Belize: Natural Landscape
Belize is located along the Caribbean coast of northeastern Central America. Known as British Honduras until 1973, its geography consists of heavily forested plains and the Maya Mountains. The Belize Barrier Reef System flanks the coastline while cays and atolls dot the reef.
The Natural Landscape of Belize: A Vibrant Tapestry of Biodiversity
Nestled along the Caribbean coast of northeastern Central America, Belize unveils a captivating natural landscape that seamlessly blends terrestrial and marine wonders. Bordered by Mexico to the north, Guatemala to the west and south, and the azure waters of the Caribbean Sea to the east, this country, formerly known as British Honduras until 1973, carries a unique heritage as the last British colony on the American mainland.
A Coral Jewel: The Belize Barrier Reef
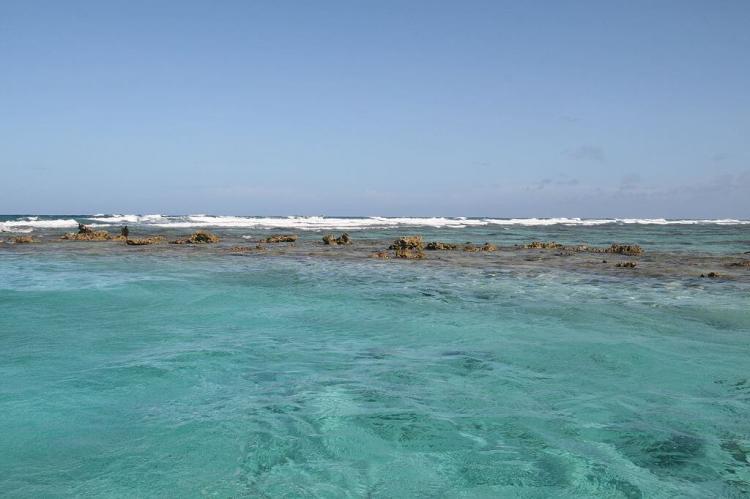
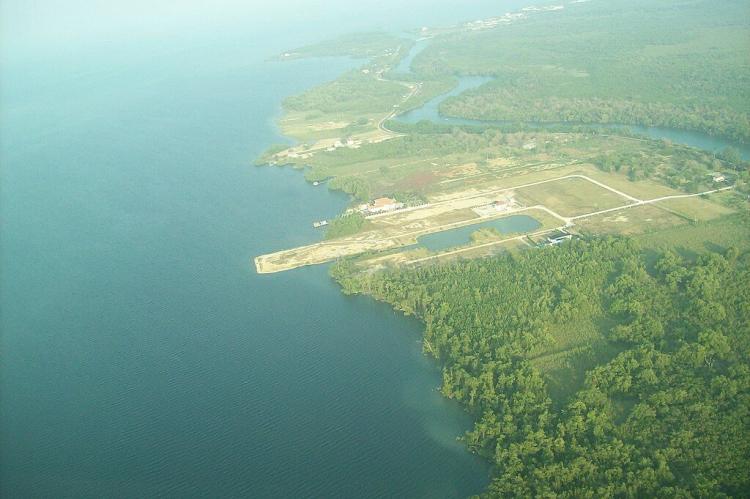
The Belize Barrier Reef is the second-longest barrier reef globally, stretching approximately 300 kilometers (190 miles). It forms a striking maritime frontier along much of Belize's predominantly marshy coastline. This remarkable natural formation, complemented by numerous small cayes (islands), creates a distinctive and visually captivating marine landscape that harbors an abundance of aquatic life.
