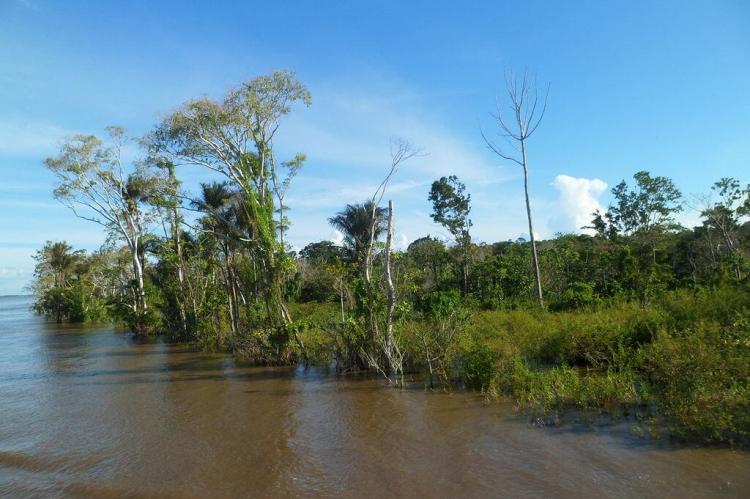
Monte Alegre Várzea: Life in the Floodplains
The Monte Alegre Várzea is a unique ecoregion located in the lower Amazon basin in Brazil. Stretching along the Amazon River and its tributaries, this ecoregion plays a pivotal role in supporting a variety of species. It serves as an essential buffer zone within the broader Amazon biome.
Monte Alegre Várzea: The Seasonal Floodplains of the Lower Amazon
The Monte Alegre Várzea is a unique ecoregion located in the lower Amazon basin in Brazil. It is a critical part of the Amazonian várzea (flooded forest) system, characterized by its seasonal flooding, high biodiversity, and ecological importance. Stretching along the Amazon River and its tributaries, this ecoregion plays a pivotal role in supporting a variety of species. It serves as an essential buffer zone within the broader Amazon biome. The Monte Alegre várzea is a reservoir of life and a dynamic and fragile ecosystem facing numerous conservation challenges.
Geographic Location and Extent
The Monte Alegre Várzea is located in northern Brazil, primarily within the state of Pará. This ecoregion lies on the right bank of the Amazon River, downstream from the confluence of the Trombetas and Nhamundá rivers. It encompasses a variety of landscapes, from the seasonally inundated floodplains near the river to upland areas that remain above the floodwaters year-round. The várzea forms part of the extensive Amazonian floodplain system, which fluctuates between wet and dry seasons, creating a constantly changing environment.
The Monte Alegre várzea is spread over approximately 27,600 square kilometers (10,600 square miles), making it one of the smaller várzea regions compared to others, like the Purus or Iquitos várzea. Despite its size, it holds significant ecological value due to its biodiversity and role in maintaining the health of the broader Amazon ecosystem.
Seasonal Flooding: The Pulse of the Monte Alegre Várzea
Like other várzea ecoregions, the Monte Alegre Várzea is defined by water levels' seasonal rise and fall. During the wet season, which can last several months, the Amazon River's floodwaters, enriched with sediments from the Andes, submerge the várzea. Water levels can rise by as much as 10 meters (33 feet), transforming forests into aquatic habitats where fish swim among the trees and aquatic plants flourish.
The floodwaters deposit nutrient-rich sediments that rejuvenate the soil, making the Monte Alegre Várzea one of the most fertile regions in the Amazon. This seasonal inundation supports high productivity in terms of plant growth and provides breeding grounds for fish and other aquatic species. The cycle of flooding and recession creates a mosaic of habitats, from flooded forests to temporary lakes and open grasslands, all essential for the survival of a wide array of species.
Biodiversity of the Monte Alegre Várzea: A Rich Tapestry of Life
The Monte Alegre Várzea boasts a remarkable plant and animal life diversity, thanks to its fertile soils and dynamic environment. The region's flora includes a variety of tree species adapted to the seasonal floods, such as the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis), the açaí palm (Euterpe oleracea), and the buriti palm (Mauritia flexuosa). These trees provide a habitat for wildlife and play a crucial role in the region's nutrient cycles by dropping fruits and leaves into the floodwaters, where they decompose and provide sustenance for aquatic organisms.
Aquatic plants, including species of water hyacinth and grasses, also thrive in the várzea, contributing to the region's high productivity. These plants provide food and shelter for fish and other aquatic species and attract predators like birds and mammals.
Fauna: A Hotspot for Birds, Fish, and Mammals
The Monte Alegre Várzea is home to an astonishing array of wildlife. Over 680 species of birds have been recorded in the region, making it a critical area for avian biodiversity in the Amazon. Species such as the red-shouldered macaw (Ara nobilis), sun parakeet (Aratinga solstitialis), and the scarlet ibis (Eudocimus ruber) are commonly seen in the várzea. Migratory birds also flock to the region during the dry season, taking advantage of the abundant food resources the flooded forests and wetlands provide.
