenamit Indigenous Community: Located near Fronteras (Rio Dulce), the Ak'tenamit Indigenous Community offers opportunities to learn about the Q'eqchi Maya culture and way of life. Visitors can participate in cultural exchange programs, attend workshops, and support community-based tourism initiatives.










