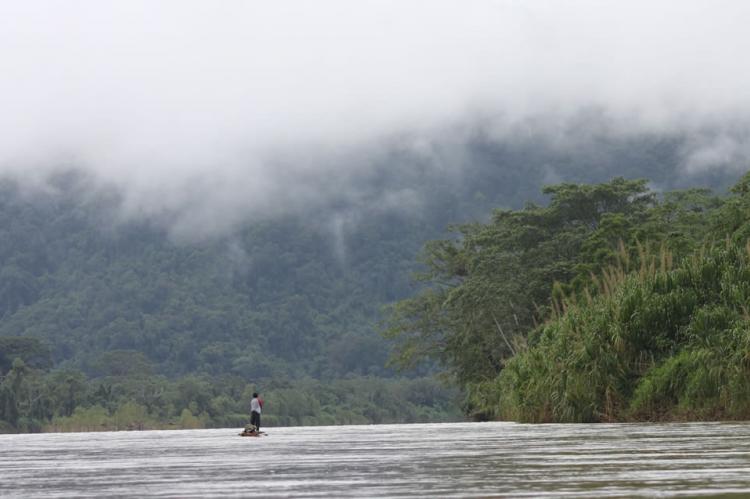
Central America's Enigmatic Mosquito Coast
The Mosquito Coast, also known as the Miskito Coast, is a region along the eastern shores of Nicaragua and Honduras. Named after the indigenous Miskito people who have inhabited the area for centuries, this coastal expanse encompasses a blend of rainforests, swamps, mangroves, and winding rivers.
Central America's Enigmatic Mosquito Coast
The Mosquito Coast, also known as the Miskito Coast, is a captivating region along the eastern shores of Nicaragua and Honduras shrouded in mystery and allure. Named after the indigenous Miskito people who have inhabited the area for centuries, this coastal enclave boasts a rich tapestry of history, culture, and natural wonders. From its historical significance as a British-influenced territory to its status as a biodiversity hotspot, the Mosquito Coast offers a fascinating glimpse into Central America's diverse heritage and ecological richness.
Historical Legacy
The Mosquito Coast's historical legacy is a captivating saga unfolding against the backdrop of colonial conquests, geopolitical intrigue, and cultural resilience. Originating from the ancient Miskito kingdom, whose roots stretch back centuries, the region became a melting pot of indigenous traditions and European ambitions. The 17th to 19th centuries witnessed the rise of British influence as colonial powers vied for control over lucrative trade routes and strategic coastal territories.
Under British patronage, the Mosquito Coast flourished as a hub of maritime activity, attracting buccaneers, traders, and explorers seeking fortune and adventure in the New World. The establishment of a Miskito monarchy, sanctioned by British authorities, lent legitimacy to the region's governance, albeit under the shadow of colonial oversight. This unique blend of indigenous sovereignty and foreign intervention shaped the cultural landscape of the Mosquito Coast, forging alliances and rivalries that reverberated across the Caribbean.
Yet, the region's sovereignty remained a point of contention, as competing claims from Britain, the United States, Nicaragua, and Honduras fueled diplomatic tensions and territorial disputes. The strategic importance of the Mosquito Coast, situated at the crossroads of global trade routes and colonial ambitions, made it a prized possession coveted by rival powers. Amidst the shifting tides of empire and diplomacy, the resilient spirit of the Miskito people endured, safeguarding their ancestral homeland against external encroachments and asserting their right to self-determination.
Geographical Marvel
Stretching along the Caribbean Sea from approximately 11°45′ to 14°10′ N latitude, the Mosquito Coast spans a narrow strip of territory along the eastern coast of Nicaragua and Honduras. Extending inland for about 60 kilometers (37 miles) and measuring roughly 400 kilometers (250 miles) from north to south, it is bordered by the Wawa River in the north, the Nicaraguan highlands in the west, and the Río Rama in the south. The region's diverse topography includes rainforests, swamps, mangroves, and rivers, shaping a landscape that has remained largely unpopulated and undeveloped.
Cultural Melting Pot
Despite its sparse population of around 200,000 inhabitants, the Mosquito Coast is a melting pot of indigenous cultures. The majority are Miskito people, alongside smaller communities of Sumo, Rama, and Garifuna descent. Bluefields, the largest city in the region, serves as a vibrant hub of trade and commerce. Puerto Lempira is the capital of Honduras's Gracias a Dios department, offering a gateway to the untamed rainforests that define the Mosquito Coast. The region's cultural diversity is reflected in its languages, traditions, and ways of life, creating a unique tapestry of indigenous heritage amidst the coastal wilderness.
Biodiversity Hotspot
Renowned for its extraordinary biodiversity, the Mosquito Coast is a sanctuary for a myriad of plant and animal species. Its dense rainforests, characterized by towering mahogany, cedar, and rosewood trees, provide crucial habitats for a diverse range of wildlife, including endangered species like jaguars and tapirs. Meanwhile, the region's swamps and mangroves serve as vital ecosystems for elusive creatures such as crocodiles, caimans, and manatees, contributing to the area's ecological richness and resilience. Additionally, the numerous rivers crisscrossing the landscape, such as the Prinzapolka and Coco, harbor a diverse array of fish species, further enhancing the region's status as a biodiversity hotspot.
Preserving Natural Heritage
In recognition of its ecological significance, significant portions of the Mosquito Coast are under protection, reflecting a commitment to preserving its rich biodiversity and unique ecosystems. Key areas, including the Río Plátano Biosphere Reserve, Patuca National Park, and Sierra de Agalta National Park, have been designated as UNESCO World Heritage Sites and national parks, underscoring their importance in conservation efforts.
These protected areas serve as vital refuges for a wide range of plant and animal species, safeguarding the region's natural heritage and ensuring its continued existence for future generations. Through sustainable management practices and community engagement initiatives, these conservation areas aim to balance human activities and environmental preservation, promoting the long-term well-being of both the ecosystem and local communities.
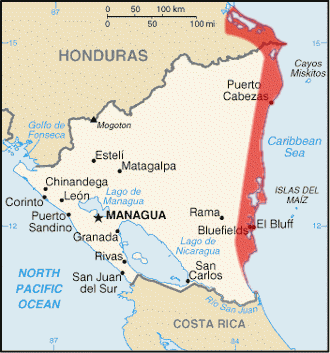
Map depicting the area of the Mosquito Coast.
