El Salvador's Aquatic Mosaic: Natural Lakes, Rivers, and Artificial Reservoirs
El Salvador is home to diverse water bodies that contribute to its natural beauty and ecological significance. From expansive lakes and picturesque lagoons to bays, gulfs, and meandering rivers, these water bodies shape the landscape and play essential roles in the country's ecosystem and economy.
Aquatic Treasures: El Salvador's Natural and Artificial Water Systems
El Salvador, the smallest nation in Central America, possesses a remarkable diversity of water bodies that fundamentally shape its landscape, economy, and ecological systems. Despite occupying only 21,041 sq km (8,124 sq mi), the country harbors an intricate network of natural lakes, meandering rivers, artificial reservoirs, and coastal waters that collectively sustain both human communities and diverse ecosystems. These aquatic features, ranging from ancient volcanic lakes to modern hydroelectric reservoirs, demonstrate the profound relationship between geography, geology, and human development in this densely populated Pacific coast nation.
Pacific Coast and Marine Waters
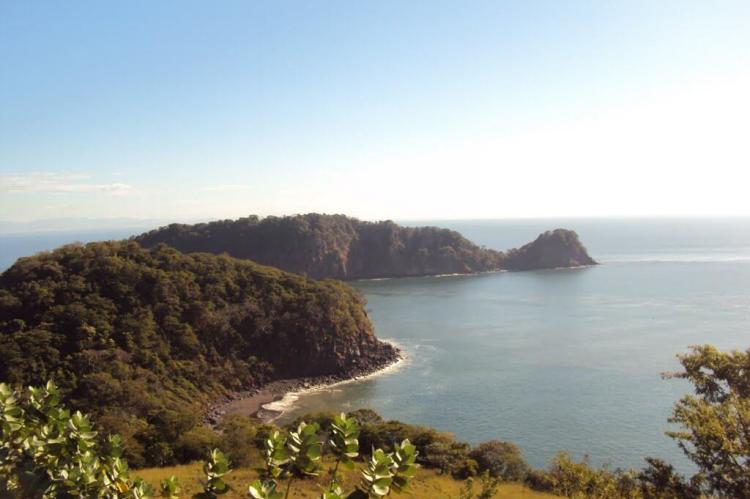
El Salvador's 307 km (191 mi) Pacific coastline encompasses a diverse range of marine environments that support both ecological and economic activities. The Gulf of Fonseca, shared with Honduras and Nicaragua, represents the country's most significant marine water body. This picturesque body of water, renowned for its ecological diversity, historical significance, and economic importance, serves as a crucial habitat for marine species and facilitates international commerce through its strategic location.
The coastal waters support extensive mangrove ecosystems that provide critical nursery grounds for fish species and serve as natural barriers against coastal erosion. These marine environments contribute significantly to El Salvador's fishing industry, which relies heavily on Pacific Ocean resources for both subsistence and commercial purposes.
Natural Lakes and Volcanic Origins
El Salvador's most prominent water bodies include four major natural lakes, each with unique characteristics shaped by the country's volcanic geography. Lake Ilopango, covering 70.1 sq km (27.1 sq mi), ranks as the largest natural lake, followed by Lake Guija at 44.1 sq km (17.0 sq mi), Lake Coatepeque at 24.8 sq km (9.6 sq mi), and Lake Olomega at 24.2 sq km (9.3 sq mi).
Lake Ilopango
Lake Ilopango, situated in the central region, occupies a massive volcanic caldera formed by ancient eruptions. The lake's considerable depth and crystal-clear waters make it a popular destination for recreational activities and tourism. Its volcanic origins have created unique chemical compositions that support specialized aquatic ecosystems.
