Madeira River: A Lifeline of the Amazon Basin
The Madeira River is a significant waterway in South America, playing a crucial role in the hydrology of the Amazon Basin. As the largest tributary of the Amazon River, it is a vital component of the region's ecosystem, spanning Bolivia and Brazil and supporting diverse flora and fauna.
Flowing Through Diversity: The Madeira River and Its Ecological Importance
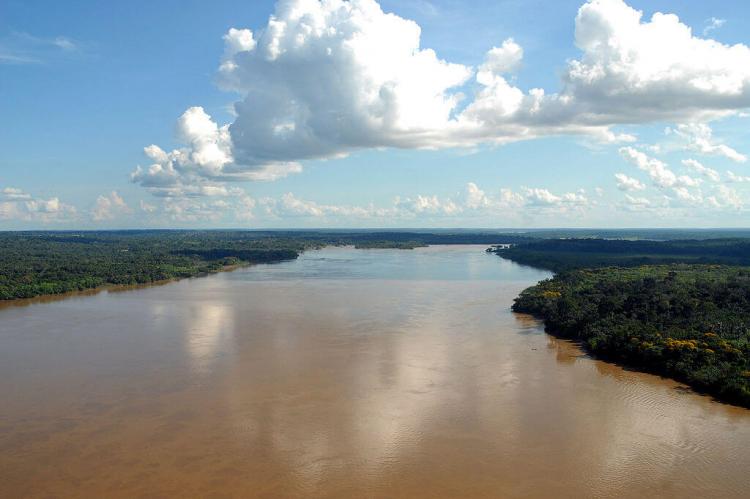
The Madeira River stands as one of South America's most significant waterways, playing a crucial role in the hydrology of the Amazon Basin. As the largest and most important tributary of the Amazon River, the Madeira contributes approximately 15% of the water in the entire basin, making it a vital component of the region's ecosystem. Spanning Bolivia and Brazil, this mighty river traverses diverse landscapes and supports an array of flora and fauna, underscoring its importance as both a natural resource and a habitat.
Geography and Course
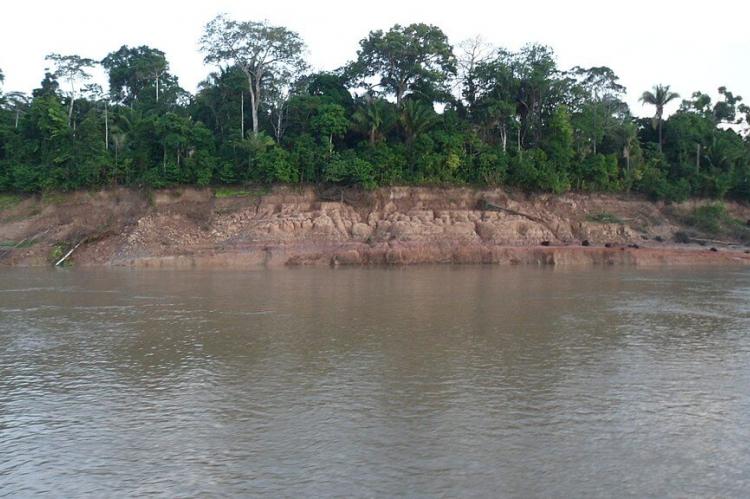
The Madeira River originates in the Bolivian Andes, approximately 3,300 kilometers (2,050 miles) from its confluence with the Amazon River and about 4,600 kilometers (2,850 miles) from the Amazon's mouth. The river's indigenous name, "Cuyari," was replaced by the Portuguese "Madeira," meaning "Wood River," due to the abundant timber carried by its waters.
