The Humboldt Current: A Lifeline in the Eastern South Pacific
The Humboldt Current, or Peru Current, is one of the world's most important ocean currents and a significant marine phenomenon in the eastern South Pacific. It is a distinct marine environment characterized by its cold, nutrient-rich waters and the unique ecological communities that thrive within it.
The Peru Current: Engine of Marine Productivity in the Eastern Pacific
The Humboldt Current, also known as the Peru Current, stands as one of Earth's most significant oceanic systems and a cornerstone of marine productivity in the eastern South Pacific. This remarkable cold-water current creates a distinct marine environment characterized by nutrient-rich waters and extraordinary biodiversity that supports some of the world's most productive fishing grounds.
Named after the pioneering German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt, who conducted extensive research in South America during the early 19th century, this oceanic giant flows northward from Antarctic waters along the western coast of South America. The current's influence extends far beyond marine ecosystems, profoundly shaping regional climate patterns, supporting millions of seabirds, and sustaining fishing industries that feed much of the world. Its cold, nutrient-laden waters drive one of nature's most efficient biological engines, transforming what might otherwise be oceanic deserts into some of the planet's most productive marine habitats.
Geographic Scope and Physical Characteristics
The Humboldt Current flows northward along South America's western coastline, extending approximately 4,000 kilometers (2,485 miles) from the southern tip of Chile to northern Peru and occasionally reaching as far as Ecuador. As an integral component of the South Pacific Gyre, this current system profoundly influences oceanic circulation patterns across the broader South Pacific Ocean.
Originating in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, the Humboldt Current carries frigid waters northward, maintaining temperatures between 14°C and 18°C (57°F to 64°F) along the Chilean coast and gradually warming to 18°C to 24°C (64°F to 75°F) as it reaches Peruvian waters. The current extends 500 to 1,000 kilometers (310 to 620 miles) offshore, creating a massive ribbon of cold water that contrasts sharply with the warmer tropical waters to the west.
The current's strength varies seasonally and with latitude, typically flowing at velocities of 0.1 to 0.4 meters per second (0.2 to 0.9 mph). Its volume transport reaches approximately 20 Sverdrups (20 million cubic meters per second) at its maximum strength, making it comparable to major ocean currents like the Gulf Stream.
The Upwelling Phenomenon
The Humboldt Current's most defining characteristic is its ability to drive intense coastal upwelling, one of nature's most efficient nutrient delivery systems. Trade winds and the Earth's rotation combine through the Coriolis effect to push surface waters westward away from the coast, creating a void filled by deep, nutrient-laden waters rising from depths of 100 to 300 meters (330 to 980 feet).
This upwelling process operates through a complex mechanism involving wind stress, Ekman transport, and bathymetric influences. The persistent southeasterly trade winds create surface stress that, combined with the Coriolis effect, generates offshore Ekman transport in the surface layer. As surface waters move away from the coast, deeper waters rich in dissolved nutrients rise to replace them, creating a continuous conveyor belt of nutrient supply.
The upwelling process brings essential nutrients—particularly nitrates, phosphates, and silicates—to the sunlit surface waters. The concentration of these nutrients can be 10 to 50 times higher than in typical tropical surface waters, creating ideal conditions for explosive phytoplankton growth. Nitrate concentrations can reach 20-30 micromoles per liter in freshly upwelled waters, compared to less than one micromole per liter in oligotrophic tropical waters. Primary productivity in upwelling zones can reach 1,000 to 3,000 grams of carbon per square meter per year, compared to just 50 to 150 grams in typical open ocean environments.
Upwelling intensity varies seasonally and with latitude, being strongest during austral winter and spring months when trade winds intensify. The process is most pronounced between 15°S and 40°S latitude, where coastal geometry and wind patterns create optimal conditions for sustained upwelling throughout much of the year.