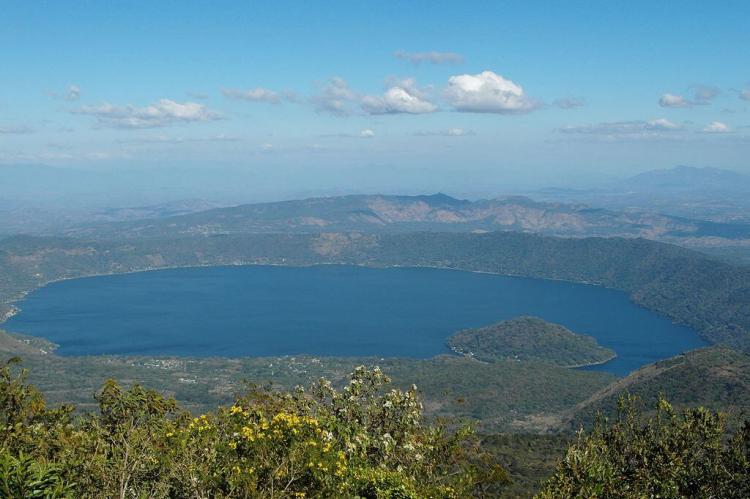
Lake Coatepeque
Lake Coatepeque, nestled within another volcanic caldera, displays spectacular turquoise waters that contrast dramatically with the surrounding mountainous terrain. The lake's exceptional clarity and depth have made it a premier recreational destination, attracting visitors with its pristine conditions and scenic beauty.
Lake Guija
Lake Guija, positioned along the Guatemala border, represents a shared water resource between the two nations. The lake's strategic location has made it historically significant for both countries, serving as a natural boundary marker while supporting cross-border ecological connections.
Lake Olomega
Lake Olomega, located in the eastern region, faces unique challenges due to its volcanic environment. One significant issue is the flow of subterranean water from the volcano to the Laguna de Olomega, which affects water quality and ecosystem dynamics.
River Systems and Drainage Networks
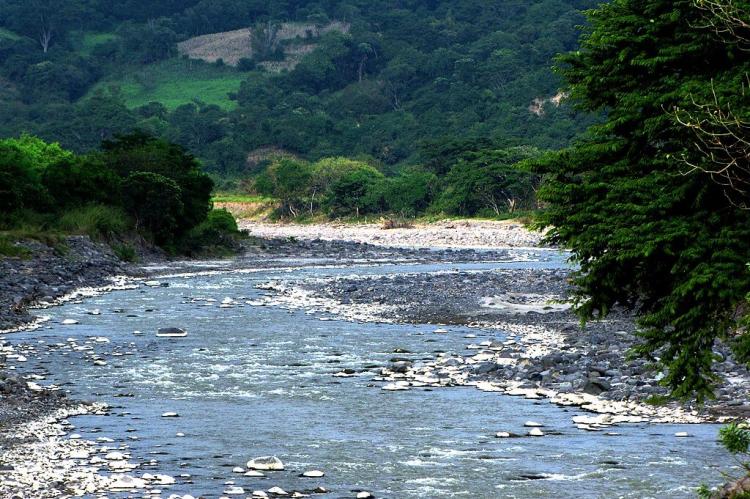
El Salvador's river systems form an intricate network that channels water from the country's mountainous interior to the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador has 350 rivers, with the largest being the Rio Lempa, which flows 241 km (150 mi) from northern to central El Salvador, forming one of the most important Pacific watersheds in Latin America.
The Lempa River System
The Lempa River stands as Central America's most significant transboundary waterway, originating in Guatemala and flowing through Honduras before entering El Salvador. The Lempa River is 422 km (262 mi) long and is shared by El Salvador, Guatemala and Honduras. Within El Salvador, the river traverses diverse landscapes, from mountainous terrain to coastal plains, supporting agriculture, hydroelectric generation, and urban water supplies.
The average flow of the Rio Lempa varies significantly along its course, measuring about 153 cubic meters per second from the Embalse Cerron Grande reservoir, about 197 cubic meters per second from the Embalse Presa Cinco de Noviembre reservoir, about 329 cubic meters per second at the Rio Torola confluence, and about 362 cubic meters per second at the Cuscatlan Bridge.
