The Midriff Islands and San Lorenzo Marine Park: A Gulf of California Sanctuary
San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago National Park is an ecologically significant marine reserve in the northern Gulf of California. Part of the Midriff Islands, it preserves marine biodiversity and serves as a sanctuary for endangered species in the fragile marine ecosystem of the Gulf.
San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago National Park and the Midriff Islands: A Haven for Biodiversity in the Gulf of California
In the northern Gulf of California, where the desert meets the sea, lies one of Mexico's most ecologically significant marine reserves: San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago National Park. Nestled between the eastern coast of Baja California and the deep waters of the Sea of Cortez, this protected region is part of the renowned Midriff Islands, a collection of islands that play a vital role in preserving the marine biodiversity of the Gulf. Encompassing 50,442 hectares (124,645 acres) of islands and maritime borders, San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago National Park is a sanctuary for endangered species and an essential component of the Gulf's fragile marine ecosystem.
Geographical Overview
San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago National Park consists of several islands, including Isla San Lorenzo, Isla Las Animas, Isla Salsipuedes, Isla Rasa, and Isla Partida, all surrounded by nutrient-rich waters. These islands, part of the Midriff Islands chain, lie within the municipality of Mexicali, Baja California. The largest and southernmost, Isla San Lorenzo, is separated from the Baja California mainland by the Salsipuedes Channel.
The park's dramatic landscape is characterized by irregular coastlines, steep sea cliffs, and a rugged topography that rises sharply from sea level to a height of 485 meters (1,590 feet) on Isla San Lorenzo. These islands were formed by tectonic forces along the San Andreas Fault, which uplifted crustal blocks to shape their distinctive features. Despite their proximity to the sea, the islands experience a desert climate with high solar radiation, making summers hot and winters relatively warm.
The Midriff Islands: A Marine Hotspot in the Gulf of California
The San Lorenzo Archipelago is part of a larger group known as the Midriff Islands, a chain of islands in the northern Gulf of California. The Midriff Islands play a critical role in the ecological dynamics of the region, as they are located in an area where deep ocean currents bring nutrient-rich waters to the surface, creating an environment teeming with marine life.
The Midriff Islands, which include Isla Ángel de la Guarda, Isla Tiburón, and Isla San Esteban, along with the islands of the San Lorenzo Archipelago, are often referred to as the "lungs" of the Gulf of California due to their role in sustaining the biodiversity of the surrounding waters. These islands are scattered across the Midriff Channel, a narrow stretch of water that funnels cold, nutrient-dense currents from the Pacific into the Gulf.
The Midriff Islands' steep underwater slopes and cold-water upwellings create ideal conditions for a wide variety of marine species, including large schools of fish, cetaceans, and seabirds. Like the San Lorenzo Archipelago, the islands are home to numerous endemic and migratory species, many of which rely on the islands' rocky shores and deep waters for breeding and feeding.
In addition to their ecological importance, the Midriff Islands have cultural and historical significance. Isla Tiburón, for example, is the traditional home of the Seri people, an indigenous group with a deep connection to the land and sea. The islands also attract ecotourists and researchers who observe the diverse wildlife and study the unique ecosystems that thrive in this part of the Gulf.
Together with the San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago, the Midriff Islands form a critical habitat within the Gulf of California, making them a priority for conservation and scientific study. Their protection is essential not only for the preservation of endangered species but also for the health of the broader marine environment.
Marine Ecosystem
The marine environment surrounding the San Lorenzo Archipelago is one of the most productive in the Gulf of California. The cold, nutrient-dense waters flowing through the Salsipuedes Channel foster abundant marine life, from invertebrates to large mammals. Rocky shores teem with mollusks, isopods, clams, and sea cucumbers, while squid, octopus, and jellyfish thrive in deeper waters. These waters also support large schools of fish, many of which are commercially important species.
The surrounding ocean is home to numerous species of marine mammals, including several endangered whales, such as the blue whale, humpback whale, and sperm whale. Dolphins, including Risso's dolphin, are also commonly observed. Marine reptiles, including the green turtle, hawksbill turtle, and olive ridley turtle, make their home in the archipelago waters. All of these turtles are protected due to their endangered status.
The park's most significant residents are the colonies of seabirds and seals that thrive along the archipelago's shores. The islands are particularly well-known for their seabird populations, with Isla Rasa playing a crucial role as a nesting site for several bird species. Additionally, shallow waters with abundant nutrients frequently lead to phytoplankton blooms, attracting many marine species to the area.