In addition to its birdlife, the Monte Alegre Várzea supports a rich diversity of fish species. The region's rivers and lakes are teeming with economically important fish such as the tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum), the pirarucu (Arapaima gigas), and the piranha (Pygocentrus nattereri). These fish are integral to the local economy, providing food for humans and wildlife. The várzea's flooded forests serve as critical spawning and nursery grounds for these fish, ensuring the sustainability of their populations.
Mammals in the Monte Alegre Várzea are also diverse, with over 200 species recorded in the region. Notable species include the jaguar (Panthera onca), the ocelot (Leopardus pardalis), and the South American tapir (Tapirus terrestris). Several primate species, such as the red howler monkey (Alouatta seniculus) and the white-fronted capuchin (Cebus albifrons), are also found in the várzea, navigating the tree canopies above the floodwaters. Aquatic mammals like the Amazon river dolphin (Inia geoffrensis) and the giant otter (Pteronura brasiliensis) are frequent inhabitants of the flooded waters, contributing to the overall richness of the region's fauna.
Ecological Importance and Productivity
The Monte Alegre Várzea plays a vital ecological role within the larger Amazon basin. Its seasonal flooding supports local biodiversity and helps regulate water flow and nutrient cycles throughout the region. The floodwaters carry essential nutrients downstream, fertilizing agricultural lands and sustaining ecosystems far beyond the várzea.
The várzea's high productivity also makes it an important resource for local communities, who rely on the region's fertile soils for agriculture and its rivers for fishing. The várzea is particularly well-suited for agroforestry systems that combine the cultivation of crops like açaí, cacao, and bananas with the sustainable management of forest resources. This integration of agriculture and forest management is essential for maintaining the region's ecological balance while supporting local people's livelihoods.
Human Impact: A Region Under Pressure
Despite its ecological importance, the Monte Alegre Várzea faces significant pressures from human activities. Deforestation, driven by the expansion of agriculture, cattle ranching, and logging, poses one of the greatest threats to the region. Large forest areas have been cleared for pastureland or converted to plantations, disrupting wildlife habitats and altering the natural flood cycles.
Overfishing is another major concern, as the high demand for commercially valuable species like the tambaqui and pirarucu has led to the depletion of fish stocks. In some areas, illegal gold mining has introduced mercury into the rivers, contaminating the water and threatening both wildlife and human health.
The lack of protected areas within the Monte Alegre Várzea exacerbates these challenges. Unlike other parts of the Amazon, this region has relatively few designated reserves or national parks, leaving it vulnerable to exploitation. The absence of comprehensive conservation measures makes it difficult to mitigate the impacts of deforestation, overfishing, and pollution.
Conservation Efforts and Sustainable Solutions
In recent years, there have been growing efforts to protect the Monte Alegre Várzea and promote sustainable land use practices. Local communities, environmental organizations, and government agencies have begun collaborating on projects to conserve the region's biodiversity while supporting sustainable development.
Agroforestry initiatives integrating crop cultivation with forest conservation have shown promise as a sustainable solution for the várzea. By planting açaí, cacao, and other high-value crops alongside native trees, farmers can generate income without resorting to deforestation. Community-based fisheries management programs have also been implemented to regulate fishing practices and ensure the long-term sustainability of fish populations.
Conservation organizations advocate for establishing protected areas within the Monte Alegre Várzea, which would help safeguard its unique ecosystems from further degradation. These efforts are crucial for preserving the region's rich biodiversity and ensuring that its natural resources are managed to benefit both people and wildlife.
Conclusion: A Vital and Vulnerable Ecosystem
The Monte Alegre Várzea is a critical component of the Amazon's vast and complex ecosystem. Its seasonal flooding, rich biodiversity, and high productivity make it a vital resource for both wildlife and local communities. However, human activities are putting increasing pressure on the region, and its future depends on the success of conservation efforts and sustainable management practices.
As one of the lesser-known but ecologically important várzea regions, the Monte Alegre Várzea reminds us of the delicate balance between nature and human development in the Amazon. Protecting this unique ecoregion will require a concerted effort to preserve its biodiversity, manage its resources sustainably, and mitigate the impacts of deforestation, overfishing, and pollution. In doing so, the Monte Alegre Várzea can continue to thrive as a vibrant and productive part of the Amazon basin for generations.
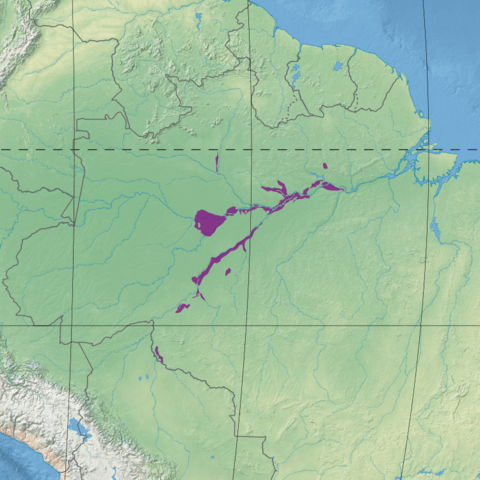
Map depicting the location of the Monte Alegre várzea (in purple).