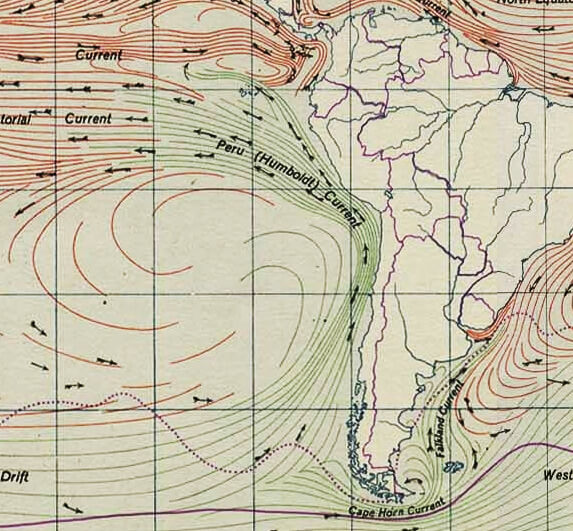
Map depicting the Humboldt / Peru Current.
Marine Biodiversity and Food Web
The nutrient-rich waters of the Humboldt Current support an intricate marine ecosystem of extraordinary productivity and remarkable biodiversity patterns. At the foundation lies a diverse phytoplankton community dominated by diatoms such as Skeletonema costatum and Chaetoceros species, which form the base of one of the world's most efficient food webs. These microscopic algae can form dense blooms visible from space, creating patches of greenish water that extend for hundreds of kilometers along the coast.
The system exhibits classic "bottom-up" control, where primary productivity drives abundance patterns throughout the food web. During peak upwelling periods, phytoplankton concentrations can exceed 100 million cells per liter, creating a rich foundation that supports massive populations of higher trophic levels. This productivity occurs in distinct zones, with the most intense biological activity concentrated within 200 kilometers (125 miles) of the coastline.
Primary Consumers
The abundant phytoplankton supports massive populations of zooplankton, particularly copepods like Calanus chilensis and euphausid krill species, including Euphausia mucronata. These small crustaceans can reach densities of thousands of individuals per cubic meter during peak seasons, forming dense swarms that can extend over thousands of square kilometers. The copepod Calanus chilensis alone can comprise up to 90% of zooplankton biomass in some areas, serving as a critical link between primary producers and fish populations.
Krill species play an especially important role, with Euphausia mucronata forming massive swarms that support numerous predator species. These krill can live for up to two years and reach lengths of 20 millimeters (0.8 inches), making them substantial prey items for fish, seabirds, and marine mammals. During peak abundance periods, krill swarms can contain billions of individuals and represent a biomass comparable to that of fish populations.
Fish Communities
The current supports some of the world's largest fish populations, most notably the Peruvian anchovy (Engraulis ringens), which often comprises the planet's largest single-species fishery by volume. During favorable conditions, anchovy populations can exceed 10 million metric tons, with individual schools sometimes extending for dozens of kilometers and containing millions of fish. These small fish, typically 8-14 centimeters (3-5.5 inches) in length, have short lifespans of 2-3 years but reproduce rapidly, allowing populations to respond quickly to environmental changes.
Other important species include the Chilean jack mackerel (Trachurus murphyi), which forms the basis of major fisheries in both Chile and Peru, Pacific sardine (Sardinops sagax), Chilean hake (Merluccius gayi), and jumbo flying squid (Dosidicus gigas). The jumbo squid, in particular, represents one of the most remarkable success stories in the system, with populations that can fluctuate from near absence to dominance within just a few years. These cephalopods can reach lengths of 2 meters (6.6 feet) and weights exceeding 50 kilograms (110 pounds), making them both important predators and valuable commercial species.
The system also supports populations of larger predatory fish, including yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares), skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis), and various billfish species that migrate through the region seasonally. These species benefit from the high prey density but are more vulnerable to environmental fluctuations than the smaller, more abundant forage fish species.
