Exploring Venezuela's Federal Dependencies: Jewels of the Caribbean
Venezuela has a collection of stunning islands and islets known as the Federal Dependencies. These offer a blend of natural beauty, biodiversity, and cultural heritage, including beaches, coral reefs, ecosystems, and historical sites. They are a treasure trove waiting to be discovered.
Exploring Venezuela's Federal Dependencies: Jewels of the Caribbean
Venezuela boasts a stunning array of islands and islets scattered across the Caribbean Sea, collectively known as the Federal Dependencies (Dependencias Federales de Venezuela). These tropical gems offer a captivating blend of natural beauty, rich biodiversity, and cultural heritage. From pristine beaches and vibrant coral reefs to unique ecosystems and historical significance, the Federal Dependencies are a true treasure trove waiting to be discovered.
The Insular Region
The Insular Region (Región Insular) encompasses all of Venezuela's islands, including the Federal Dependencies and the state of Nueva Esparta. This region is divided into several archipelagos and islands, each with its distinct character and allure.
Los Roques Archipelago
A Paradise for Beach Lovers and Marine Enthusiasts
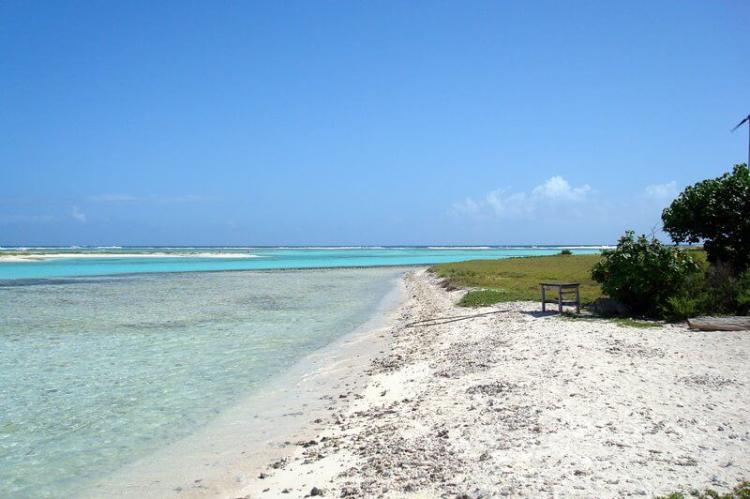
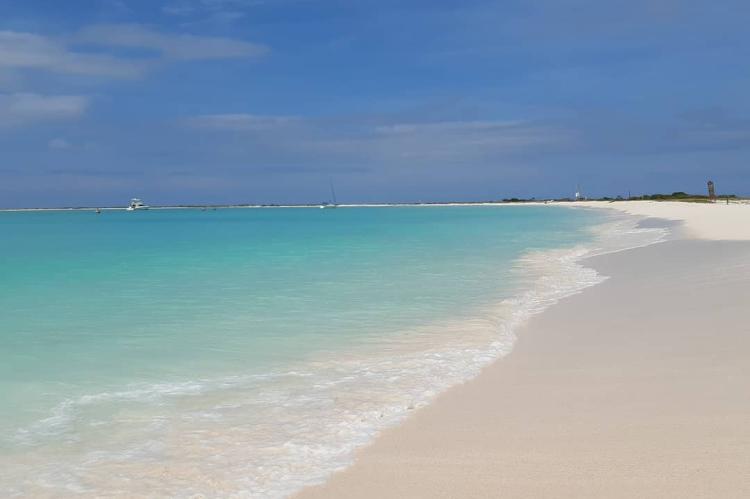
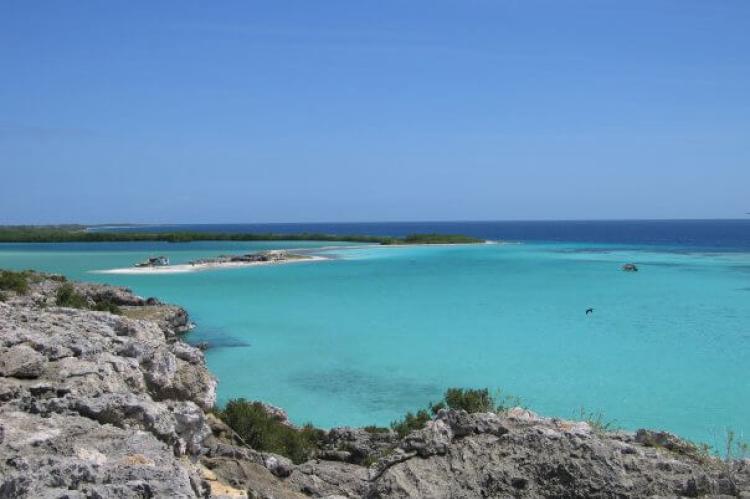
Situated approximately 80 km (50 mi) north of the Venezuelan coast, the Los Roques Archipelago is a breathtaking collection of over 350 islands and cays. This popular tourist destination is renowned for its picturesque beaches, crystal-clear waters, and abundant marine life. Visitors can indulge in various water activities, such as snorkeling, diving, and fishing, while basking in the natural beauty of this Caribbean paradise.
