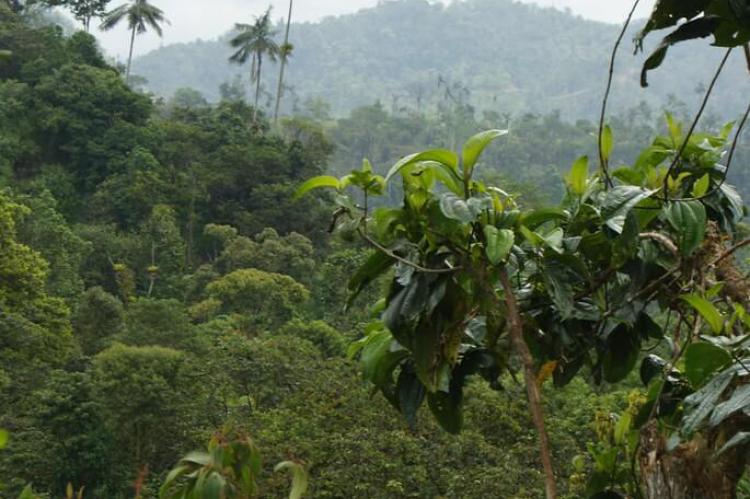
The Lush and Biodiverse Western Ecuador Moist Forests
Nestled along the western slopes of the Andes Mountains in Ecuador lies a captivating ecoregion known as the Western Ecuador Moist Forests. This expansive, verdant landscape stretches from the Colombian border in the north to the Guayas River basin in the south.
An Overview of the Western Ecuador Moist Forests
Nestled along the western slopes of the Andes Mountains in Ecuador lies a captivating ecoregion known as the Western Ecuador Moist Forests. This expansive, verdant landscape stretches from the Colombian border in the north to the Guayas River basin in the south, covering an area of approximately 35,000 square kilometers.
The Western Ecuador Moist Forests are part of the Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena biodiversity hotspot, one of Earth's most species-rich yet threatened regions. Characterized by a tropical, humid climate and diverse elevations, this ecoregion is home to an astonishing array of plant and animal life, much of which is found nowhere else on the planet.
Diverse Ecosystems and Habitats
The Western Ecuador Moist Forests encompass a variety of distinct ecosystems, each with its unique characteristics and inhabitants. This ecoregion boasts a remarkable diversity of habitats, from the lush, towering lowland rainforests to the misty, cloud-shrouded montane forests.
In the lowland regions, forests are dominated by towering trees, such as the majestic ceibas and tropical hardwoods. These trees provide a dense canopy that filters the sunlight and creates a cool, humid environment. These lowland forests are home to a vast array of lianas, epiphytes, and understory plants, all contributing to the ecoregion's stunning biodiversity.
As the elevation increases, the forests transition into the montane ecosystems, where the trees become shorter and more gnarled, their branches draped with various mosses, ferns, and bromeliads. These cloud forests are shrouded in a near-constant mist, creating a mystical and enchanting atmosphere home to a unique assemblage of species adapted to the cooler, wetter conditions.
Remarkable Biodiversity
The Western Ecuador Moist Forests are renowned for their exceptionally high levels of biodiversity, with many species found nowhere else on Earth. This ecoregion is a genuine hotspot of endemism, hosting a vast array of plants, animals, and fungi that have evolved in isolation within its boundaries.
Among the most notable residents of the Western Ecuador Moist Forests are the numerous species of birds, with over 700 species recorded—nearly half the total number found in all of Ecuador. Many of these birds, such as the stunning Ecuadorian Trogon and the elusive Plate-billed Mountain Toucan, are endemic to this region and play crucial roles in the ecosystem's intricate web of life.
The forests are also home to various mammals, including the charismatic Andean Spectacled Bear, the endangered Ecuadorian White-fronted Capuchin, and the secretive Puma. Additionally, the ecoregion boasts a remarkable diversity of amphibians, reptiles, and invertebrates, many of which remain poorly studied and undescribed by science.
Threats and Conservation Efforts
Despite the remarkable biodiversity of the Western Ecuador Moist Forests, this ecoregion faces a range of threats that jeopardize its long-term survival. Deforestation, driven by agricultural expansion, logging, and infrastructure development, has already claimed a significant portion of the original forest cover.
Additionally, the effects of climate change, including increased temperatures and altered precipitation patterns, pose a growing threat to the delicate balance of the forest ecosystems. As the climate shifts, many species may be unable to adapt, leading to potential declines or even extinctions.
Various conservation efforts have been undertaken to protect the Western Ecuador Moist Forests in response to these threats. These include establishing national parks and protected areas, such as Cotacachi-Cayapas Ecological Reserve and Mache-Chindul Ecological Reserve, and initiatives to promote sustainable forestry practices and ecotourism.
The Importance of the Western Ecuador Moist Forests
The Western Ecuador Moist Forests are a remarkable natural wonder and a vital component of the broader Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena biodiversity hotspot. These lush, diverse forests play a crucial role in regulating the region's climate, providing essential ecosystem services, and supporting the livelihoods of local communities.
Moreover, the Western Ecuador Moist Forests represent a living laboratory for scientific exploration and discovery, with countless species yet to be documented and studied. Preserving and protecting this ecoregion is an ecological imperative and a moral obligation, ensuring that the rich tapestry of life within it can be appreciated and safeguarded for generations to come.
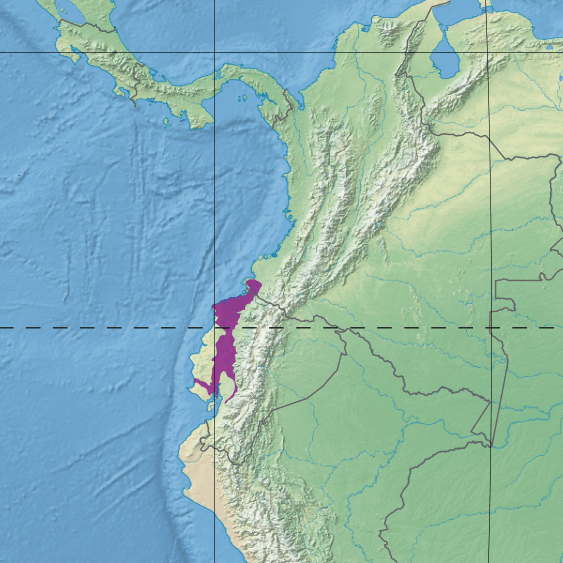
Map depicting the location of the Western Ecuador moist forests ecoregion (in purple).
