Bolivia's Sacred Summits: A Journey Through the Nation's Highest Peaks
Bolivia is one of the world's highest nations, with peaks piercing thin air and high-altitude plateaus stretching to the horizon. Its dramatic topography includes spectacular Andes mountain scenery, featuring volcanic summits, glacier-covered massifs, and pristine alpine environments.
The Rooftop of South America: Bolivia's Majestic Mountain Landscapes
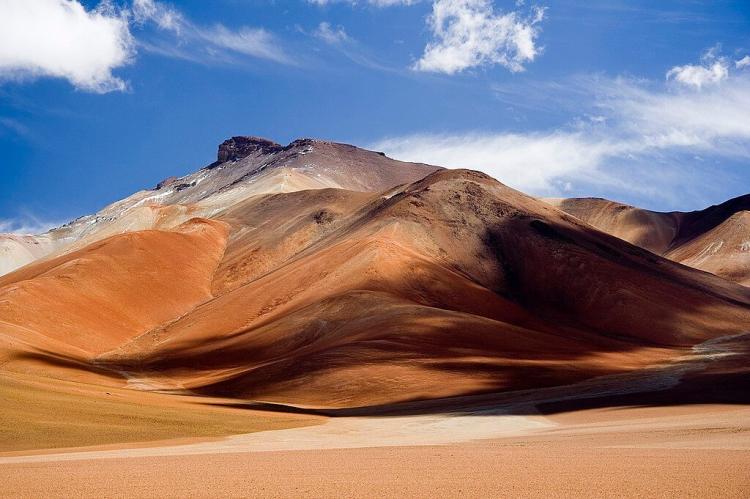
Bolivia stands as one of the world's most elevated nations, where towering peaks pierce thin air and vast high-altitude plateaus stretch beyond the horizon. The country's dramatic topography encompasses some of the most spectacular mountain scenery in the Andes, featuring volcanic summits, glacier-covered massifs, and pristine alpine environments that have captivated explorers and mountaineers for generations. From the volcanic giants of the Cordillera Occidental to the knife-edged ridges of the Cordillera Real, Bolivia's mountains represent a geological masterpiece that continues to shape the nation's climate, culture, and character.
The Bolivian Andes: A Geological Marvel
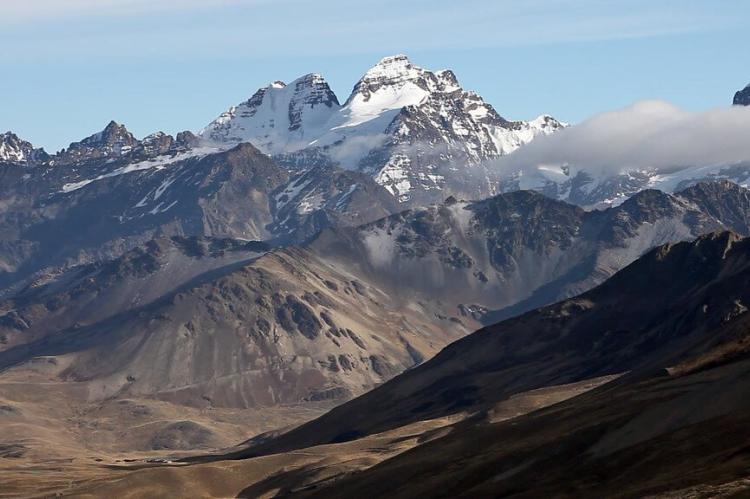
The Andes in Bolivia are characterized by distinct eastern and western ranges—the Cordillera Oriental and the Cordillera Occidental—with intervening plateaus and depressions. This complex mountain system creates one of the most geologically diverse landscapes in South America, where ancient granitic cores meet relatively recent volcanic formations.
The Bolivian Andes reach their greatest width in the central region, creating a massive highland zone that encompasses nearly half of the country's territory. This elevated realm, much of which lies above 3,500 m (11,483 ft), represents one of the world's most extensive high-altitude environments and serves as the foundation for Bolivia's unique mountain ecosystems.
The Cordillera Occidental: Land of Fire and Ice
The western mountain range of Bolivia forms a dramatic boundary with Chile and represents one of the most volcanically active regions in the Andes. The most prominent peak is Nevado Sajama, the highest mountain in Bolivia, which rises to 6,542 m (21,463 ft). This magnificent stratovolcano dominates the surrounding landscape and serves as a symbol of Bolivia's mountaineering heritage.