Flora and Terrestrial Ecosystem
While the San Lorenzo Archipelago is primarily celebrated for its marine biodiversity, the terrestrial environment of its islands is equally distinctive. Due to their desert climate, vegetation on the islands is sparse and adapted to arid conditions. Plant life consists of xerophytic species that can endure the harsh, dry climate, including cacti, small shrubs, and other drought-resistant flora.
The islands' arid landscape is also home to several endemic species uniquely adapted to the challenging environment. The limited freshwater resources and high evaporation rates due to intense solar radiation shape the islands' biological diversity, creating a fragile but resilient ecosystem.
Conservation Significance
San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago National Park was established to protect one of the most ecologically sensitive areas in the Gulf of California. The park's designation as a protected area reflects its importance in safeguarding a wide range of species, particularly those listed as endangered, such as the blue whale, killer whale, and totoaba, a critically endangered fish species endemic to the Gulf of California.
The park's proximity to the Midriff Islands, known as a hotspot for marine biodiversity, further underscores its role in conserving the rich marine life of the Gulf. The region's cold waters and steep underwater topography create ideal conditions for the survival and growth of many species, ranging from small invertebrates to large marine predators. In addition, the park serves as a critical breeding and feeding ground for numerous migratory species, linking the region's ecological health with the broader marine ecosystems of the Pacific Ocean.
Challenges and Future Preservation
Despite its protected status, the San Lorenzo Archipelago and the surrounding marine environment face ongoing challenges. Human activities like commercial fishing, tourism, and climate change continue to put pressure on the region's delicate ecosystems. Conservation efforts must prioritize the sustainable management of marine resources, ensuring that fishing practices are carefully monitored and that the habitats of endangered species are safeguarded.
Ongoing research and monitoring programs are essential to understanding the full impact of environmental changes on the park's ecosystems. As the Gulf of California continues to experience rising sea temperatures and shifts in ocean currents due to climate change, the resilience of the San Lorenzo Archipelago's ecosystems will depend on collaborative conservation efforts at the local, national, and international levels.
Conclusion
San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago National Park is a vital ecological sanctuary within the Gulf of California, playing a central role in preserving the biodiversity of the region's marine and terrestrial environments. Its rugged islands and nutrient-rich waters support an array of species, from endangered whales to seabird colonies, making the park a cornerstone of conservation in the northern Gulf. Protecting this unique archipelago is critical to ensuring the long-term survival of its ecosystems and the countless species that depend on its resources. Through continued conservation efforts, the San Lorenzo Archipelago and the wider Midriff Islands will remain a haven for biodiversity in one of Mexico's most important marine reserves.
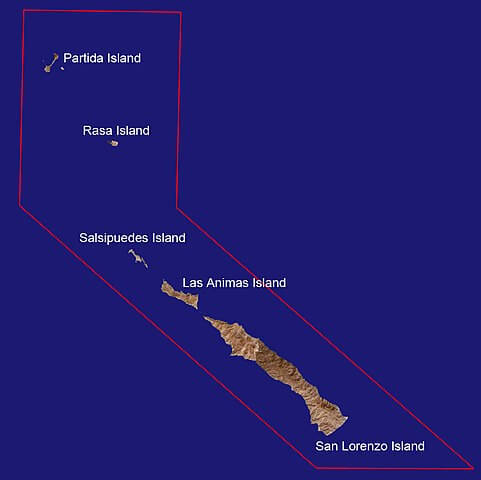
Aerial map of San Lorenzo Marine Archipelago National Park.
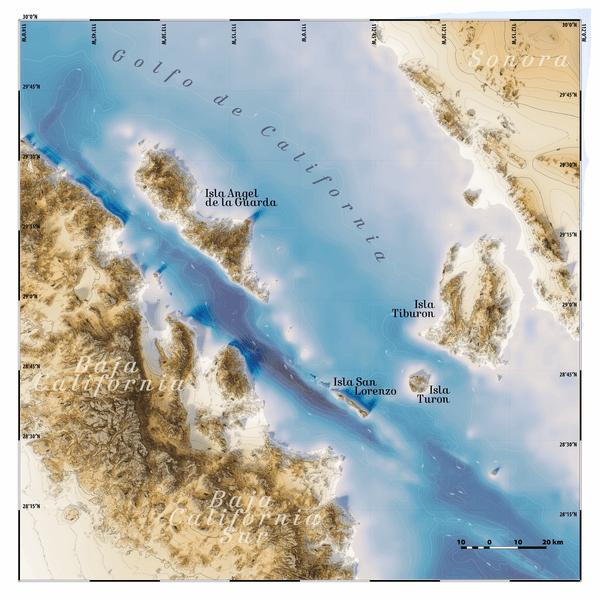
Topographic map of some of the Midriff Islands in the Gulf of California.