Diverse Terrestrial Realms
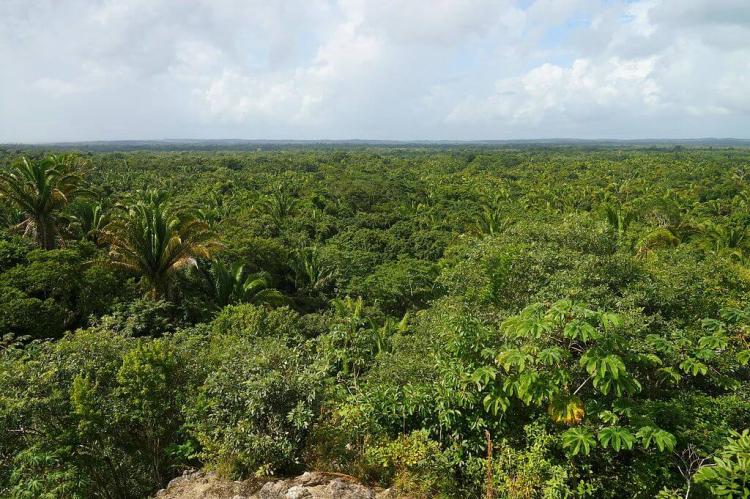
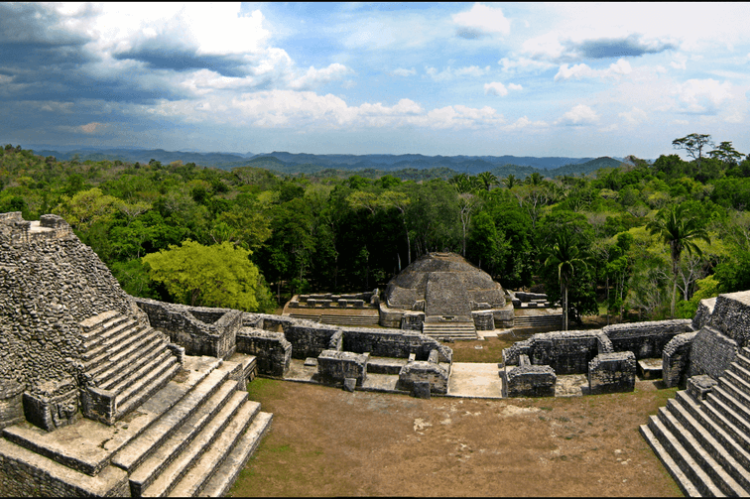
Inland, Belize's northern region is characterized by flat and swampy coastal plains, densely blanketed by lush forests that stretch across various areas. In contrast, the southern section is marked by the low-lying Maya Mountains, contributing to the country's diverse and visually striking geography.
A Biodiversity Hotspot
Belize boasts a remarkable biodiversity, spanning diverse ecosystems that range from coastal mangroves and wetlands to tropical rainforests. Its strategic location and varied habitats contribute to a rich tapestry of plant and animal species. The Belize Barrier Reef Reserve System, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, serves as a haven for marine biodiversity, hosting a vibrant array of coral, fish, and other aquatic life.
The country's terrestrial realms are home to a wealth of wildlife, including numerous bird species, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians. Despite its modest size, Belize ranks an impressive 67th in the Global Biodiversity Index, showcasing its significant ecological richness. The statistics testify to its natural wealth, with 531 bird species, 37 amphibian species, 650 fish species, 148 mammal species, 140 reptile species, and an astonishing 4,192 vascular plant species.
Conservation: A Continuous Commitment
Conservation in Belize represents a continuous and essential commitment to safeguarding the nation's diverse ecosystems, wildlife, and natural resources. Renowned for its pristine tropical rainforests, coral reefs, and abundant biodiversity, the government significantly emphasizes conservation initiatives to preserve these natural assets while fostering sustainable development.
However, conservation efforts face challenges such as illegal logging, unsustainable fishing practices, habitat destruction, and potential impacts from climate change. These challenges underscore the importance of ongoing conservation endeavors to ensure the longevity of the country's environmental treasures.
A Tropical Embrace
Belize's tropical climate envelops the land with warm and humid conditions throughout the year, boasting a mean annual temperature of 27°C (81°F) and an average humidity of 85%. The climate exhibits two distinct seasons: the wet season, spanning June to November, marked by substantial rainfall and elevated humidity, and the dry season, from December to May, featuring reduced rainfall and lower humidity. Even during the dry season, some precipitation graces the landscape.
Temperature variations are influenced by elevation, coastal proximity, and the mitigating impact of northeast trade winds from the Caribbean Sea. Coastal regions tend to be warmer and more humid. At the same time, the mountainous western areas experience cooler and less humid conditions, adding to the diversity of microclimates within this small yet captivating nation.
