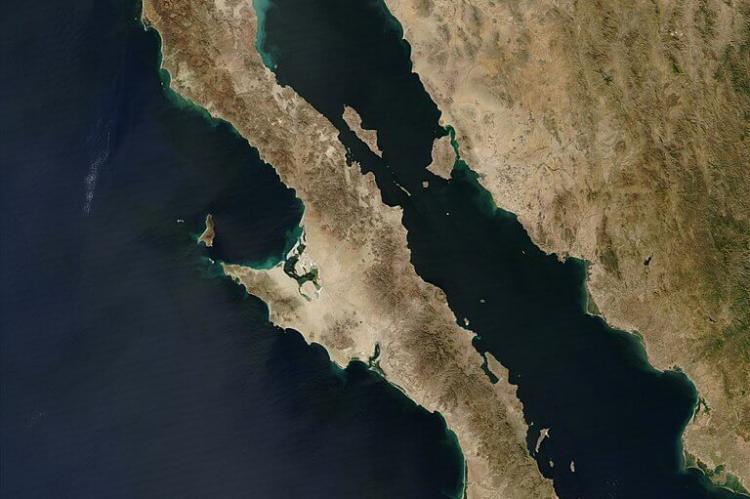
Between Two Seas: Exploring the Baja California Peninsula
Stretching like a finger into the Pacific Ocean, the Baja California Peninsula stands as one of Mexico's most remarkable geographical features. This landmass extends from Mexicali in the north to Cabo San Lucas in the south, creating a unique corridor where desert landscapes meet coastal splendor.
The Baja California Peninsula: A Desert Peninsula of Extremes
Stretching like a narrow finger into the Pacific Ocean, the Baja California Peninsula stands as one of Mexico's most remarkable geographical features. This 1,247-kilometer (775-mile) landmass extends from the bustling border city of Mexicali in the north to the tourist paradise of Cabo San Lucas in the south, creating a unique corridor where desert landscapes meet coastal splendor. As the second-longest peninsula in the world after Southeast Asia's Malay Peninsula, Baja California represents a fascinating study in geological evolution, ecological adaptation, and human settlement in one of the planet's most challenging yet beautiful environments.
Geographical Dimensions and Boundaries
The Baja California Peninsula occupies a strategic position on Mexico's western edge, bounded by the United States to the north, the vast Pacific Ocean to the west, and the Gulf of California to the east. This positioning creates a unique geographical identity that influences everything from climate patterns to cultural development. The peninsula's dimensions are as impressive as they are varied—at its widest point, it spans 320 kilometers (200 miles), while at its narrowest section, it contracts to just 40 kilometers (25 miles), demonstrating the dramatic geographical variations that characterize this remarkable landmass.
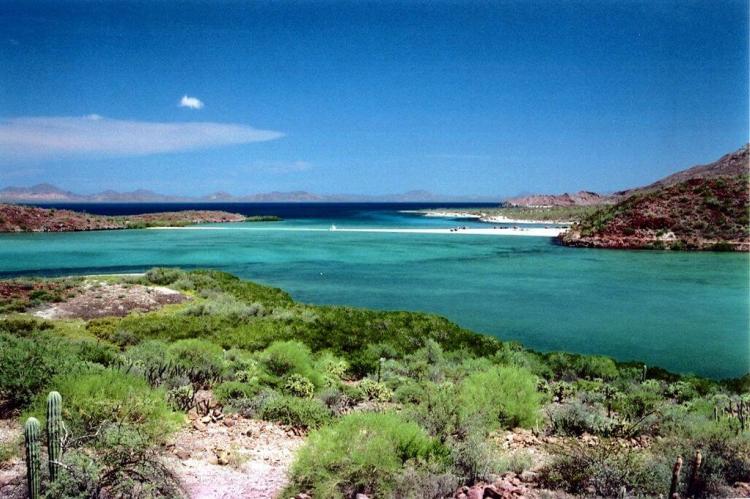
Covering approximately 143,390 square kilometers (55,360 square miles), the peninsula boasts an extensive coastline of roughly 3,000 kilometers (1,900 miles). This extensive shoreline is punctuated by 65 islands of various sizes, each contributing to the region's complex marine and terrestrial ecosystems. The peninsula's elongated shape creates diverse microclimates and ecological zones, from the Mediterranean-like conditions of the northern Pacific coast to the tropical desert environments of the southern tip.