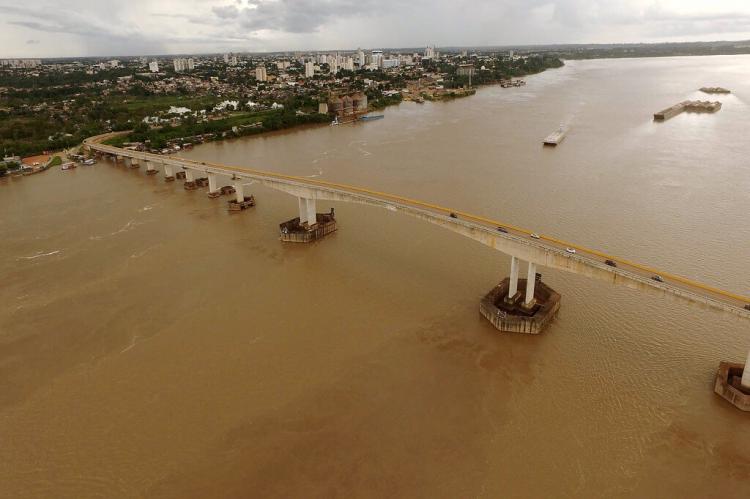
The Madeira is formed by the confluence of several major rivers, including the Madre de Dios, Beni, and Mamoré rivers. From this confluence, the Madeira flows northward, forming a natural border between Bolivia and Brazil before entering Brazil, where it continues its journey through the states of Rondônia and Amazonas. The river ultimately discharges into the Amazon near the town of Itacoatiara, within the metropolitan region of Manaus. The Madeira River covers a distance of approximately 1,425 kilometers (885 miles) as it traverses Brazilian territory.
Tributaries
The Madeira River's expansive watershed is nourished by a network of tributaries that significantly contribute to its volume and enhance its ecological diversity. These tributaries, originating from the Andes and surrounding regions, play a crucial role in shaping the Madeira's hydrology and supporting the rich ecosystems along its course.
One of the primary tributaries is the Madre de Dios River, which flows from the Peruvian Andes. It brings sediments that fertilize the surrounding floodplains. This river is known for its biological richness and is a vital artery within the upper Amazon Basin.
Another major tributary, the Beni River, originates in the Bolivian Andes. It meanders through diverse landscapes, from high-altitude forests to lowland jungles, before joining the Madeira. The Beni River's waters are rich in nutrients, which are essential for maintaining the fertility of the forests and wetlands it traverses.
Further contributing to the Madeira's flow is the Mamoré River, which forms part of the border between Bolivia and Brazil. The Mamoré is a significant waterway in its own right, draining vast areas of the Bolivian lowlands. Its confluence with the Beni River marks the beginning of the Madeira River, symbolizing the merging of waters from two major Andean tributaries.
The Guaporé River is another critical tributary known for its clear waters and biodiversity. Flowing from the Brazilian state of Rondônia, the Guaporé adds both water volume and ecological richness to Madeira. Its basin is home to numerous species of fish, reptiles, and birds, contributing to the region's overall diversity.
The Machado River further enhances the Madeira's flow, draining the southwestern Amazon and carrying a mix of sediments and nutrients that sustain the dense rainforests along its banks. Similarly, the San Miguel River and the Blanco River add to the Madeira's flow, each bringing unique ecological characteristics from the areas they traverse.
Lastly, the San Martin River joins the Madeira, completing the intricate tributary network that sustains this mighty river. Each of these rivers contributes to the Madeira's flow and enriches its waters with sediments, nutrients, and biodiversity, creating a dynamic and life-sustaining environment throughout the river's course.
This complex interplay of tributaries ensures that the Madeira River remains a vital lifeline for the Amazon, supporting diverse ecosystems and species that depend on its waters for survival.
Seasonal Flooding and Climate
The Madeira River is known for its dramatic seasonal fluctuations. During the wet season, the river's water levels can rise by about 15 meters (50 feet), causing extensive flooding that inundates the surrounding forests. This seasonal flooding is vital for maintaining the health of the riverine ecosystems, as it deposits nutrient-rich sediments that support plant and animal life.
The climate along the Madeira River varies as the river flows through different regions, ranging from arid conditions in the south to more humid climates further north. This climatic diversity influences the river's hydrology and the types of ecosystems that it supports.
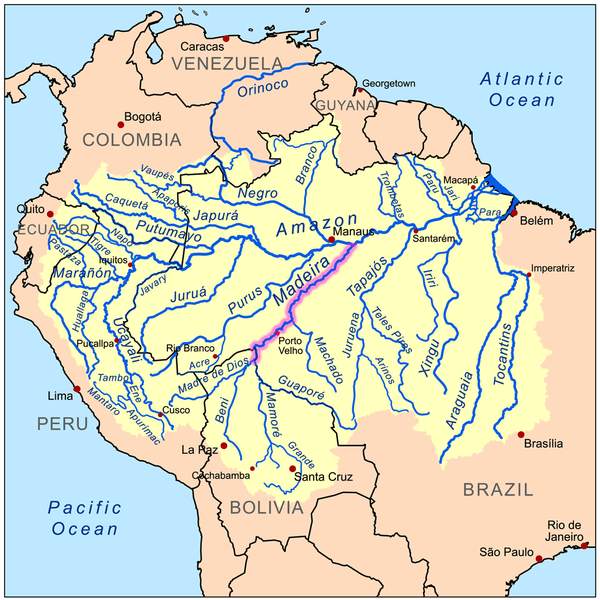
Map depicting the Amazon River drainage basin with the Madeira River highlighted.
