French Guiana: Natural Landscape
French Guiana, a French overseas department on South America's northeastern coast, is mainly covered by dense rainforests and rivers. Most of its population resides near the capital, Cayenne. As the smallest mainland territory in South America, it is known for its exceptional biodiversity and ecological richness.
The Natural Landscape of French Guiana: An Untamed Wilderness
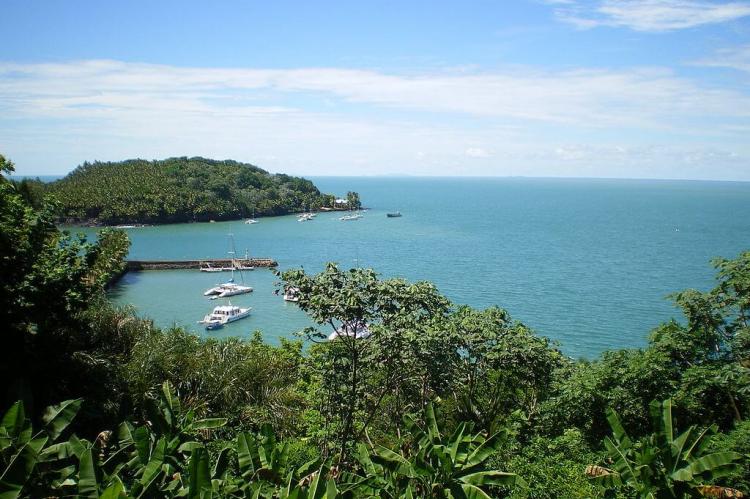
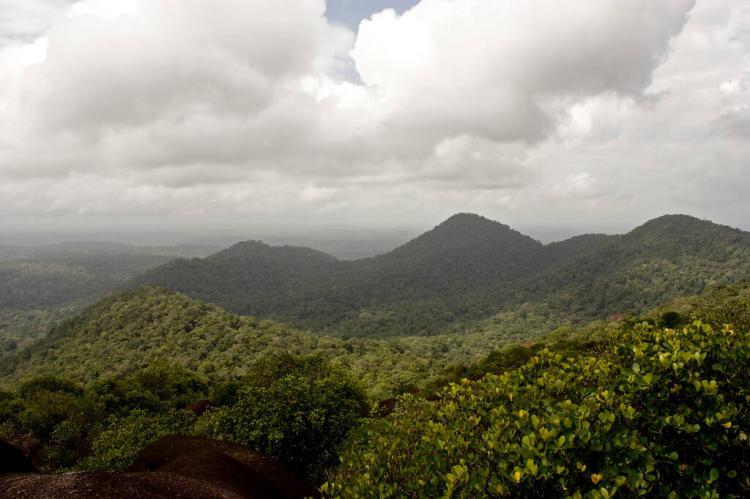
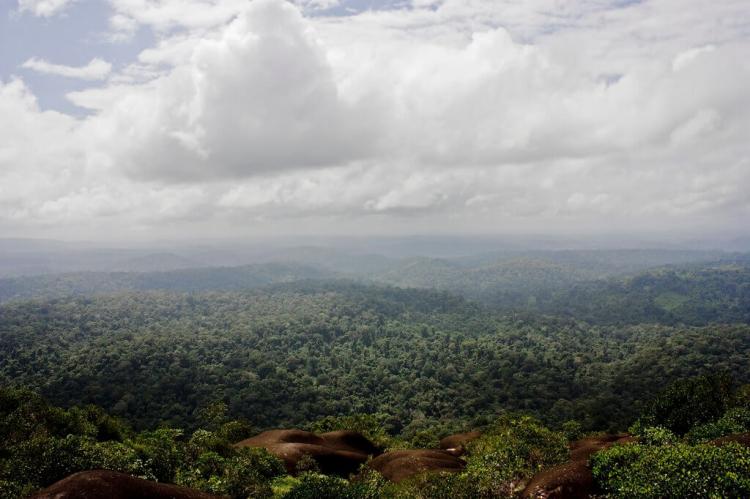
French Guiana (Guyane), a French overseas department on South America's northeastern coast, shares borders with Suriname to the west, Brazil to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the north. Stretching across 378 km (235 mi) of the Atlantic coastline, French Guiana's dense rainforests and network of rivers offer a captivating landscape largely untouched by human development. The capital, Cayenne, lies on the coast, with most of the population living along this coastal strip, leaving the interior rainforests sparsely inhabited and mysterious. Part of the broader Guianas region that includes Suriname and Guyana, French Guiana covers 83,534 sq km (32,253 sq mi), making it the smallest mainland territory in South America. Despite its size, it hosts one of the continent's most biodiverse and ecologically intact landscapes.
