The Orinoco River: South America's Arc of Life
The Orinoco River, one of South America's largest, flows through Venezuela and Colombia, serving as a crucial waterway for transportation. It originates in the Sierra Parima mountains and empties into the Atlantic Ocean. The river supports rich ecosystems, indigenous cultures, and human populations.
The Orinoco River: A Vital Lifeline of Northern South America
The Orinoco River, one of South America's largest and most significant rivers, winds through Venezuela and Colombia, serving as a crucial waterway for transportation and sustenance. With a length of over 2,736 kilometers (1,700 miles), it ranks as one of the continent's longest rivers, and by discharge volume, it is the third-largest river in the world. Originating in the Sierra Parima mountains of the Guiana Highlands, the Orinoco flows through some of the most biodiverse and ecologically important regions in northern South America before reaching its vast delta and emptying into the Atlantic Ocean. The river and its basin are vital natural resources, supporting rich ecosystems, indigenous cultures, and human populations.
Geography and Course of the Orinoco River
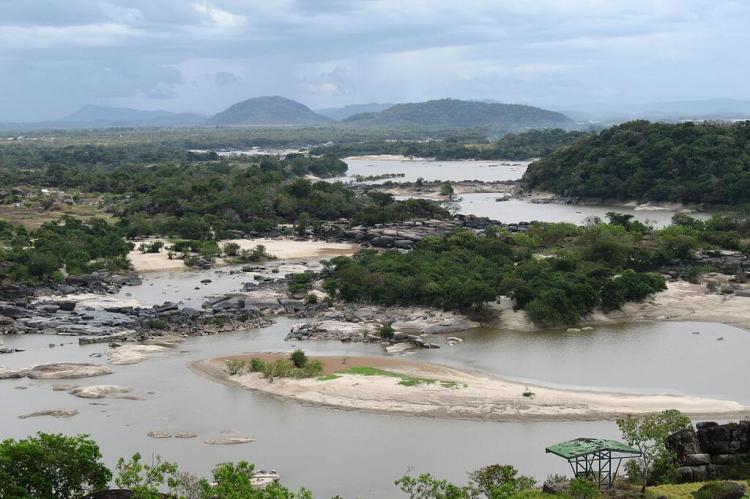
The Orinoco River begins its journey high in the Sierra Parima Mountains, which form part of the border between Venezuela and Brazil. From there, the river follows a massive arc, flowing north, west, and finally east across Venezuela. For a portion of its course, it serves as a natural border between Venezuela and Colombia. Along its path, the river passes through a variety of landscapes, including dense rainforests and vast savannas, before forming a sprawling delta as it drains into the Atlantic Ocean.
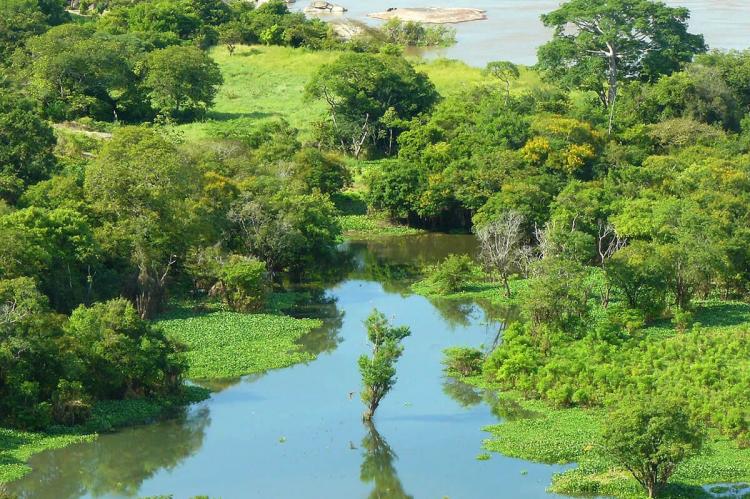
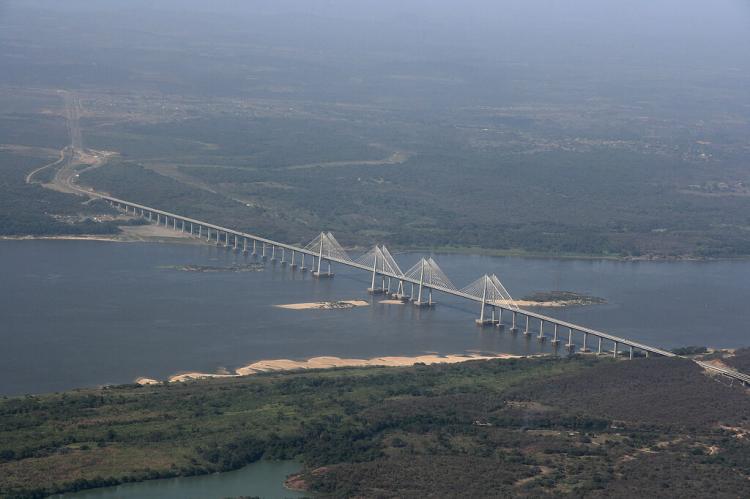
Throughout its journey, the Orinoco connects several vital regions, including the impenetrable rainforests of southern Venezuela and the expansive grasslands known as the Llanos. These Llanos occupy most of the Orinoco Basin and are vital to the region's agriculture and wildlife. The river is a geographic feature and an essential means of transportation, enabling the movement of goods and people between remote interior areas and the country's coastal regions.