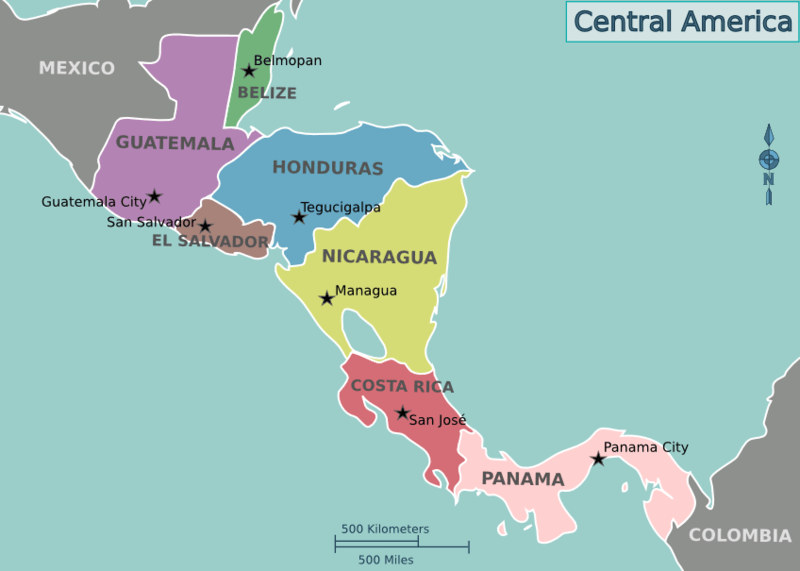
Location map of the countries of Central America
Natural Geography of Belize
Geographic Regions
Belize can be divided into four main geographic regions: the northern limestone lowlands, the Maya Mountains in the south, the narrow coastal plain, and the offshore atolls and cayes.
Northern Lowlands
The country's northern half consists of limestone lowlands and swamps less than 60 m (200 ft) above sea level. Eighteen rivers and many perennial streams drain these low-lying areas. Flat agricultural fields, small farming towns, and lowland rainforests dominate the region.
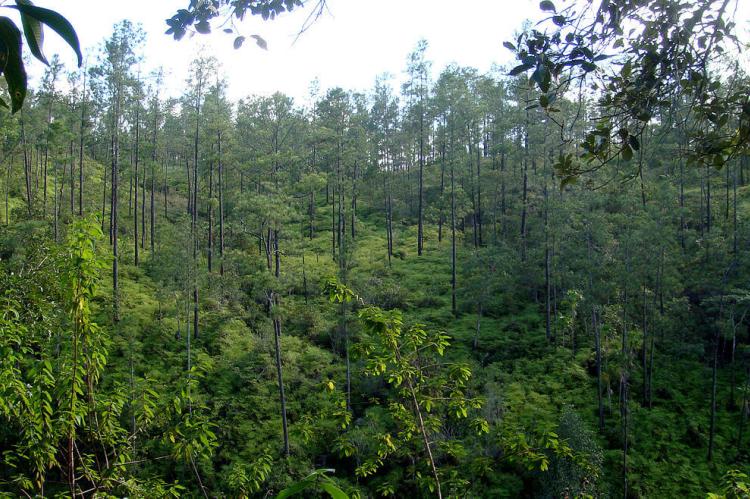
Westward from the northern coastal areas, the terrain changes from mangrove swamps to tropical pine savannah and hardwood forest. The flora here is highly diverse.
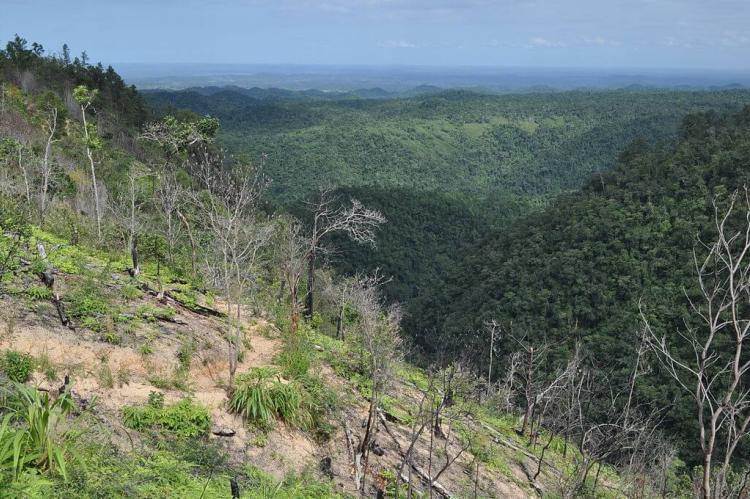
Maya Mountains
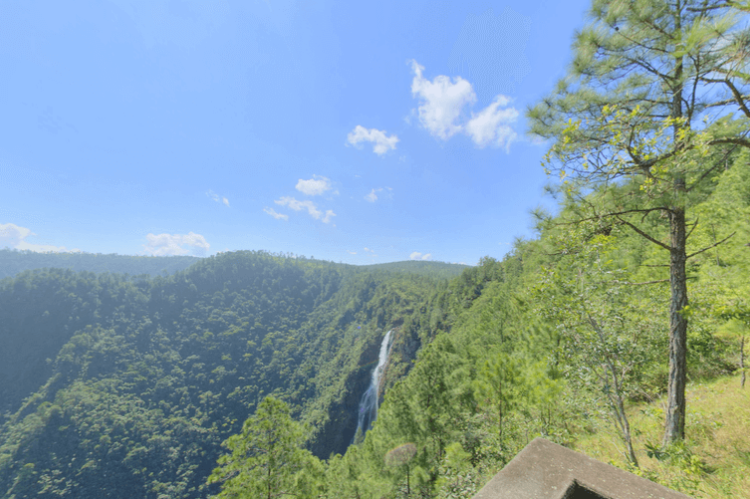
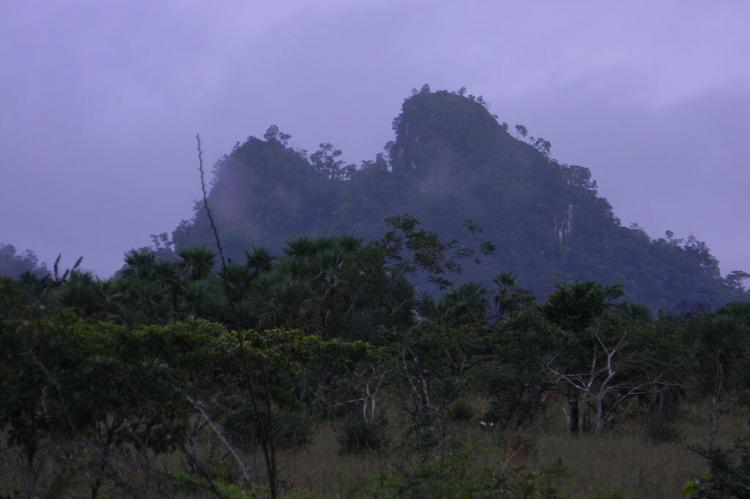
The Maya Mountains of the south dominate all but the narrow coastal plain. A plateau of igneous rock cut by erosion into hills and valleys, the rugged but relatively low mountains stretch southwesterly to northeasterly. The highest point is Victoria Peak, at 1,120 m (3,674 ft).