The Guiana Shield and Rich Ecosystems
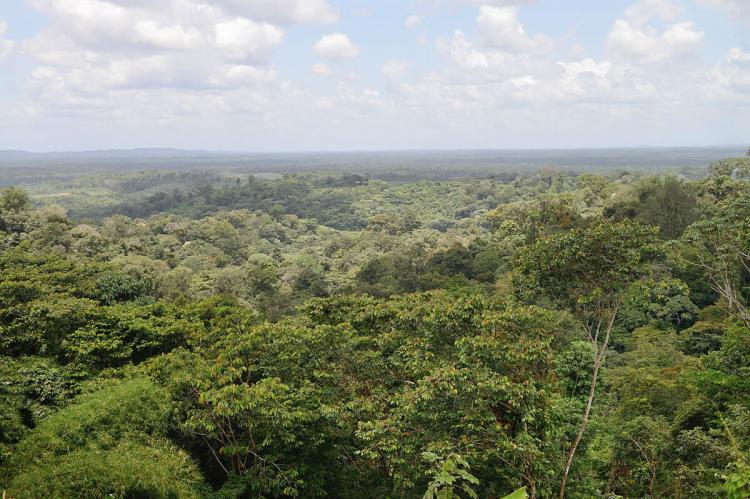
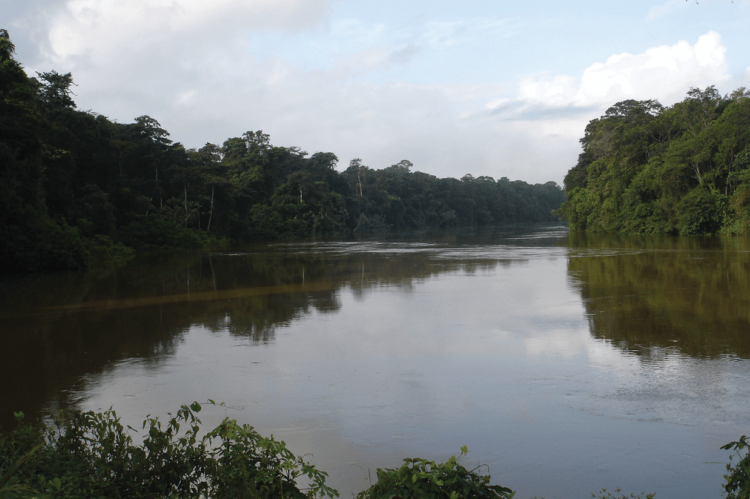
French Guiana forms part of the Guiana Shield, one of the world's oldest geological formations, spanning parts of Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, and Brazil. This ancient shield supports ecosystems ranging from tropical rainforests and mountainous terrains to wetlands and coastal mangroves, creating a mosaic of biodiversity. The rainforest here is often called "the lungs of the planet" due to its role in carbon sequestration, making it a critical component of global environmental health. Unlike many regions, French Guiana's primary mode of interior access is via rivers and streams, as much of the area remains roadless, preserving the pristine nature of the landscape.
