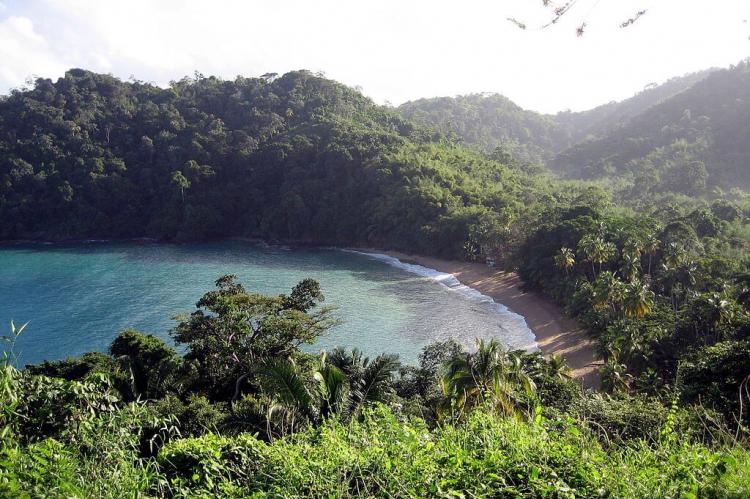
The Diverse and Captivating Trinidad and Tobago Moist Forests
The Trinidad and Tobago moist forests ecoregion covers most of the two-island nation located off the northeastern coast of South America. While small portions of the islands are home to other habitat types, the moist forests dominate the landscape and support an exceptionally diverse flora and fauna.
The Diverse and Captivating Trinidad and Tobago Moist Forests
The Trinidad and Tobago moist forests ecoregion covers most of the two-island nation located off the northeastern coast of South America. While small portions of the islands are home to other habitat types, such as mangroves and dry forests, the moist forests dominate the landscape and support an exceptionally diverse array of flora and fauna.
Geographical Context
The islands of Trinidad and Tobago are situated on the South American continental shelf in the Caribbean Sea. Trinidad lies just 12 kilometers (7.5 miles) off the coast of Venezuela, while Tobago is approximately 30 kilometers (19 miles) further northeast, closer to the open waters of the Atlantic Ocean. This strategic location means the islands are directly influenced by the outflow of the mighty Orinoco River to the south and the strong South Equatorial Current flowing in from the southeast.
Vegetation Communities
The Trinidad and Tobago moist forests ecoregion is home to four major vegetation communities:
- Coastal Woodland: These forest habitats are found along the islands' coastlines.
- Deciduous Seasonal Woodland: Forests that shed their leaves during the dry season adapted to the seasonal variations in rainfall.
- Rainforest: The predominant vegetation type, consisting of lush, evergreen tropical rainforest.
- Swamp Forests: Wetland forest habitats are found in areas with high soil moisture or standing water.
Flora
The moist forests of Trinidad and Tobago support an incredibly diverse array of plant life, with approximately 175 families and 2,500 species of plants documented. This diversity includes numerous characteristic tree species such as crabwood, kapok, and hog plum. The forests are also home to a wealth of lianas (woody vines) and epiphytes (plants growing on trees), including many species of orchids, bromeliads, and ferns. Remarkably, around 110 plant species found in Trinidad and Tobago are believed to be endemic to the islands, found nowhere else on Earth, including various endemic palm species.
Fauna
The diverse habitats of the Trinidad and Tobago moist forests support an equally impressive array of animal life. Over 400 species of birds have been documented, most of which belong to the Passeriform (perching bird) order and are found on the island of Trinidad.
Approximately 100 species of mammals have been recorded, with bats and rodents being the most numerous. Other notable mammal species include various armadillo species, primates such as the red howler monkey, deer, and several species of small cat predators.
The reptile diversity is also exceptional, with around 85 species documented, including 40 species of snakes and 25 species of lizards. The moist forests are also home to 30 different amphibian species, including the iconic and endemic golden tree frog.
Conclusion
The Trinidad and Tobago moist forests ecoregion represents a unique and biodiverse tropical ecosystem, shaped by its strategic location on the South American continental shelf and the influential ocean currents and river systems surrounding it. The diverse array of vegetation communities and the remarkably high number of endemic plant and animal species make this ecoregion a true ecological gem of the Caribbean.
Map depicting the location of the Trinidad and Tobago moist forests (islands in the blue box, lower right).