The Cockscomb Range, a spur of the Maya Mountains, runs toward the sea and rises to its highest point at Doyle's Delight at 1,124 m (3,687 ft). Because Doyle's Delight is just a spur slightly higher than the surrounding mountain range rather than an actual peak, it had no official name for most of the country's history. These heavily forested highlands are sparsely inhabited and are covered with shallow, highly erodible soils of low fertility.
Coastal Plain
The coastline is flat and swampy, with many lagoons, especially in the northern and central parts of the country. Scattered oaks, pines, and palmetto palms on the southern coastal plain and inland from Belize City mark the open savanna (grassland).
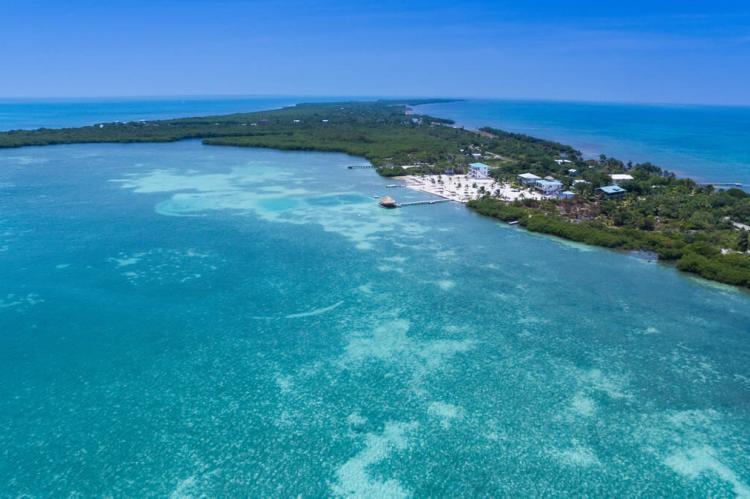
Offshore Cayes and Atolls
Almost countless offshore cayes, atolls, and lagoons fringe the Caribbean coastline. The Belize Barrier Reef system comprises the most significant barrier reef in the northern hemisphere, offshore atolls, several hundred sand cays, mangrove forests, coastal lagoons, and estuaries.