Seabirds
The Humboldt Current ecosystem supports approximately 20 million seabirds, making it one of the world's most important seabird habitats. Key species include the Peruvian pelican (Pelecanus thagus), Peruvian booby (Sula variegata), Guanay cormorant (Leucocarbo bougainvillii), and Humboldt penguin (Spheniscus humboldti). These birds have evolved specialized feeding strategies to exploit the system's abundant fish populations, with different species targeting different prey sizes and depths.
The Guanay cormorant, weighing 1.5-2.2 kilograms (3.3-4.9 pounds), can dive to depths of 25 meters (82 feet) and consume up to 1 kilogram (2.2 pounds) of anchovies daily during peak feeding periods. Peruvian boobies, slightly larger at 1.5-2.5 kilograms (3.3-5.5 pounds), are specialized plunge-divers that can accurately target individual fish from heights of 10-20 meters (33-66 feet) above the surface.
These birds historically produced vast quantities of guano, which served as a crucial source of fertilizer and an economic driver for Peru in the 19th century. At peak production periods, Peru's guano islands supported over 60 million seabirds and produced more than 200,000 metric tons of guano annually. This natural fertilizer was so valuable that it sparked international conflicts and provided Peru with its primary source of government revenue for several decades.
The Humboldt penguin, endemic to the region, represents one of the most specialized adaptations to the upwelling ecosystem. These penguins, standing 56-70 centimeters (22-28 inches) tall, can dive to depths of 150 meters (490 feet) and hold their breath for up to 2.5 minutes while hunting for anchovies and sardines. Their current population of approximately 32,000 individuals faces significant conservation challenges from climate change and human activities.
Marine Mammals
The system supports diverse marine mammal populations, including the South American sea lion (Otaria flavescens), South American fur seal (Arctocephalus australis), dusky dolphin (Lagenorhynchus obscurus), and several whale species during migration periods.
Climate Influence
The Humboldt Current has a profound impact on regional climate patterns along South America's western coast. Its cold waters suppress evaporation and create a stable atmospheric inversion layer that prevents precipitation, directly contributing to the formation of the Atacama Desert in northern Chile—Earth's driest non-polar desert—and Peru's Sechura Desert.
The current generates persistent coastal fog known locally as "garúa," which provides crucial moisture for coastal ecosystems and human settlements. This fog can extend 50 to 100 kilometers (31 to 62 miles) inland and provides the primary water source for many unique plant communities adapted to these conditions.
El Niño-Southern Oscillation Connection
The Humboldt Current plays a pivotal role in the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, which has a significant impact on global weather patterns. During normal conditions, strong upwelling maintains the current's characteristic cold temperatures. However, during El Niño events, weakened trade winds reduce upwelling, allowing warm water to spread eastward and dramatically alter the entire ecosystem. El Niño events typically occur every 2 to 7 years and can cause water temperature increases of 4°C to 8°C (7°F to 14°F), collapse of fish populations, particularly anchovies, mass seabird mortality and breeding failure, increased rainfall along normally arid coasts, and disruption of global weather patterns.
Economic Significance
The Humboldt Current supports one of the world's most valuable fishing industries, generating billions of dollars annually and providing direct employment for over 200,000 people across Peru and Chile. Peru and Chile together account for approximately 15-20% of global marine fish catches, with the Peruvian anchovy fishery alone sometimes exceeding 8 million metric tons annually—more than any other single-species fishery worldwide.
The economic impact extends far beyond direct fishing activities. Fish meal production, primarily derived from anchovies, represents a multi-billion-dollar industry that is crucial for global aquaculture and livestock feed. Peru produces approximately 1-1.5 million metric tons of fish meal annually, supplying roughly 28% of global demand. This protein-rich product commands premium prices in international markets, particularly in Asia, where the expansion of aquaculture drives continued demand growth.
The fishing industry supports extensive supply chains, including vessel construction and maintenance, processing facilities, cold storage, transportation networks, and export operations. Major Peruvian ports, such as Chimbote, Paita, and Callao, have developed into significant industrial centers, primarily based on fishing-related activities. Similarly, Chilean ports such as Valparaíso, Antofagasta, and Arica serve as major fish processing and export hubs.