Secondary River Systems
Beyond the Lempa, El Salvador's river network comprises numerous smaller waterways that contribute to the country's regional water resources. Major rivers include the Acelhuate River, Ostúa River, Sumpul River, Torola River, Paz River, Pululuya River, Río Grande de San Miguel, Sensunapan River, and Sirama River. Each of these waterways serves specific regional functions, from agricultural irrigation to urban water supply.
The Torola River, a significant tributary of the Lempa, contributes substantially to the main river's flow and supports extensive agricultural activities in the eastern regions. The Paz River, which forms part of the border with Guatemala, underscores the international significance of El Salvador's water resources.
Artificial Reservoirs and Hydroelectric Development
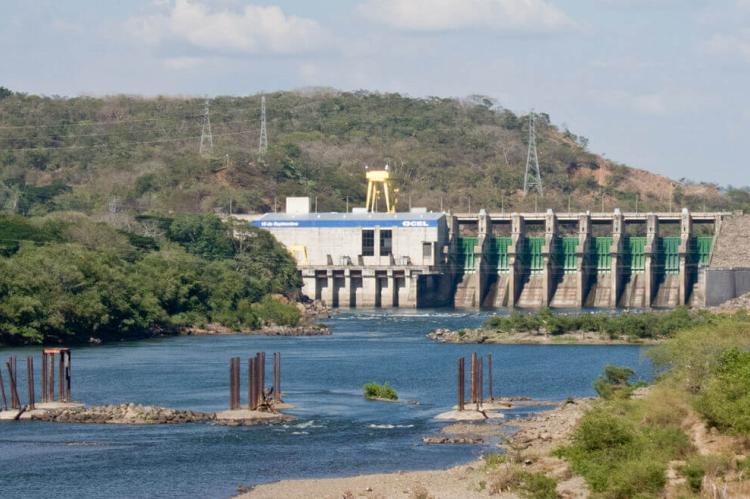
El Salvador has developed an extensive system of artificial reservoirs to harness water resources for hydroelectric power generation and water supply. The major reservoirs include the Embalse Cerron Grande, covering 135 sq km (52.1 sq mi), Embalse Presa Cinco de Noviembre, covering 20 sq km (7.7 sq mi), and Embalse Quince de Septiembre (also called Embalse del San Lorenzo), covering 35 sq km (13.5 sq mi).
Cerron Grande Reservoir
The Cerron Grande Reservoir represents El Salvador's largest artificial water body and serves as a critical component of the national electrical grid. However, the reservoir faces significant environmental challenges, including pollution from upstream sources that threaten its ecological integrity and utility for power generation.
Hydroelectric Infrastructure
These reservoirs form the backbone of El Salvador's renewable energy infrastructure, converting the country's abundant water resources into electrical power. The strategic placement of dams along the Lempa River system maximizes energy generation while providing flood control and water storage capabilities.
Groundwater Resources and Aquifer Systems
El Salvador's water resources extend beyond surface features to include substantial groundwater reserves. The best aquifers are located in the coastal zone and the valleys of the central plateau. These underground water sources provide crucial backup supplies during dry seasons and support agricultural activities in regions with limited access to surface water.
The volcanic geology that created the country's lakes also contributes to groundwater recharge, as porous volcanic soils facilitate water infiltration and storage. However, increasing population density and industrial development pose challenges to groundwater quality and availability.
Environmental Challenges and Conservation
El Salvador's water bodies face mounting environmental pressures from urbanization, industrial development, and climate change. Pollution from both domestic and industrial sources impacts water quality, while deforestation in watersheds exacerbates erosion and sedimentation. The country's high population density intensifies these challenges, requiring comprehensive water management strategies to ensure sustainable resource utilization.
Conservation efforts focus on protecting watersheds, controlling pollution, and promoting sustainable water use practices. International cooperation, particularly regarding transboundary waters like the Lempa River and Lake Guija, plays a crucial role in maintaining regional water security.