The Cordillera Occidental makes a natural border between Bolivia and Peru & Chile, separating the Bolivian highlands from the Atacama Desert. The range features numerous other significant volcanic peaks, including Parinacota and Pomerape, which straddle the Chilean-Bolivian border, creating a dramatic skyline of snow-capped cones rising from the high desert.
The volcanic nature of the Cordillera Occidental has created a landscape of extraordinary contrasts, where glaciated summits tower above salt flats and geothermal fields. Many of these volcanoes remain active or dormant, with sulfurous gases escaping from fumaroles and creating otherworldly environments that attract scientists and adventurers alike.
Major Peaks of the Cordillera Occidental
Nevado Sajama stands not only as Bolivia's highest peak but also as one of the world's highest volcanoes. The mountain's perfectly symmetrical cone rises majestically from the Altiplano, offering challenging climbing routes through varied terrain including rock, ice, and snow. The peak's accessibility from nearby villages has made it a popular objective for mountaineers seeking to experience Bolivia's high-altitude environment.
Other notable volcanic peaks in the range include Licancabur, famous for its near-perfect conical shape, and numerous other stratovolcanoes that create a dramatic volcanic landscape stretching along Bolivia's western frontier. These mountains serve as vital water sources for the surrounding communities and ecosystems, capturing moisture from the atmosphere and storing it in the form of snow and ice.
The Cordillera Real: Granite Spires and Glaciated Massifs
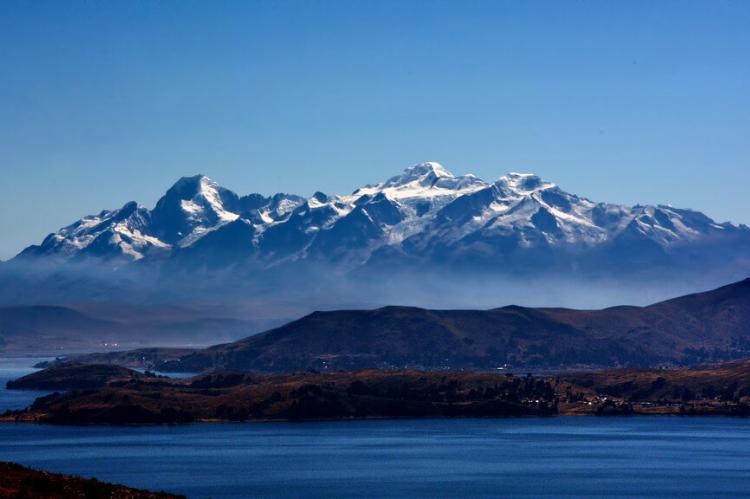
The Cordillera Real, or Royal Range, represents the crown jewel of Bolivian mountaineering and contains the most technically challenging and visually stunning peaks in the country. The range is home to some of Bolivia's highest peaks, including Illimani and Illampu, and is located near La Paz, offering stunning views of the surrounding valleys and lakes.
This granite massif extends roughly 160 km (99 mi) north-south and contains numerous peaks exceeding 6,000 m (19,685 ft). The range's proximity to La Paz, Bolivia's administrative capital, makes it easily accessible to climbers and provides a dramatic backdrop to one of South America's highest capital cities.
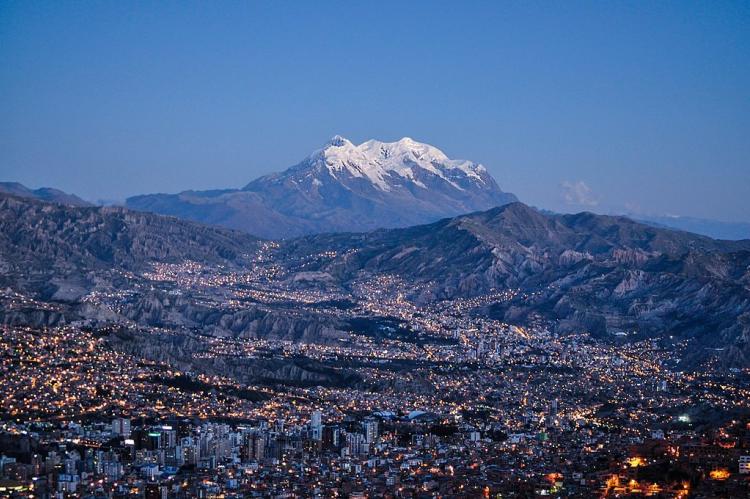
Illimani: The Guardian of La Paz
Illimani reaches 6,460 m (21,194 ft) and stands as one of Bolivia's most recognizable peaks. The mountain has four main peaks, with the highest being the south summit, Nevado Illimani, which is popular among mountain climbers. The peak's imposing presence dominates the skyline above La Paz, earning it the nickname "Guardian of La Paz."