Beyond industrial fishing, the system supports important artisanal fisheries that provide food security and livelihoods for coastal communities throughout the region. These smaller-scale operations target diverse species, including various coastal fish, shellfish, and algae, contributing to local food systems and cultural traditions that have persisted for thousands of years. Archaeological evidence suggests that coastal peoples have exploited resources of the Humboldt Current for at least 14,000 years, developing a sophisticated understanding of seasonal patterns and sustainable harvest practices.
Environmental Challenges and Conservation
The Humboldt Current system faces increasing pressures from multiple sources:
Climate Change
Rising global temperatures threaten to alter upwelling patterns and ocean chemistry. Projections suggest potential changes in wind patterns could reduce upwelling intensity by 10-20% by 2100, with cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
Overfishing
Heavy fishing pressure has led to population collapses of several key species. The Peruvian anchovy population has experienced dramatic booms and busts, with catches varying from nearly zero to over 10 million metric tons depending on environmental conditions and fishing pressure.
Ocean Acidification
Increased atmospheric CO₂ absorption is lowering ocean pH, particularly affecting shell-forming organisms like pteropods and juvenile shellfish that form crucial food web components. The Humboldt Current region experiences some of the most severe acidification conditions globally, with pH levels already 0.3-0.4 units lower than pre-industrial values in some areas. This acidification is compounded by the upwelling of naturally acidic deep waters, creating conditions that challenge calcifying organisms throughout the food web.
Studies indicate that pteropod shells are already showing signs of dissolution in the most acidic waters, potentially disrupting food webs that depend on these small but abundant organisms. Mussel and oyster populations along the coast face similar challenges, with implications for both ecosystem function and aquaculture operations.
Pollution
Coastal development, mining activities, and agricultural runoff introduce contaminants that can bioaccumulate through the food chain, affecting everything from plankton to marine mammals. Heavy metals from mining operations, particularly copper from Chile's extensive mining industry, have been detected throughout the marine food web. Plastic pollution represents an emerging threat, with microplastics now found in fish, seabirds, and marine mammals throughout the system.
Agricultural runoff containing pesticides and fertilizers can create localized eutrophication events that disrupt natural nutrient cycles and promote harmful algal blooms. Urban sewage and industrial discharge from major coastal cities add additional pollutant loads, particularly in areas near Lima, Santiago, and other major population centers.
Several countries have established marine protected areas within the Humboldt Current system, including Chile's Humboldt Penguin National Reserve, Peru's Paracas National Reserve, and various smaller protected areas along the coast.
Research and Monitoring
Scientific understanding of the Humboldt Current continues to evolve through international research collaborations. Advanced satellite monitoring, autonomous underwater vehicles, and sophisticated modeling systems now provide unprecedented insights into current dynamics and ecosystem changes. Key research focuses include long-term climate variability and its impacts on ecosystems, fish population dynamics and sustainable harvest levels, changes in ocean chemistry and their biological effects, and the application of ecosystem-based management approaches.
Conclusion
The Humboldt Current represents far more than a simple oceanic flow—it is a complex, dynamic system that sustains extraordinary marine productivity and influences regional and global climate patterns. From its Antarctic origins to its profound impacts on South American coastal ecosystems and economies, this current continues to demonstrate the intricate connections between physical oceanography, marine biology, and human societies.
As environmental pressures intensify, understanding and protecting the Humboldt Current system becomes increasingly crucial. Its continued health depends on coordinated international efforts to address climate change, implement sustainable fishing practices, and protect critical habitats. The current's remarkable productivity and biodiversity make it not only a regional treasure but a global asset worthy of our most dedicated conservation efforts.
The Humboldt Current stands as a testament to nature's interconnectedness and productivity, reminding us that the health of our oceans directly impacts the well-being of countless species—including our own. As we face an uncertain environmental future, this cold-water giant serves as both an inspiration and a responsibility, challenging us to become better stewards of Earth's marine ecosystems.