Summary
El Salvador's water bodies represent a complex and vital network of natural and artificial aquatic systems that sustain the nation's economic, ecological, and social well-being. From the expansive volcanic lakes that attract tourism and support biodiversity to the engineered reservoirs that generate renewable energy, these water resources demonstrate the intricate relationship between natural geography and human development. The country's river systems, dominated by the transboundary Lempa River, provide essential water supplies and transportation corridors while connecting El Salvador to regional watershed networks. As environmental pressures intensify, the careful management and conservation of these aquatic treasures becomes increasingly critical for ensuring sustainable development and ecological integrity in Central America's most densely populated nation.
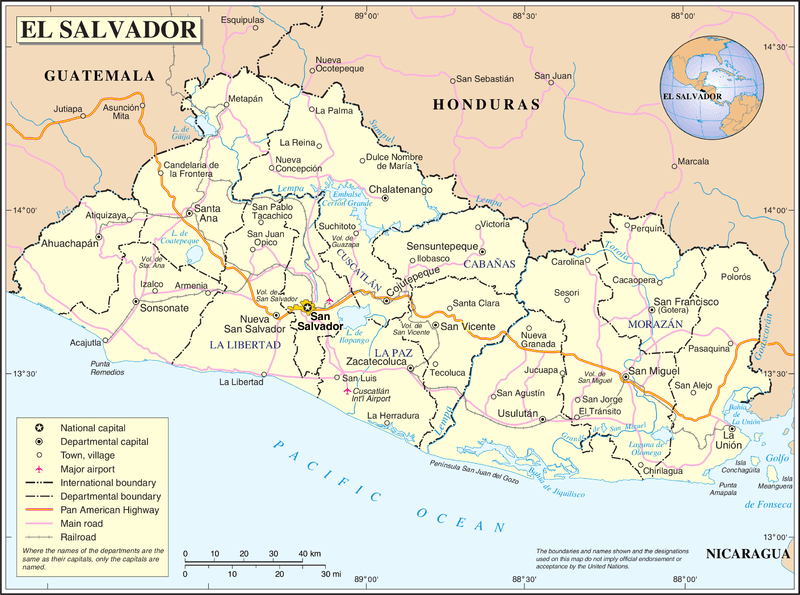
Map of El Salvador.
Notable Water Bodies of El Salvador
Natural Lakes
- Lake Ilopango: 70.1 sq km (27.1 sq mi) - Central region, volcanic caldera, maximum depth 230 m (755 ft), largest natural lake
- Lake Guija: 44.1 sq km (17.0 sq mi) - Western region, Guatemala border, shared binational water body, average depth 8 m (26 ft)
- Lake Coatepeque: 24.8 sq km (9.6 sq mi) - Western region, volcanic caldera, maximum depth 115 m (377 ft), pristine turquoise waters
- Lake Olomega: 24.2 sq km (9.3 sq mi) - Eastern region, volcanic formation, faces environmental challenges from volcanic activity
Lagoons and Smaller Water Bodies
- Jocotal Lagoon: Eastern region, seasonal wetland, important bird habitat
- El Jocotal National Park Lagoon: Protected wetland area, migratory bird sanctuary
- Laguna El Espino: Coastal lagoon, western region
- Laguna de Alegría: Volcanic crater lake, Tecapa Volcano, eastern region
- Laguna Verde: Crater lake, Cerro Verde National Park
- Laguna de las Ninfas: Small crater lake, central highlands
Major Rivers and Primary Watersheds
- Lempa River: 422 km (262 mi) total length, 241 km (150 mi) within El Salvador - Transboundary with Guatemala and Honduras, primary watershed draining 57% of national territory
- Torola River: 118 km (73 mi) - Major tributary of Lempa, eastern region, confluence near Cuscatlán Bridge
- Paz River: 134 km (83 mi) - Guatemala border, western region, forms international boundary
- Río Grande de San Miguel: 95 km (59 mi) - Eastern region, independent Pacific drainage
- Acelhuate River: 54 km (34 mi) - Central region, flows through the San Salvador metropolitan area
- Sumpul River: 108 km (67 mi) - Northern region, forms part of the Honduras border, tributary of Lempa
- Ostúa River: 42 km (26 mi) - Central region, Lempa tributary
- Pululuya River: 35 km (22 mi) - Central region, urban watershed
- Sensunapan River: 67 km (42 mi) - Western region, independent Pacific drainage
- Sirama River: 52 km (32 mi) - Eastern region, flows to the Gulf of Fonseca
- Jiboa River: 61 km (38 mi) - Central region, independent Pacific drainage
Secondary Rivers and Tributaries