The snow line lies at about 4,570 m (15,000 ft) above sea level, with glaciers found on the northern face at 4,982 m (16,350 ft). The mountain presents a significant mountaineering challenge, requiring technical ice and snow climbing skills as well as excellent acclimatization to the extreme altitude.
Ancohuma and Illampu: Technical Challenges
Ancohuma rises to 6,430 m (21,096 ft), while Illampu reaches 6,362 m (20,873 ft). Illampu is particularly renowned for its technical difficulty, with routes rated as having "the hardest normal route on any of the 6,000 metre peaks in Bolivia," with the easiest route featuring snow slopes up to 65 degrees.
These peaks represent the ultimate test for experienced mountaineers, combining extreme altitude with technical climbing challenges that demand both physical fitness and advanced mountaineering skills. The granite spires and ice-covered faces create some of the most beautiful and demanding climbing in South America.
Huayna Potosí: The Accessible Giant
Huayna Potosí stands at 6,094 m (19,993 ft) and has gained recognition as one of the world's most accessible 6,000 m peaks. The mountain is often referred to as the easiest 6,000 m climb because the elevation gain from the trailhead to the summit is less than 1,400 m, with easy access from La Paz.
Despite its relative accessibility, Huayna Potosí remains a serious high-altitude mountaineering objective that requires proper acclimatization and technical skills. The peak serves as an excellent training ground for aspiring high-altitude climbers and provides spectacular views of the surrounding Cordillera Real.
The Cordillera Apolobamba: Pristine Wilderness
Located in the northern part of the Cordillera Real, the Cordillera Apolobamba is characterized by its pristine landscapes. This remote range extends along the Peruvian border and contains numerous peaks exceeding 5,000 m (16,404 ft), offering wilderness experiences in one of Bolivia's most untouched mountain environments.
The Apolobamba region serves as an important watershed and biodiversity hotspot, containing unique high-altitude ecosystems that support specialized flora and fauna adapted to extreme elevation and climate conditions. The range's remoteness has helped preserve traditional Indigenous cultures and practices that have coexisted with the mountain environment for centuries.
The Altiplano: High Plains Between the Ranges
Between the Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Oriental lies the Altiplano, a vast high-altitude plateau that averages 3,500-4,000 m (11,483-13,123 ft) in elevation. This unique geographical feature represents one of the world's most extensive high plains and creates a distinctive environment that supports specialized ecosystems and human communities.
The Altiplano serves as a crucial component of Bolivia's mountain system, collecting water from the surrounding peaks and creating important wetland habitats, including Lake Titicaca, the world's highest navigable lake. The plateau's elevation and climate create challenging conditions that have shaped both natural ecosystems and human adaptations over thousands of years.
Geological Formation and Tectonic Activity
Bolivia's mountain ranges reflect millions of years of complex geological processes, primarily driven by the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate. The ongoing tectonic activity continues to shape the landscape, creating new volcanic features while uplifting existing mountain ranges.
The western ranges show clear evidence of recent volcanic activity, with numerous active and dormant volcanoes contributing to the region's dynamic geology. The eastern ranges display more ancient granite formations that have been sculpted by glacial action over thousands of years, creating the spectacular spires and cirques that characterize the Cordillera Real.
Climate and Environmental Zones
Bolivia's mountain ranges create dramatic climate variations within relatively short distances. The combination of tropical latitude and extreme elevation produces unique environmental conditions that vary from subtropical valleys to arctic summit zones within the span of a single mountain face.