The Madeira Basin
The Madeira River is part of the larger Madeira Basin, which encompasses approximately 1,300,000 square kilometers (502,000 square miles) and covers about 19% of the entire Amazon Basin. The basin extends across Bolivia, Brazil, and Peru, with roughly 50% of its area in Bolivia, 40% in Brazil, and 10% in Peru. The Mamoré and Guaporé-Iténez rivers form a natural border between Brazil and Bolivia within the basin.
Savanna landscapes characterize the southern part of the Madeira Basin, while most of the basin falls within the lowland rainforest zone. Wetlands also cover significant areas within the basin, with the Llanos de Moxos region in Bolivia's Beni Department being the most notable. The Llanos de Moxos wetlands, covering approximately 180,000 square kilometers (69,500 square miles), are the most extensive savanna wetlands in the Amazon Basin, playing a crucial role in the region's hydrology and biodiversity.
Biodiversity and Ecological Significance
The Madeira Basin is a hotspot of biodiversity, supporting a wide range of species, some of which are endangered. The region's varied habitats, from rainforest to savanna and wetlands, provide refuge for iconic wildlife such as the spotted jaguar (Panthera onca), giant otter (Pteronura brasiliensis), and pink river dolphin (Inia geoffrensis).
The Madeira River is a critical migratory route for an estimated 750 fish species, many of which travel up to 4,500 kilometers (1,700 miles) annually to spawn and feed in its nutrient-rich, muddy waters. These migrations are essential for the reproduction and survival of fish populations, supporting local communities and the broader Amazon ecosystem.
Conclusion
The Madeira River is much more than a tributary of the Amazon; it is a lifeline for the ecosystems and communities that depend on it. Its waters nourish the rainforest, support a staggering diversity of life, and connect distant regions of the Amazon Basin. The river's seasonal floods, diverse tributaries, and extensive basin make it a cornerstone of South America's natural heritage. Protecting the Madeira River and its basin is essential for maintaining the ecological balance of the Amazon and ensuring the continued survival of its myriad species.
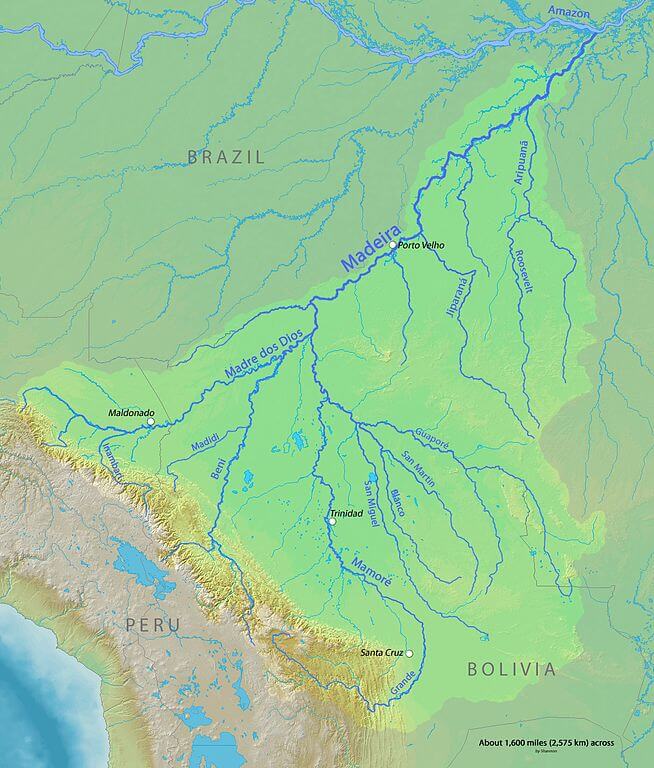
Map depicting the Madeira River watershed in Brazil, Bolivia, and Peru.