Physical map of Mexico.
Geological Heritage and Tectonic Activity
The geological story of Baja California reads like a dramatic tale of continental drift and tectonic forces. Originally part of the North American Plate, the peninsula has undergone a remarkable transformation over millions of years. Today, it sits on the Pacific Plate, moving steadily north-northwestward as a result of activity along the East Pacific Rise. This ongoing tectonic movement continues to shape the peninsula's landscape, creating the rugged terrain and geological complexity that define the region.
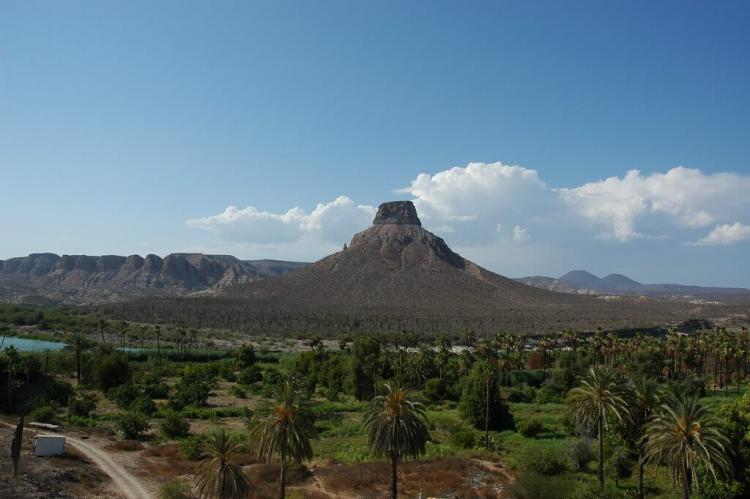
The peninsula's geological history is marked by significant volcanic activity, particularly evident north of Santa Rosalia in Baja California Sur. Volcanic eruptions and earthquakes have sculpted the landscape over millennia, creating dramatic mountain ranges, deep valleys, and unique rock formations. The Sierra de Baja California, the peninsula's primary mountain range, runs along its length and reaches elevations of over 3,000 meters (10,000 feet) in some areas. These mountains not only provide dramatic scenery but also create rain shadows that contribute to the region's arid character.
The tectonic forces that separated Baja California from mainland Mexico also created the Gulf of California, making the peninsula's geological history intimately connected with the formation of this remarkable sea. Ongoing seismic activity serves as a constant reminder of the dynamic forces that continue to shape this region, with earthquakes occurring regularly along various fault systems.
Ecological Diversity and Desert Ecosystems
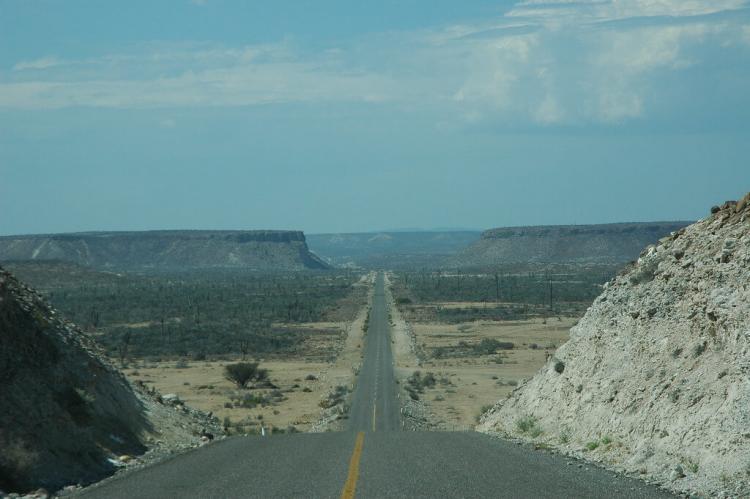
Despite its arid reputation, Baja California supports remarkable ecological diversity across several distinct ecoregions. The peninsula is primarily characterized by deserts and xeric shrublands, with four main desert areas each possessing unique characteristics and species compositions. The San Felipe Desert in the northeast represents the most austere environment, while the Central Coast Desert, Vizcaíno Desert, and Magdalena Plain Desert each offer their own distinctive landscapes and ecological niches.