Indigenous Peoples and the Cultural Landscape
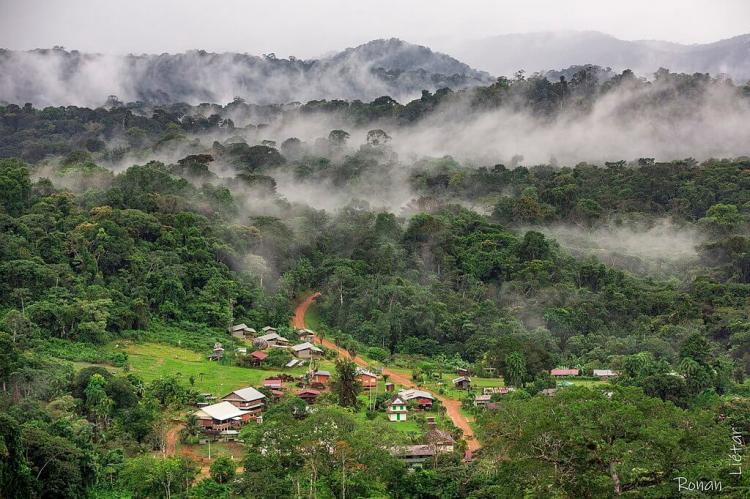
Six Indigenous communities reside in French Guiana, including the Kali'na Tileuyu, Lokono, and Pahikweneh along the coast, and the Wayãpi, Teko, and Wayana in remote inland territories along the Oyapock and Maroni Rivers. These communities play a significant role in preserving traditional knowledge and sustainable practices, essential for maintaining the delicate balance of the natural ecosystem. Their cultural and environmental stewardship helps conserve local biodiversity and protect sacred natural sites, contributing to a deeper understanding of the region's landscape.
Biodiversity: A Haven for Unique Flora and Fauna
The rainforests of French Guiana are biodiversity hotspots, home to thousands of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic. The area is believed to house over 5,500 plant species, including 1,000 tree varieties. French Guiana's fauna is equally impressive, with over 700 bird species, 177 mammals, 109 amphibians, and more than 500 fish species, nearly half of which are found nowhere else in the world. This diverse habitat supports rare and remarkable animals, such as pumas, ocelots, tapirs, caimans, and the capybara, the world's largest rodent. French Guiana is also home to various primates, including the howler and capuchin monkeys, along with sloths, great anteaters, and a plethora of reptilian and amphibian life. The rich birdlife, ranging from colorful macaws to the elusive harpy eagle, underscores French Guiana's importance as a sanctuary for avian diversity.
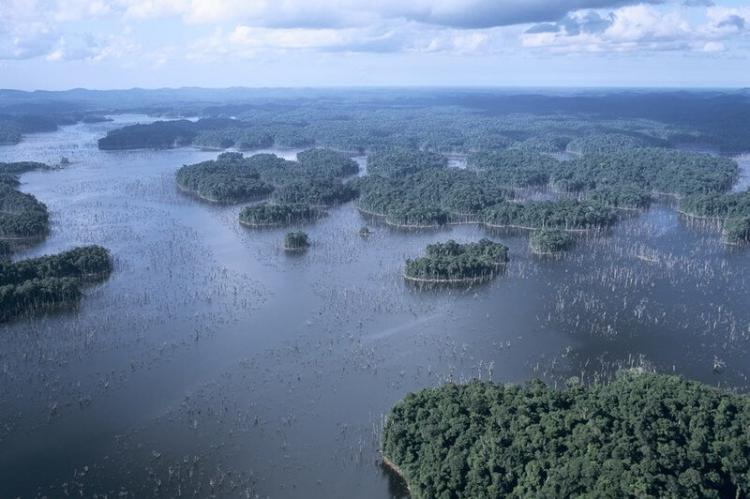
The extensive network of rivers in French Guiana also provides vital habitats for fish, aquatic mammals, and plants, contributing to the complex interconnectivity of the ecosystem. These rivers serve as the lifelines of the rainforest, facilitating species migration, nutrient distribution, and even cultural exchange among Indigenous communities.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting a Natural Legacy
Conservation in French Guiana is a top priority, given its ecological value and status as one of the few remaining intact tropical rainforests on Earth. National parks, nature reserves, and wildlife sanctuaries cover vast portions of the land and marine territories, underscoring the region's commitment to environmental preservation. Among the most prominent conservation sites are the Guiana Amazonian Park (Parc Amazonien de Guyane) and the Maroni River Nature Reserve.
