Étang Saumâtre: Exploring Haiti's Hidden Oasis
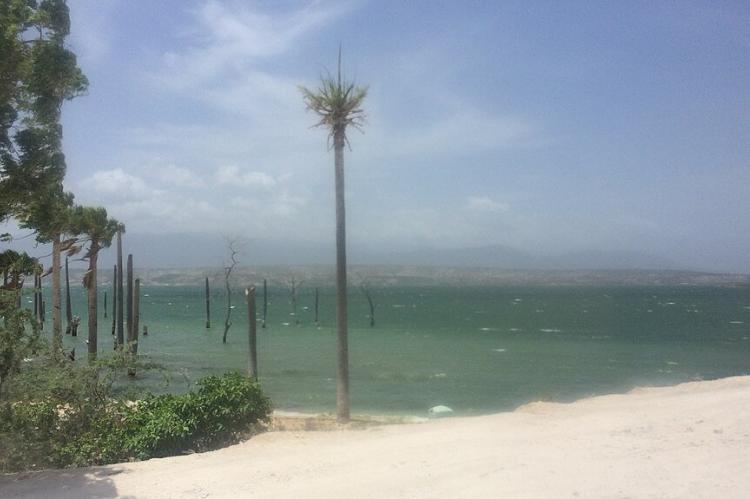
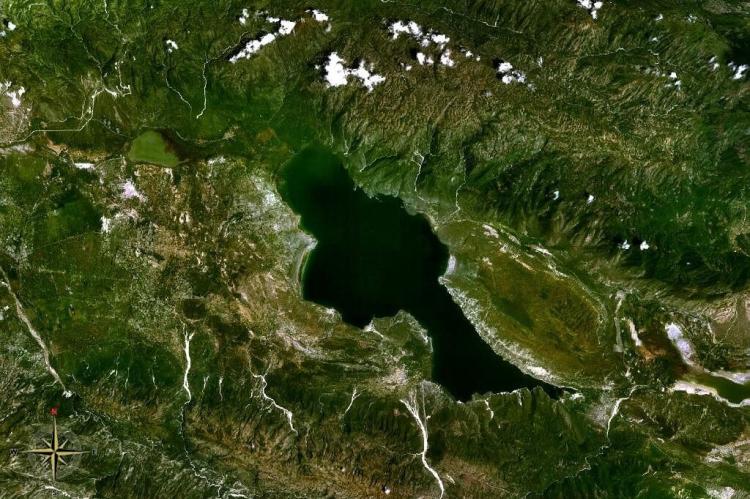
Amidst the rugged terrain of southeastern Haiti lies an oasis of unparalleled beauty and ecological significance: Étang Saumâtre, also known as Lake Azuéi. As the largest lake in Haiti, this salty water body embodies the essence of Haiti's natural landscape, offering a sanctuary in the heart of the Caribbean.
Étang Saumâtre: Exploring Haiti's Hidden Oasis
Nestled amidst the rugged terrain of southeastern Haiti lies a hidden oasis of unparalleled beauty and ecological significance: Étang Saumâtre, also known as Lake Azuéi. As the largest lake in Haiti and the second largest in Hispaniola after Lake Enriquillo in the Dominican Republic, this salty water body embodies the essence of Haiti's natural landscape, offering a sanctuary of tranquility and biodiversity in the heart of the Caribbean.