See more: Cayes, Reefs, and Atolls of Belize
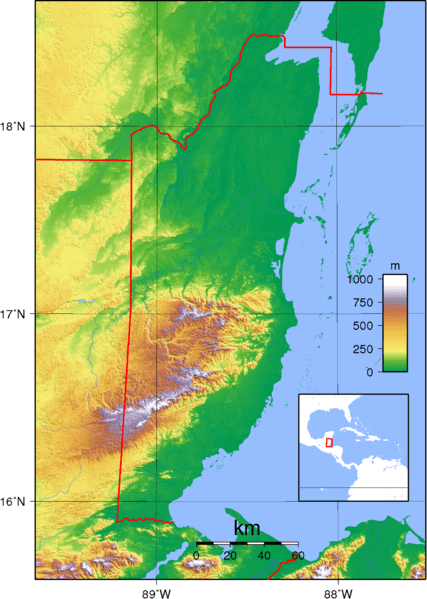
Topographic map of Belize.
Natural Regions
Approximately 60% of Belize is forested, comprising at least 50 tree species. Savanna, scrubland, and wetland constitute the remainder of the landscape. Important mangrove ecosystems are also represented.
Ecological Regions
The following is a list of terrestrial ecoregions in Belize, as defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). Belize is in the Neotropical realm. Ecoregions are classified by biome type - the major global plant communities determined by rainfall and climate.
Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests
Peten-Veracruz moist forests
Tropical and subtropical coniferous forests
Belizian pine forests
Mangroves
Belizean Reef mangroves
Belizean Coast mangroves
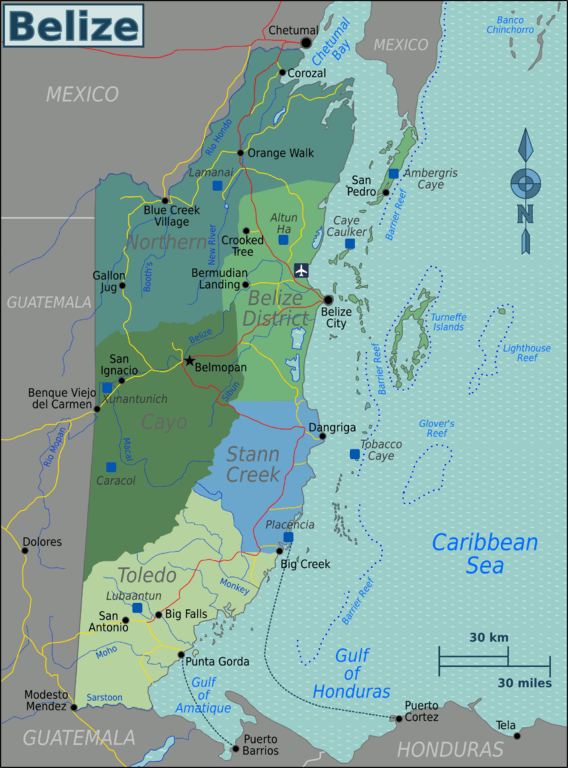
Map depicting the regions of Belize.
Bodies of Water
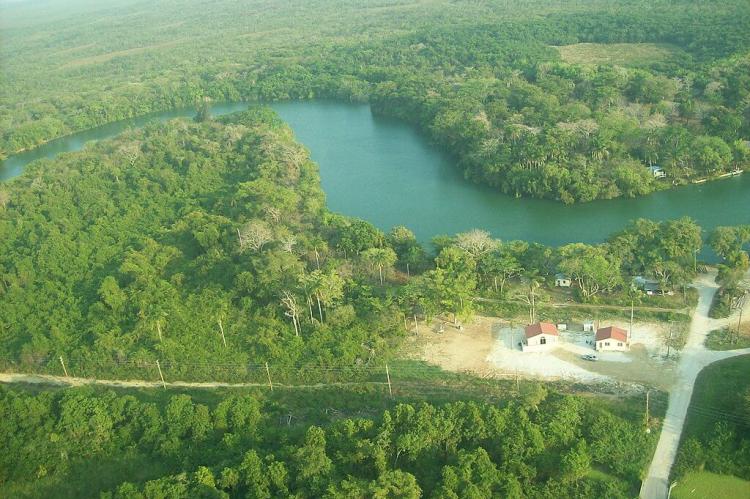
Belize has many lakes, lagoons, and approximately 35 major rivers, the longest of which is the Belize River. The bodies of water are essential for drinking, agriculture, and hydroelectric power generation. They are also popular for recreation, such as fishing, swimming, and rafting.