La Tortuga Island
A Haven for Turtle Nesting and Marine Conservation
Approximately 80 km (50 mi) north of the Venezuelan coast lies La Tortuga Island, a small yet significant destination for turtle conservation efforts. This island is known for its turtle-nesting beaches, where several species, including the endangered green turtle, come to lay their eggs. La Tortuga Island also boasts abundant marine life, making it a prime spot for snorkeling and diving.
La Blanquilla Island
Seabirds and Scenic Beauty
Situated about 120 km (75 mi) north of the Venezuelan coast, La Blanquilla Island is a true gem for nature lovers. This small island is renowned for its beautiful beaches and abundance of seabirds, providing a unique opportunity to witness these winged creatures in their natural habitat. Visitors can explore the island's trails and birdwatch and enjoy the serene atmosphere of this unspoiled paradise.
Los Frailes Archipelago
Rugged Cliffs and Turquoise Waters
Approximately 130 km (80 mi) north of the Venezuelan coast lies the Los Frailes Archipelago, a group of four rugged rock islets. This archipelago, known for its dramatic cliffs, turquoise waters, and abundant marine life, offers a unique and breathtaking landscape. Whether exploring the rugged terrain or diving beneath the waves, Los Frailes promises an unforgettable adventure.
Other Notable Islands: Los Monjes Archipelago, La Sola Island
Aves Archipelago
A Remote Haven for Scientific Research and Marine Conservation
While often associated with the nearby Los Roques Archipelago, the Aves Archipelago is a distinct group of islands and islets, including Aves de Sotavento, Aves de Barlovento, and Aves de Barlovento Sur. The Venezuelan government designated these remote islands as marine protected areas that serve as a sanctuary for scientific research and conservation efforts.
Economic Activities and Biodiversity
Sustainable Tourism and Fishing
Tourism is a significant economic activity in the Federal Dependencies, particularly in places like Los Roques, where visitors flock to enjoy the pristine beaches, water sports, and natural beauty. Fishing is another crucial economic activity for the local communities, focusing on lobster and other seafood.
The Federal Dependencies are home to diverse ecosystems and wildlife, including coral reefs, seagrass beds, coastal forests, nesting seabirds, sea turtles, dolphins, and whales. This rich biodiversity underscores these islands' ecological significance and the importance of conservation efforts.
Conservation Efforts and Environmental Challenges
Preserving Paradise
Several protected areas have been established within the Federal Dependencies to preserve fragile ecosystems and marine life. These conservation efforts contribute to the sustainability of the region's fisheries and the preservation of its natural wonders.
However, the Federal Dependencies face environmental threats, including climate change, coral bleaching, and overfishing. Ongoing initiatives, such as sustainable tourism practices, marine protected areas, and community-based conservation programs, aim to mitigate these challenges and ensure the long-term preservation of these Caribbean jewels.
Conclusion
Venezuela's Federal Dependencies is a true gem in the Caribbean Sea, offering a captivating blend of natural beauty, rich biodiversity, and cultural heritage. Each island and islet presents a unique opportunity for exploration, relaxation, and conservation opportunity, from the iconic Los Roques Archipelago to the remote Aves Archipelago. By embracing sustainable practices and preserving these precious ecosystems, Venezuela can ensure that these federal dependencies remain a source of pride and wonder for future generations.
Map depicting the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela.