The Guiana Amazonian Park, one of France's largest national parks, covers a massive area of rainforest and mountainous terrain, protecting countless species and supporting sustainable practices within Indigenous territories. Meanwhile, the Maroni River Nature Reserve conserves the waterways and wetlands essential for migratory birds, aquatic life, and the communities relying on these resources.
French Guiana faces significant environmental challenges despite strong conservation measures, including illegal gold mining, deforestation, and habitat degradation. The impacts of illegal mining, in particular, are severe, as unregulated operations contaminate rivers with mercury and disrupt ecosystems. Balancing sustainable development with environmental protection is critical to ensuring that the natural wealth of French Guiana remains intact for future generations.
Climate: Tropical, Humid, and Distinctly Seasonal
French Guiana's tropical climate is marked by warm temperatures and high humidity throughout the year. The average temperature is around 27 °C (81 °F), and humidity hovers near 85%. The region's climate is split into two main seasons: a wet season and a dry season, each of which uniquely shapes the landscape and ecosystems in unique ways.
- The Wet Season: Lasting from December to July, the wet season is characterized by heavy rainfall, with annual averages often exceeding 3,000 mm (118 in). The rains transform the landscape, swelling rivers and nourishing forests and contributing to the lush, dense vegetation that defines French Guiana's rainforests.
- The Dry Season: From August to November, rainfall decreases, creating slightly drier conditions. This period offers opportunities for easier access to certain areas and rivers, which become more navigable as water levels recede.
Within these broad patterns, regional climate variations exist. The coastal areas experience more intense humidity and warmth than the interior, while the southern highlands and mountain ranges are relatively cooler and less humid. These climatic variations help shape the flora and fauna, with some species adapting specifically to these micro-environments.
Marine and Coastal Ecosystems: Riches of the Atlantic
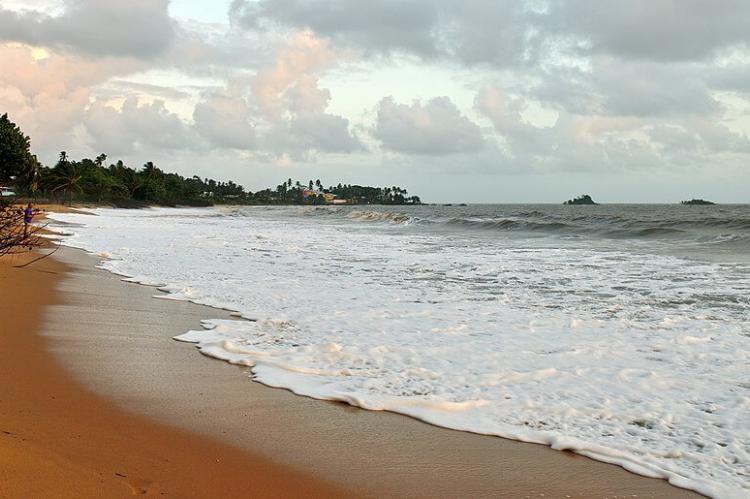
In addition to its rainforests, French Guiana boasts a dynamic coastal ecosystem comprising mangroves, beaches, and estuaries. Mangrove forests line much of the coastline, protecting against erosion, acting as nurseries for marine life, and serving as feeding grounds for migratory birds. The beaches of French Guiana are also crucial nesting sites for endangered sea turtles, including the leatherback and green turtles, which make annual migrations to the coast to lay eggs. Conservation efforts aim to protect these habitats from pollution, overfishing, and other environmental pressures that threaten marine biodiversity.