- Sucio River: Lempa tributary, central region
- Desagüe River: Northwestern region, flows to Lake Guija
- Banderas River: Western region, Paz River tributary
- Chalchuapa River: Western region, flows near Santa Ana
- Chimalapa River: Eastern region, flows to the Gulf of Fonseca
- Goascorán River: Eastern region, forms part of the Honduras border
- Sapo River: Central region, flows through volcanic terrain
- Suquiapa River: Central region, urban watershed
- Titihuapa River: Central region, Acelhuate tributary
- Comalapa River: Central region, agricultural watershed
Artificial Reservoirs and Hydroelectric Facilities
- Cerron Grande Reservoir (Embalse Cerrón Grande): 135 sq km (52.1 sq mi) - Lempa River, largest artificial water body, 172 MW capacity
- Embalse Quince de Septiembre (San Lorenzo): 35 sq km (13.5 sq mi) - Lempa River, 180 MW capacity
- Embalse Presa Cinco de Noviembre: 20 sq km (7.7 sq mi) - Lempa River, 81.4 MW capacity
- Embalse del Guajoyo: 8.2 sq km (3.2 sq mi) - Northwestern region, Rio Desagüe, 15 MW capacity
- El Chaparral Reservoir: Small irrigation reservoir, central region
- Atiocoyo Reservoir: Agricultural water storage, western region
River Basins and Watersheds
El Salvador contains 58 river basins organized into major watershed systems:
- Lempa River Basin: 10,255 sq km (3,958 sq mi) total, 57% within El Salvador
- Paz River Basin: 2,328 sq km (899 sq mi), shared with Guatemala
- Río Grande de San Miguel Basin: 2,072 sq km (800 sq mi), eastern region
- Goascorán River Basin: 1,396 sq km (539 sq mi), shared with Honduras
- Jiboa River Basin: 1,590 sq km (614 sq mi), central coastal drainage
- Sensunapan River Basin: 1,223 sq km (472 sq mi), western coastal drainage
- Sirama River Basin: 694 sq km (268 sq mi), eastern coastal drainage
Coastal and Marine Waters
- Gulf of Fonseca: 1,161 sq km (448 sq mi) total area, shared with Honduras and Nicaragua, maximum depth 60 m (197 ft)
- Pacific Ocean: 307 km (191 mi) of coastline along El Salvador's southern border
- Estero de Jaltepeque: Coastal estuary and mangrove system, central coast
- Bahía de Jiquilisco: Protected bay area, UNESCO Biosphere Reserve
- Isla Meanguera: Largest island in the Gulf of Fonseca, 15.5 sq km (6.0 sq mi)
- Isla Conchagüita: Volcanic island in the Gulf of Fonseca, 5.8 sq km (2.2 sq mi)
- Isla Martín Pérez: Small island in Gulf of Fonseca
Springs and Thermal Waters
- Termas de Santa Teresa: Natural hot springs, western region
- Aguas Termales de Ahuachapán: Geothermal springs, western region
- Los Chorros: Natural spring pools, central highlands
- El Boquerón Springs: Volcanic crater springs
- Tamanique Springs: Coastal springs and waterfalls
Wetlands and Protected Aquatic Areas
- Barra de Santiago: Coastal wetland complex, western region
- Complejo Los Cóbanos: Marine protected area with coral reefs
- Laguna El Jocotal: Ramsar Convention wetland site
- Complejo Jaltepeque: Mangrove and estuary system
- El Imposible National Park: Contains numerous streams and seasonal pools