Ecology and Wildlife of the Orinoco River
The Orinoco River is a biological hotspot, supporting a wide range of species, many of which are endangered or unique to the region. One of the most iconic creatures of the Orinoco is the Orinoco crocodile, a critically endangered species that can grow up to 7 meters (23 feet) in length. Other notable wildlife include the giant river otter, giant anaconda, and the river dolphin, all thriving in the river's diverse ecosystems.
Fish diversity is also astounding, with over 1,000 species inhabiting the Orinoco's waters. These include piranhas, electric eels, and various catfish. The river also attracts a rich variety of birdlife, such as flamingos, scarlet ibises, and colorful parrots. The surrounding rainforests and savannas are equally diverse, hosting everything from jaguars and capybaras to myriad insect and amphibian species.
The Orinoco River Basin
The Orinoco River Basin spans an immense area of approximately 948,000 square kilometers (366,000 square miles), encompassing around 80% of Venezuela and 25% of Colombia. The basin is bordered by the Andes Mountains to the west and north, the Guiana Highlands to the east, and the Amazon Basin to the south. Within this region, the Llanos savannas dominate the landscape, stretching across Venezuela and Colombia. The Llanos are marked by their seasonal flooding, which enriches the soil and supports the diverse plant and animal life.
The basin is also defined by its network of major tributaries, which feed into the Orinoco from all directions. Among the most significant are:
- Apure River: Flowing from Venezuela into the Orinoco.
- Arauca River: Originating in Colombia and merging with the Orinoco.
- Guaviare River: A major tributary from Colombia.
- Caroní River: Flowing from the Guiana Highlands, it provides a significant portion of the Orinoco's discharge.
- Atabapo, Ventuari, and Caura Rivers: These rivers also contribute to the Orinoco's flow from Venezuela's eastern highlands.
- Meta and Vichada Rivers: Flowing from Colombia into the Orinoco.
One of the most unique features of the basin is the Casiquiare Canal. This natural distributary connects the Orinoco with the Amazon River via the Negro River, creating a rare interconnection between two of the world's largest river systems.
The Orinoco Delta
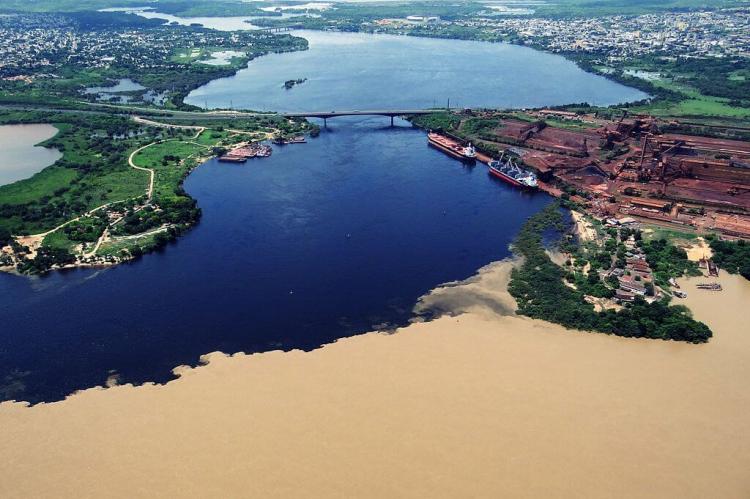
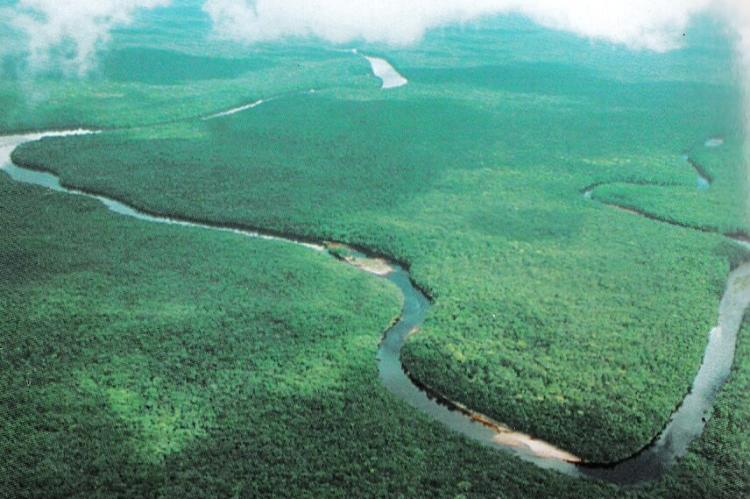
As the Orinoco approaches the Atlantic Ocean, it forms a massive delta covering more than 40,000 square kilometers (15,400 square miles). This fan-shaped delta, located in eastern Venezuela, splits the river into a network of distributaries known locally as caños. These waterways meander through the swampy, forested delta, eventually draining into the ocean. The Orinoco Delta is one of Venezuela's eight natural regions and is recognized for its ecological significance.