The San Felipe Desert, extending from the Colorado River delta southward, features some of the most extreme desert conditions on the peninsula. Here, massive cardon cacti, the world's largest cacti species, dominate the landscape alongside various endemic succulents and desert shrubs. The Central Coast Desert, influenced by Pacific Ocean currents, supports fog-dependent vegetation and unique plant communities adapted to coastal desert conditions.
The Vizcaíno Desert, occupying much of the central peninsula, is famous for its vast plains dotted with enormous boojum trees (Fouquieria columnaris), whose bizarre, upside-down appearance creates an otherworldly landscape. The Magdalena Plain Desert in the south represents a transition zone where Sonoran Desert species blend with more tropical elements.
Surprisingly, the mountainous regions at both the northern and southern ends of the peninsula support pine-oak forests, creating islands of temperate vegetation in an otherwise arid landscape. These montane forests harbor species more typical of higher latitudes and elevations, including endemic pines and oaks adapted to the peninsula's unique conditions.
The southern tip of the peninsula holds special biological significance, as it was once an island separated from the mainland. This isolation allowed for unique evolutionary processes, and today the region shares species affinities with tropical Mexico while maintaining its endemic flora and fauna. Many plant and animal species found here exist nowhere else on Earth, making conservation of these areas particularly important.
Climate Patterns and Seasonal Variations
Baja California's climate reflects its position between temperate and tropical zones, creating a complex pattern of seasonal and geographical variations. The peninsula's climate is primarily arid to semi-arid, characterized by hot summers and mild winters. However, this general description masks significant regional variations that create distinct climatological zones.
The northern regions experience a Mediterranean-style climate with winter rainfall patterns, receiving most of their limited precipitation between November and March. These winter storms originate from the Pacific Ocean and bring much-needed moisture to support the region's vegetation and replenish groundwater supplies. Temperatures in the north can be surprisingly cool in winter, with occasional frost in mountainous areas and even rare snowfall at higher elevations.
In contrast, the southern portions of the peninsula experience a more tropical desert climate with summer rainfall patterns. Here, moisture arrives primarily during the summer months through tropical storms and hurricanes moving north from the Pacific. This summer precipitation pattern supports different vegetation communities and creates growing seasons that contrast sharply with the northern regions.
Coastal areas benefit from the moderating influence of the ocean, experiencing smaller temperature ranges and higher humidity levels than inland desert regions. The cold California Current along the Pacific coast creates fog and marine layer conditions that support unique plant communities dependent on atmospheric moisture. Meanwhile, inland desert areas can experience extreme temperature variations, with scorching summer days exceeding 45°C (113°F) and surprisingly cool winter nights.
Human Settlement and Urban Development
Despite its challenging desert environment, Baja California supports a population of over one million people distributed across several major urban centers. Tijuana, the largest city, has grown into a major metropolitan area and important border crossing, serving as a gateway between Mexico and the United States. Its proximity to San Diego has created a unique binational urban corridor with significant economic and cultural exchange.
Mexicali, the capital of Baja California state, sits in the peninsula's northeastern corner in one of Mexico's most productive agricultural valleys. Despite being located in a desert region, the city has thrived due to irrigation from the Colorado River and has become an important agricultural and industrial center.
Ensenada, positioned on the Pacific coast, has developed into Mexico's premier wine-producing region, taking advantage of its Mediterranean-like climate to create a thriving viticulture industry. The city also serves as an important port and fishing center, while its coastal location makes it popular with tourists and expatriate communities.
La Paz, the capital of Baja California Sur, combines the functions of government center, commercial hub, and tourist destination. Its protected bay location provides shelter from Pacific storms while maintaining access to both the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of California.