Ecotourism: Experiencing French Guiana's Natural Wonders
As ecotourism grows in popularity, French Guiana is emerging as a unique destination for those seeking an authentic nature experience. Visitors are drawn to exploring untouched rainforests, encountering rare wildlife, and engaging with Indigenous communities that have lived in harmony with the land for centuries. Sustainable tourism initiatives focus on minimizing environmental impact while promoting awareness and appreciation of the region's biodiversity. Ecotourism also provides valuable income for local communities and raises awareness about the importance of conservation, making it an essential component of French Guiana's sustainable development strategy.
Preserving French Guiana's Natural Landscape for the Future
French Guiana's wilderness, marked by its pristine rainforests, diverse ecosystems, and ancient rivers, holds immense ecological value and provides invaluable scientific research, conservation, and education resources. Addressing threats like illegal mining, habitat loss, and pollution requires strong governance, international cooperation, and community engagement. Initiatives that empower Indigenous communities and incorporate traditional ecological knowledge into conservation practices strengthen the protection of French Guiana's environment.
French Guiana aims to protect its natural legacy through continued conservation efforts, sustainable development, and responsible ecotourism, ensuring that its lush rainforests, complex ecosystems, and vibrant biodiversity remain resilient for future generations. In this territory where land and sea converge in a dance of ecological richness, French Guiana offers a compelling example of how natural beauty and biodiversity can thrive alongside responsible stewardship.
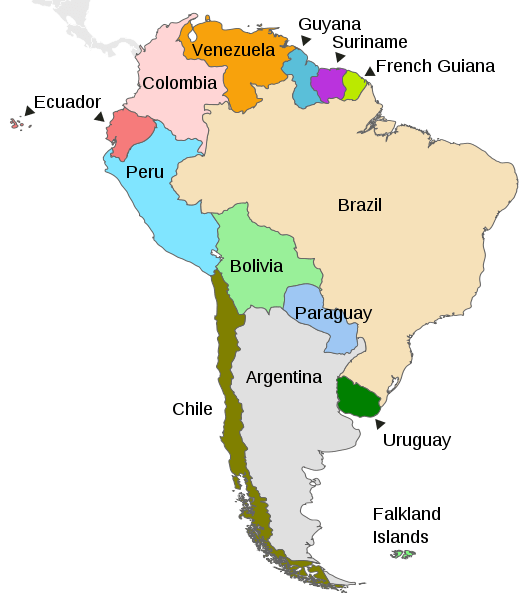
Map depicting the countries on the continent of South America
Natural Geography of French Guiana
Geographic Regions (Zones)
French Guiana's diverse terrain can be divided into two primary geographical regions or zones:
- Coastal Strip: Located in the north along the coast, this coastal strip is home to most of the population. Known as the "Terres Basses" (lowlands), it is a small, low, and swampy coastal area with a width varying from 10 to 30 km (6 - 19 mi).
- Interior Region: Comprising the expansive interior, this region is defined by a granite peneplain called the "Terres Hautes" (highlands). Erosion has shaped it into steps, forming a series of low, steep hills.
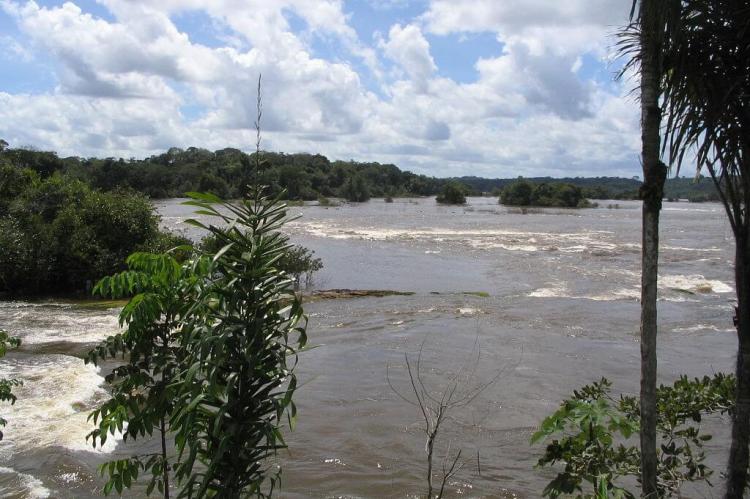
Dense, largely unexplored rainforests predominantly cover French Guiana's landscape. The rainforests are crisscrossed by numerous large rivers and streams punctuated by rapids. These waterways are the primary natural means of penetration into the interior.