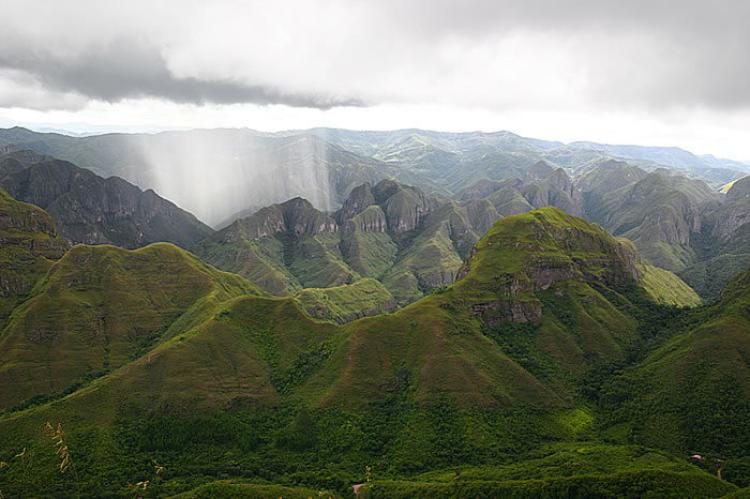
The eastern slopes of the Andes capture moisture from the Amazon basin, creating lush cloud forests and contributing to significant biodiversity. The western slopes face the Atacama Desert and experience extremely arid conditions, resulting in stark landscapes where glaciated peaks rise directly from desert floors.
These climate variations support an extraordinary range of ecosystems, from high-altitude grasslands and shrublands to temperate forests and alpine tundra. The mountains serve as a crucial habitat for numerous endemic species, including vicuñas, chinchillas, and various high-altitude birds that have adapted to the challenging conditions.
Cultural and Economic Significance
Bolivia's mountains have played a central role in shaping the nation's cultural identity and economic development. Indigenous peoples, including the Aymara and Quechua, have maintained strong spiritual connections to the peaks, viewing them as sacred entities that influence weather, agriculture, and the well-being of their communities.
The mountains contain significant mineral wealth, including tin, silver, and lithium deposits that have driven Bolivia's economy for centuries. The mining industry continues to play a crucial role in national development, though it also presents environmental challenges that require careful management.
Tourism and mountaineering contribute increasingly to regional economies, with thousands of climbers and trekkers visiting Bolivia annually to experience the country's spectacular mountain landscapes. The accessibility of peaks like Huayna Potosí has made Bolivia a popular destination for high-altitude mountaineering, while the technical challenges of peaks like Illampu attract expert climbers from around the world.
Indigenous Heritage and Sacred Peaks
Bolivia's mountains hold profound spiritual significance for Indigenous communities who have inhabited the region for thousands of years. Many peaks are considered sacred entities or apu (mountain spirits) that require respect and offerings from those who venture into their domain.
Traditional practices include ceremonies and rituals performed before climbing expeditions, reflecting the deep cultural connections between local communities and their mountain environment. These traditions continue to influence modern mountaineering practices and contribute to the unique cultural experience of climbing in Bolivia.
Conservation Challenges and Opportunities
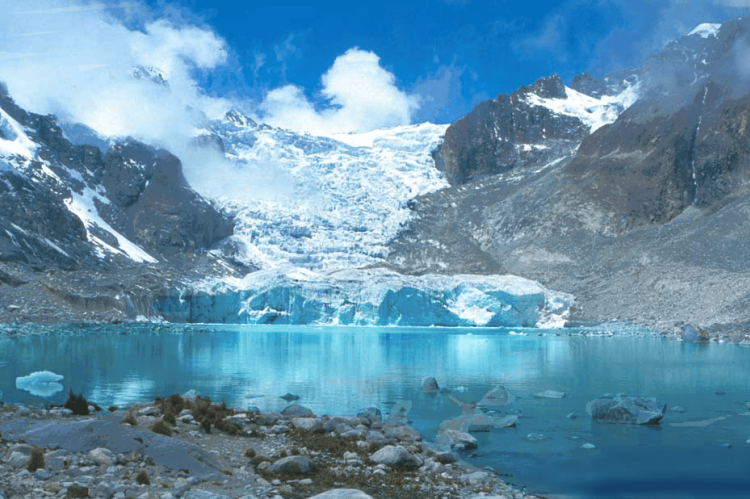
The preservation of Bolivia's mountain environments faces numerous challenges, including climate change, mining activities, and increasing tourism pressure. Glacial retreat throughout the Cordillera Real and other ranges poses significant concerns for water resources and ecosystem stability.