Geographical Marvel
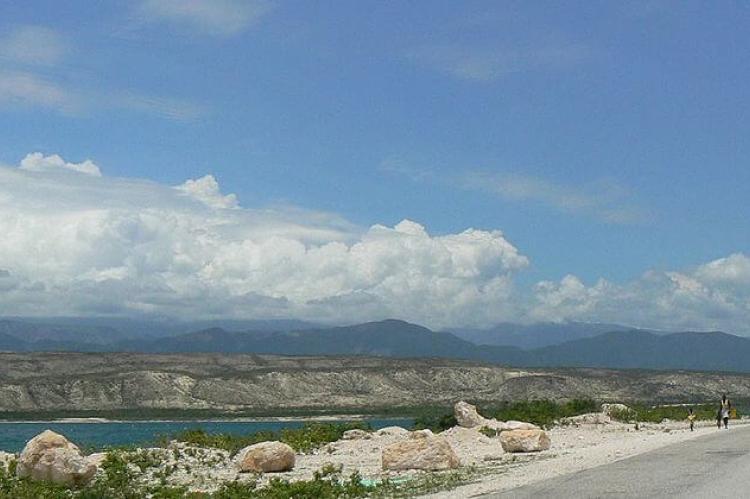
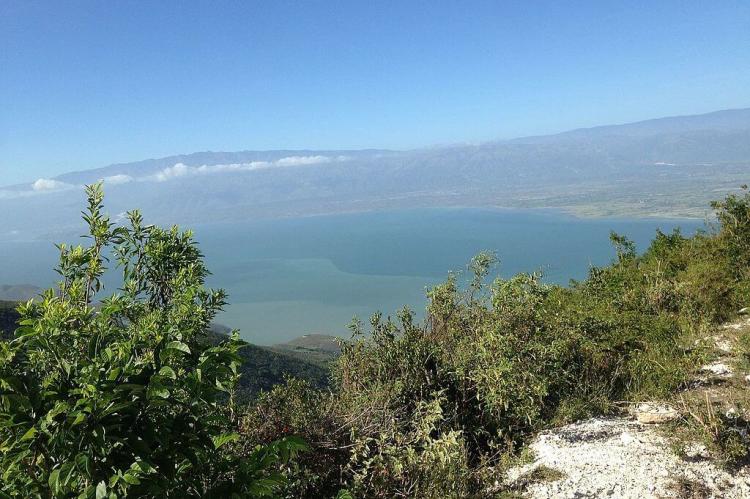
Étang Saumâtre's geographical location is nothing short of spectacular. Partially situated along the border with the Dominican Republic, this majestic lake occupies a prime position within the Cul-de-Sac Plain, cradled between the towering peaks of the Massif de la Selle to the south and the rugged Montagnes Noires to the north. Its expansive waters, covering approximately 170 square kilometers (65 square miles), create a captivating scene against Haiti's diverse landscape.
From its tranquil shores to depths plunging 30 meters (98 feet) below the surface, Étang Saumâtre exudes an aura of mystery and allure. The lake's ever-changing shoreline, characterized by sandy beaches, shallow lagoons, and mudflats, offers a haven for both terrestrial and aquatic life forms to thrive.
Ecological Sanctuary
Étang Saumâtre's brackish waters harbor a rich tapestry of biodiversity, showcasing Haiti's natural heritage in all its splendor. The lake's unique salinity gradient, resulting from the interplay between freshwater springs and evaporative processes, creates a mosaic of habitats supporting many plant and animal species.
Mangrove forests, with their labyrinthine roots and verdant canopies, fringe the western shores of Étang Saumâtre, providing sanctuary to various bird species and reptiles, including the formidable American crocodile. Salt flats and marshes dotting the landscape teem with life, breeding grounds for brine shrimp and other invertebrates that form the backbone of the lake's intricate food chain.
Above the azure waters of Étang Saumâtre, the skies come alive with the graceful flight of over 100 species of waterfowl, from the elegant American flamingo to the majestic herons and egrets that call this sanctuary home. Against the lake's tranquil surface, these avian inhabitants find solace and sustenance amidst the lush grasslands and sparse vegetation that fringe its shores.
Cultural Significance
Beyond its ecological significance, Étang Saumâtre holds a special place in the hearts of the Haitian people, serving as a source of inspiration and sustenance for generations. The lake's fertile shores have sustained local communities for centuries, providing fish for sustenance and livelihoods for those who call its shores home. Its tranquil waters have also been a backdrop for cultural and recreational activities, from fishing expeditions to leisurely boat rides under the Caribbean sun.
Preserving Haiti's Natural Heritage
As Haiti continues its sustainable development and conservation journey, Étang Saumâtre remains a shining example of its commitment to preserving its natural treasures. Efforts to protect the lake's fragile ecosystems, coupled with initiatives to promote eco-tourism and environmental education, ensure that future generations will have the opportunity to marvel at the beauty and diversity of this hidden oasis.
In conclusion, Étang Saumâtre is a testament to Haiti's ecological richness and environmental resilience. From its breathtaking landscapes to its vibrant biodiversity, this hidden gem invites visitors to embark on a journey of discovery and appreciation for the natural wonders that abound in the heart of the Caribbean.