The Tumuc Humac Mountains, located near the Brazilian border, are an important geographic feature. They are an eastern extension of the Acarai Mountains and are part of the northern watershed of the Amazon River basin. The mountains add a distinct elevation to the southern landscape, creating a geographical contrast that defines the captivating blend of French Guiana's coastal lowlands, interior highlands, and the impressive Tumuc Humac Mountains.
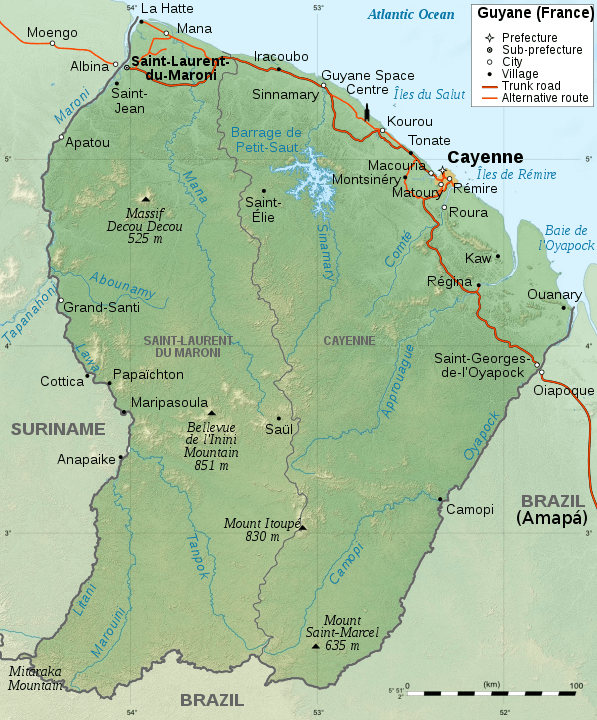
Geographic map of French Guiana.
Natural Features
Barrage de Petit-Saut: The Barrage de Petit-Saut gravity dam, situated approximately 36 km (22 mi) south of Sinnamary along the Sinnamary River, creates an artificial lake, contributing to hydroelectricity generation.
Islands:
- Salvation Islands (Îles du Salut): This group, positioned around 11 km (7 mi) off the Atlantic coast, encompasses Devil's Island, Royale Island, and Saint-Joseph Island.
- Constable Islands (Îles du Connétable): Grand Connétable and Petit Connétable, located approximately 18 km (11 mi) offshore from the Approuague estuary, are integral components of the Île du Grand Connétable Nature Reserve.
Mountain Peaks: French Guiana showcases notable mountain peaks, adding elevation to its landscape:
- Mont Bellevue de l'Inini: 851 m (2,792 ft)
- Mont Machalou: 782 m (2,566 ft)
- Pic Coudreau: 711 m (2,333 ft)
- Mont St Marcel: 635 m (2,083 ft)
- Mont Favard: 200 m (656 ft)
- Montagne du Mahury: 156 m (512 ft)
These natural features contribute to French Guiana's geographical diversity, encompassing dams, islands, and mountain peaks that collectively define the region's captivating landscape.