Protected areas, including Sajama National Park and Madidi National Park, play crucial roles in preserving mountain ecosystems and biodiversity. These conservation areas not only protect natural habitats but also provide opportunities for sustainable tourism development and scientific research.
The challenge of balancing economic development with environmental protection remains ongoing, requiring careful planning and international cooperation to ensure that Bolivia's mountain heritage is preserved for future generations.
Summary
Bolivia's mountain ranges represent one of South America's most spectacular and diverse highland regions, encompassing volcanic peaks, granite spires, and vast high-altitude plateaus that create unique environments found nowhere else on Earth. The Cordillera Occidental contains the country's highest peak, Nevado Sajama at 6,542 m (21,463 ft), along with numerous other volcanic summits that form a dramatic western frontier. The Cordillera Real features technically challenging peaks, including Illimani, Ancohuma, and Illampu, which rank among the world's most demanding high-altitude climbing objectives.
These mountain systems continue to shape Bolivia's climate, ecology, and human activities, serving as vital sources of water resources, mineral wealth, and tourism revenue. The geological processes that formed these peaks remain active, ensuring that Bolivia's mountains will continue to evolve while providing inspiration and challenge to future generations. From the sacred peaks revered by Indigenous communities to the world-class mountaineering objectives that attract climbers globally, Bolivia's mountains stand as monuments to the dynamic forces that shape our planet and the enduring human spirit that seeks to explore and understand these magnificent landscapes.
The combination of extreme altitude, technical climbing challenges, and rich cultural heritage makes Bolivia's mountains unique among the world's great ranges, offering experiences that blend physical challenge with cultural immersion and natural wonder. As climate change and development pressures continue to impact these environments, the preservation of Bolivia's mountain heritage becomes increasingly important for maintaining both ecological integrity and cultural continuity in one of the world's most remarkable highland regions.
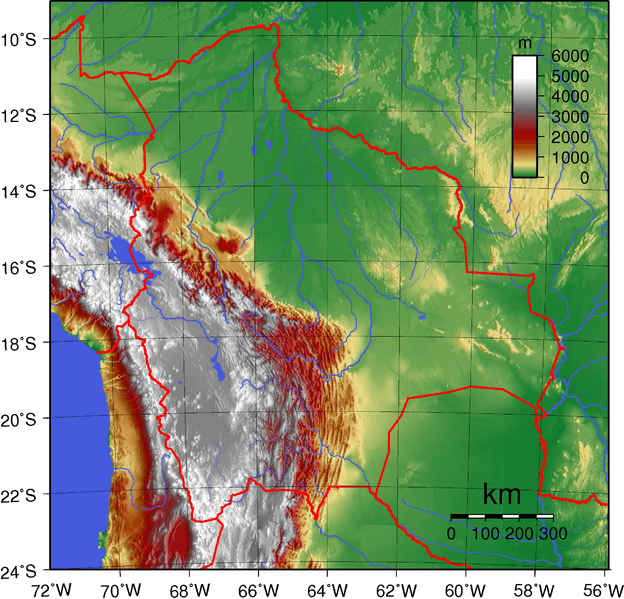
Topographical map of Bolivia.