The delta's predominant vegetation is found within the Orinoco Delta swamp forests ecoregion, which is rich in biodiversity. Along the river margins and coastlines, Amazon-Orinoco-Southern Caribbean mangroves dominate, particularly in the Guianan mangroves ecoregion. The delta also contains significant areas of seasonally flooded freshwater swamp forests and permanent wetlands, which provide critical habitats for various species, including fish, birds, and aquatic mammals.
Economic and Environmental Significance
The Orinoco River is a major transportation artery for eastern Venezuela and the interior of Colombia. It provides essential routes for transporting goods, people, and resources, particularly in regions with sparse road infrastructure. The river also supports agriculture, fishing, and small-scale trade, which are vital to the livelihoods of local populations. Additionally, the Orinoco Basin holds significant oil and natural gas reserves, making it an important region for Venezuela's economy.
However, the river and its surrounding ecosystems face environmental challenges. Deforestation, oil extraction, and mining activities have degraded habitats and polluted parts of the basin. Efforts are being made to balance economic development with environmental conservation, particularly in the Orinoco Delta and along the river's key tributaries.
Indigenous Communities and Cultural Importance
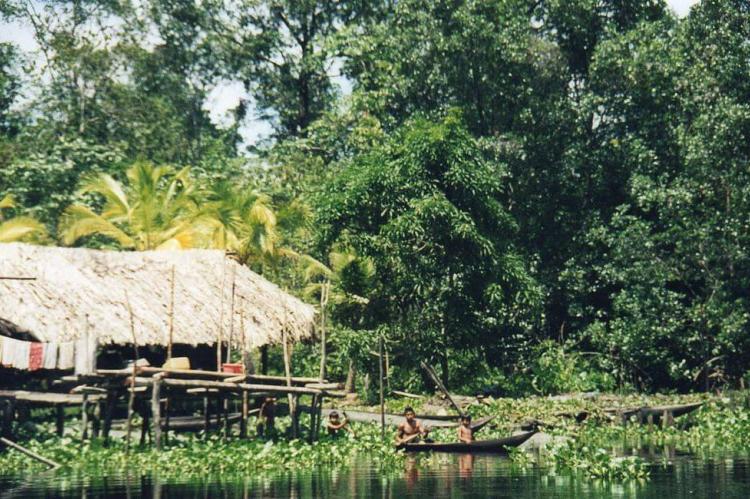
The Orinoco River has long been home to Indigenous communities that rely on its waters for fishing, transportation, and sustenance. Among these are the Warao people, who live in the Orinoco Delta. Their name, "Warao," means "people of the canoe," reflecting their deep connection to the river. The Warao build their homes on stilts above the water and have developed a way of life intimately tied to the river's cycles.
Other indigenous groups in the Orinoco Basin include the Piaroa, Ye'kuana, and Yanomami, who live in various parts of the basin, particularly along the river's upper reaches and tributaries. These communities have adapted to the seasonal rhythms of the river and the surrounding rainforest, maintaining traditional ways of life despite external pressures from development and environmental change.
Conclusion
The Orinoco River is a natural resource for Venezuela, Colombia, and the wider South American continent. Its vast basin supports rich biodiversity, indigenous cultures, and economic activities, making it one of the most important river systems in the region. The river's ecological diversity and its role as a transportation lifeline highlight its significance for the environment and human development. However, the ongoing environmental pressures on the river and its basin underscore the need for sustainable management to preserve this vital waterway for future generations.
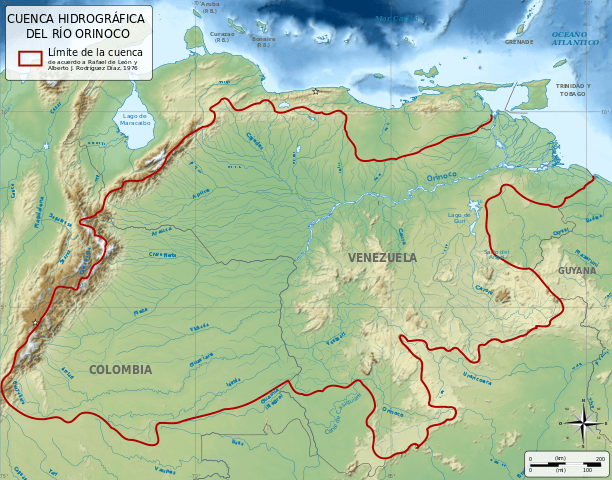
Map depicting the Orinoco Basin.