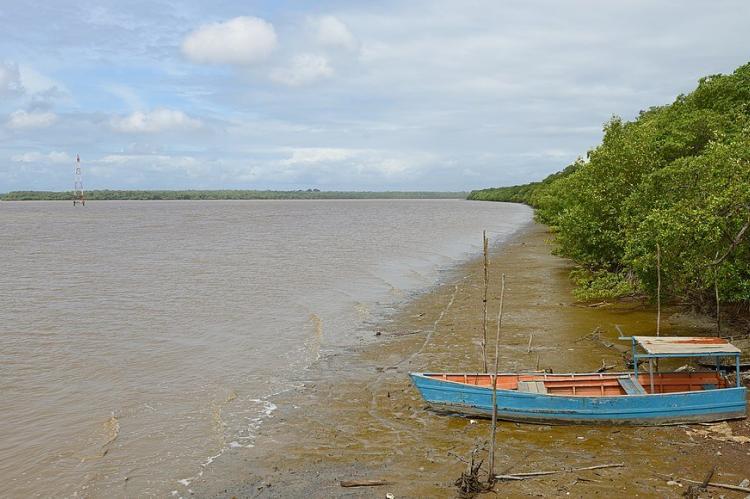
Bodies of Water
French Guiana hosts diverse bodies of water, contributing to its unique ecological and cultural landscape. These water bodies are essential in supporting local communities, sustaining biodiversity, and providing opportunities for ecotourism, fishing, and other recreational activities.
See: Water Bodies of French Guiana
Administrative Divisions
French Guiana is divided into three arrondissements, and each is subdivided into a total of 22 cantons.
See more: Cultural Landscape of French Guiana
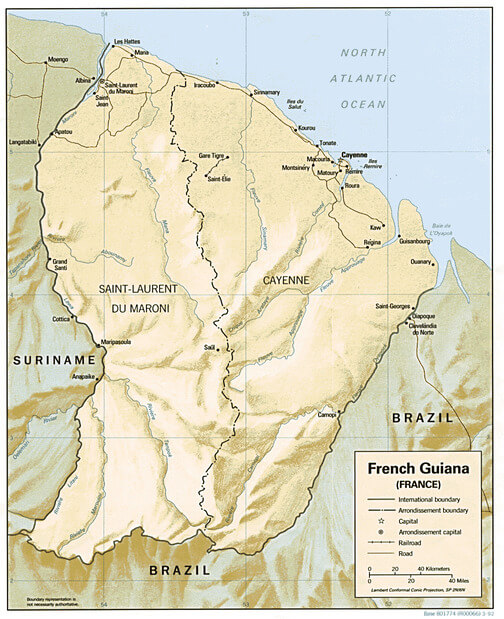
Relief map of French Guiana.
Natural Regions
French Guiana has many ecosystems: tropical rainforests, coastal mangroves, savannahs, inselbergs (isolated hills), and wetlands. It also lies within three ecoregions.
Ecological Regions
The following is a list of terrestrial ecoregions in French Guiana, as defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). French Guiana is in the Neotropical realm. Ecoregions are classified by biome type - the major global plant communities determined by rainfall and climate.
Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests
Guianan Highlands moist forests
Mangroves
Guianan mangroves
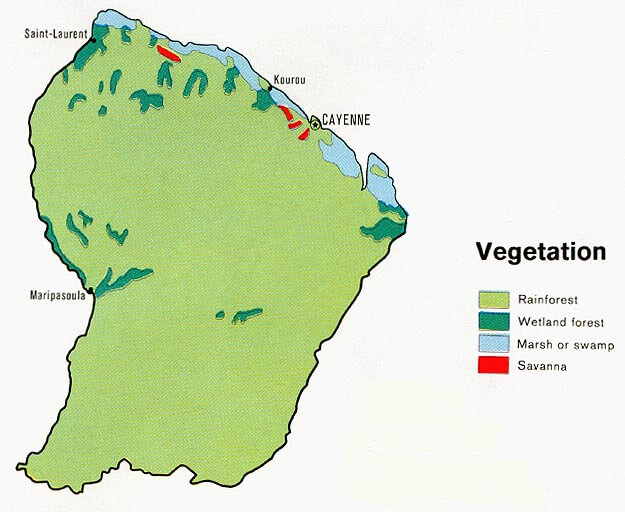
Vegetation map of French Guiana