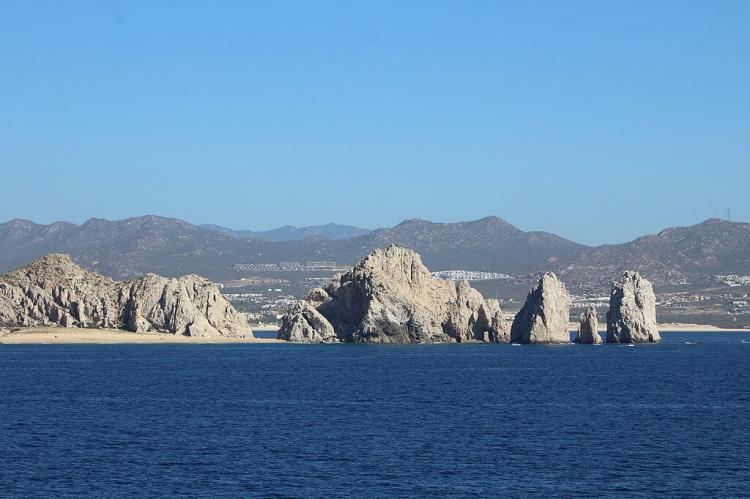
Cabo San Lucas, at the peninsula's southern tip, has transformed from a small fishing village into one of Mexico's premier resort destinations. Its dramatic landscape, where desert meets ocean, combined with excellent fishing and beautiful beaches, has made it a favorite destination for international tourists and retirement communities.
Economic Activities and Resources
The Baja California Peninsula's economy has diversified significantly beyond traditional activities like fishing and agriculture. Manufacturing has become increasingly important, particularly in Tijuana, where maquiladora industries take advantage of the proximity to U.S. markets and a skilled workforce. These manufacturing operations span various sectors, from electronics and automotive parts to textiles and medical devices.
Agriculture remains vital in certain regions, particularly the Mexicali Valley, where irrigation from the Colorado River supports extensive cultivation of cotton, wheat, and vegetables. The Guadalupe Valley near Ensenada has gained international recognition for wine production, with numerous wineries producing world-class vintages from grapes grown in the region's unique microclimate.
Tourism represents a growing economic sector, with visitors attracted by the peninsula's natural beauty, recreational opportunities, and relatively affordable costs compared to similar destinations. Adventure tourism, including off-road racing, surfing, sportfishing, and whale watching, has become particularly important. The peninsula's dramatic landscapes and abundant wildlife provide endless opportunities for eco-tourism and outdoor recreation.
Mining has historically played a role in the peninsula's economy, with operations extracting salt, gypsum, and other minerals. The salt works at Guerrero Negro represent one of the world's largest salt production facilities, taking advantage of the region's arid climate and access to seawater.
Conservation Challenges and Efforts
The unique ecosystems of Baja California face numerous conservation challenges, from urban development pressure to climate change impacts. Coastal development for tourism and residential purposes has altered natural habitats, while water scarcity issues affect both human communities and natural ecosystems. The peninsula's endemic species are particularly vulnerable, as many have limited distributions and specific habitat requirements.
Several protected areas have been established to conserve the peninsula's most important ecosystems. The Vizcaíno Biosphere Reserve protects critical desert habitats and breeding lagoons for gray whales. Sierra de San Pedro Mártir National Park preserves high-elevation pine-oak forests and provides habitat for endemic species. Various state and federal reserves protect coastal wetlands, desert areas, and marine environments.
International cooperation has become increasingly important for conservation efforts, particularly for migratory species that cross national boundaries. Partnerships between Mexican and U.S. organizations work to protect shared species and ecosystems, while research collaborations help scientists better understand the peninsula's complex ecological relationships.
Conclusion
The Baja California Peninsula stands as a testament to the power of geological forces and evolutionary adaptation. Its unique position, complex history, and diverse ecosystems create a landscape unlike anywhere else on Earth. From its rugged mountains to its pristine deserts, from its bustling cities to its remote wilderness areas, the peninsula offers a compelling blend of natural wonders and human achievement.
As the region continues to develop and grow, the challenge lies in balancing economic progress with environmental protection. The peninsula's future depends on maintaining the delicate equilibrium between human needs and ecological preservation, ensuring that this remarkable landscape remains a source of wonder and inspiration for generations to come. The story of Baja California continues to unfold, shaped by the same forces of change and adaptation that have defined its character for millions of years.