See more: Water Bodies of Belize
Administrative Divisions
Belize's administrative divisions include six districts, each located in a different geographic region.
See more: Cultural Landscape of Belize
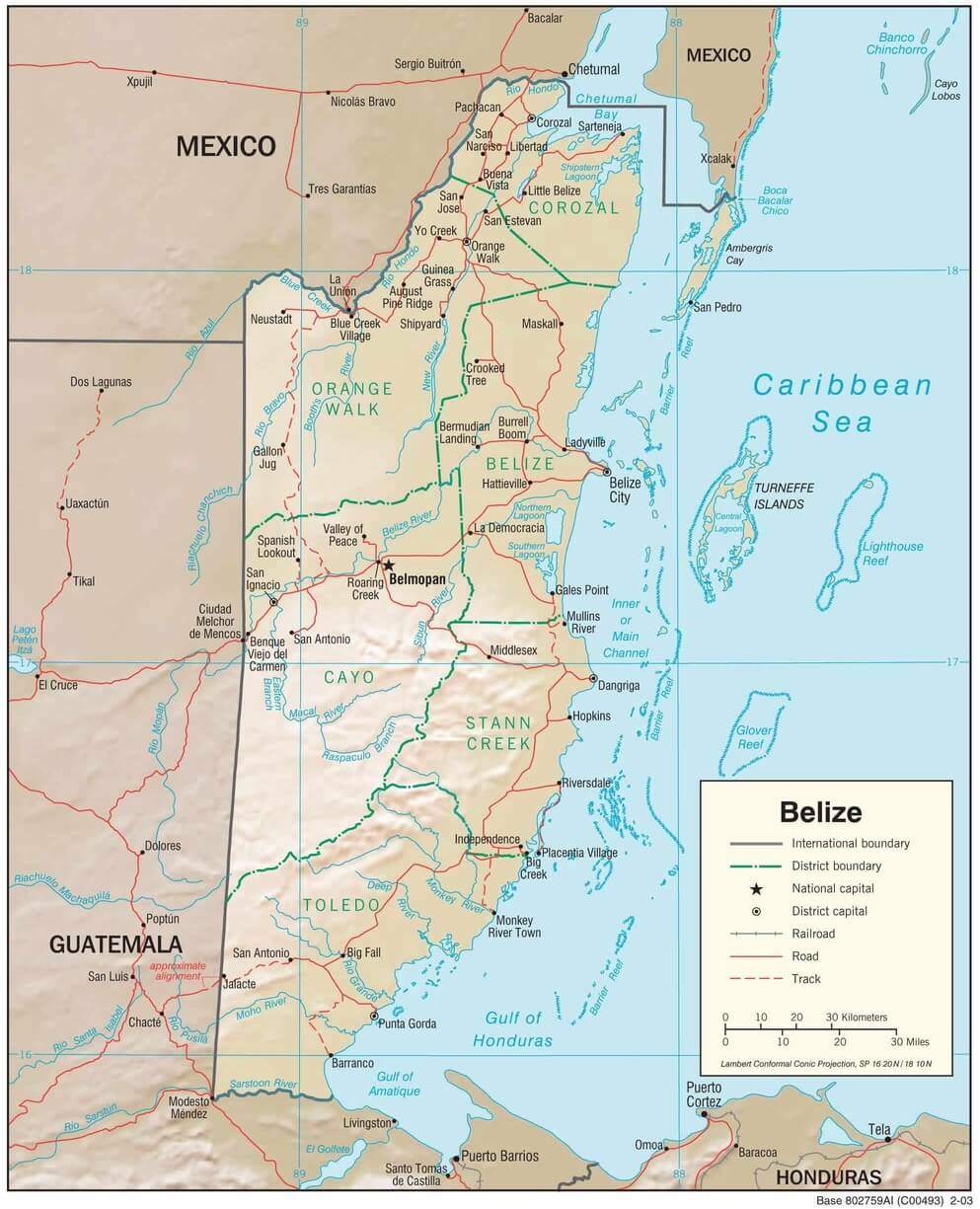
Belize physiographic map.