Major Peaks of the Bolivian Andes
Peaks Within Bolivia
High Peaks (Above 6,000m)
- Nevado Sajama - 6,542m (21,463ft) - Bolivia's highest peak
- Illimani - 6,439m (21,122ft)
- Janq'u Uma - 6,427m (21,086ft)
- Illampu - 6,368m (20,892ft)
- Wayna Potosí - 6,088m (19,974ft)
Mid-Range Peaks (5,000-6,000m)
- Cabaraya - 5,860m (19,226ft)
- Nevado Anallajsi - 5,750m (18,865ft)
- Tata Sabaya - 5,430m (17,815ft)
- Chacaltaya - 5,422m (17,789ft)
- Macizo de Pacuni - 5,400m (17,720ft)
- Patilla Pata - 5,300m (17,390ft)
- Laram Q'awa - 5,182m (17,001ft)
Peaks on the Bolivia-Chile Border
High Border Peaks (Above 6,000m)
- Parinacota - 6,380m (20,930ft)
- Pomerape - 6,282m (20,610ft)
- Acotango - 6,052m (19,856ft)
Mid-Range Border Peaks (5,000-6,000m)
- Licancabur - 5,920m (19,423ft)
- Paruma - 5,420m (17,782ft)
- Olca - 5,407m (17,740ft)
- Michincha - 5,305m (17,405ft)
- Iru Phutunqu - 5,163m (16,939ft)
Key Facts
- Nevado Sajama at 6,542 m (21,463 ft) is Bolivia's highest peak
- Illimani is Bolivia's second-highest peak at 6,439 m (21,122 ft)
- Parinacota reaches 6,380 m (20,930 ft) above sea level
- The border peaks are part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes and straddle the Chile-Bolivia border
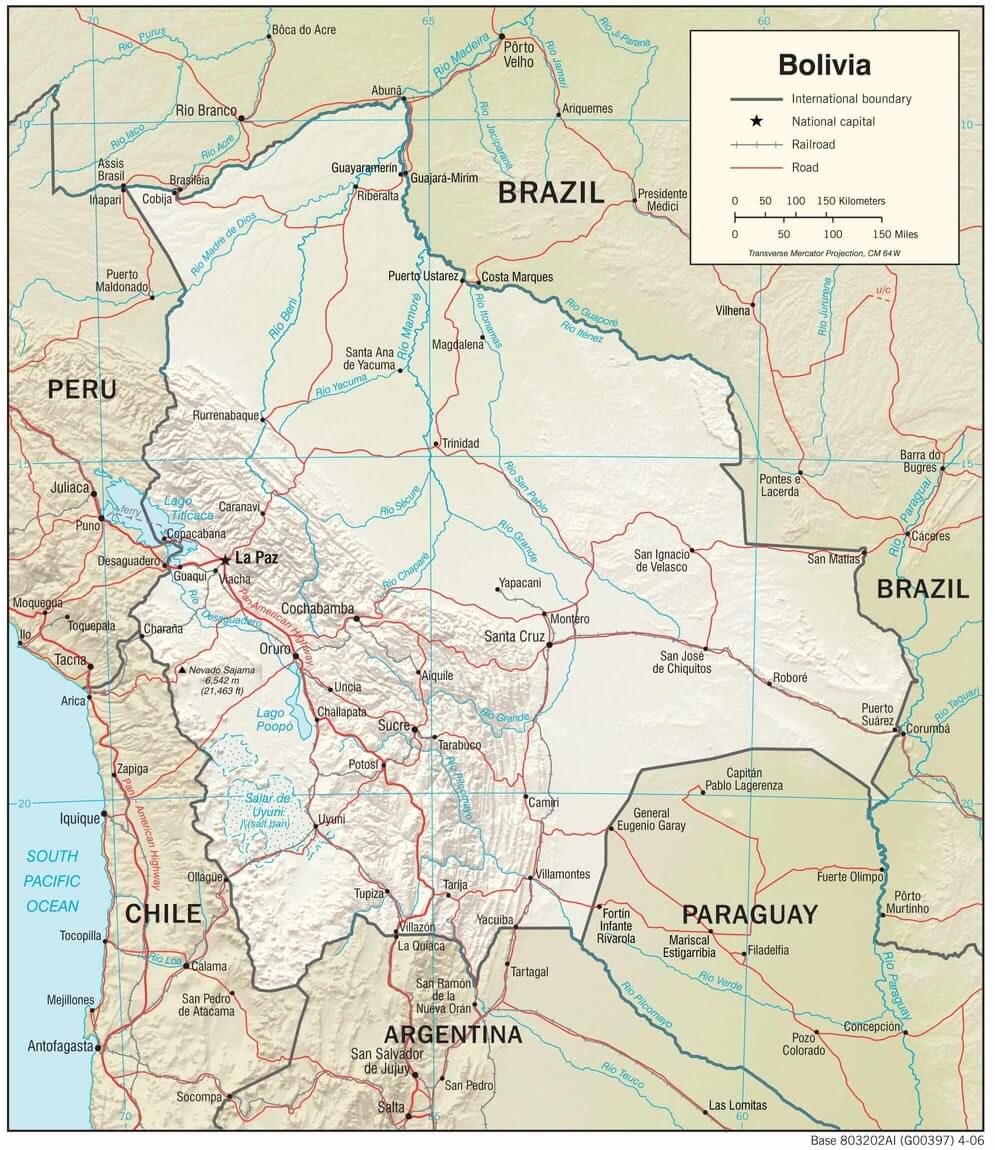
Bolivia physiographic map





