Uruguay's Diverse Aquatic Landscape: From Estuary to Highland Stream
Uruguay, South America's second-smallest nation, boasts a diverse network of water bodies that shape its geography, economy, and culture. Located between Brazil and Argentina, it benefits from its strategic position where the Uruguay and Paraná rivers merge to form the Río de la Plata estuary.
Rivers, Lakes, and Coastlines: Uruguay's Aquatic Tapestry
Uruguay, South America's second-smallest nation, possesses a remarkably diverse and extensive network of water bodies that fundamentally shape its geography, economy, and cultural identity. Despite covering only 176,215 square kilometers (68,037 square miles), the country boasts an impressive hydrographic system that includes major rivers, artificial reservoirs, coastal lagoons, and 660 kilometers (410 miles) of Atlantic Ocean coastline. Nestled between Brazil and Argentina, Uruguay benefits from its strategic position at the convergence of major river systems, most notably where the Uruguay and Paraná rivers merge to form the vast Río de la Plata estuary. The nation's water resources extend beyond surface features to encompass significant groundwater reserves, including portions of the massive Guarani Aquifer System. These aquatic resources serve as vital arteries for agriculture, energy production, transportation, and recreation, while also defining much of Uruguay's natural beauty and ecological richness.
The Río de la Plata: Uruguay's Liquid Highway
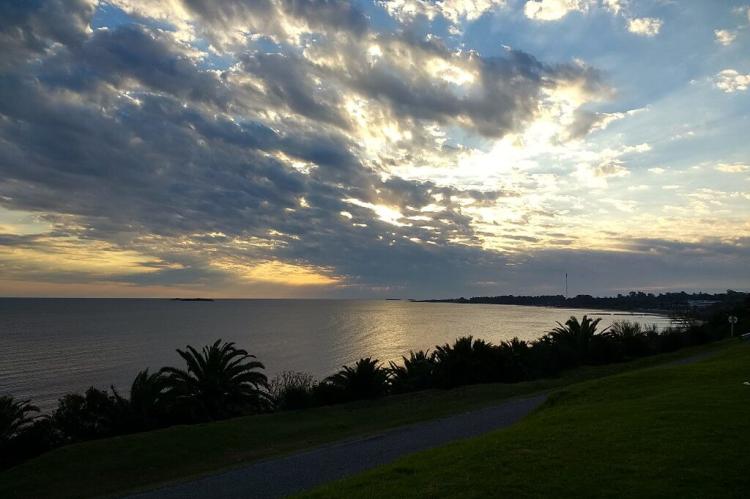
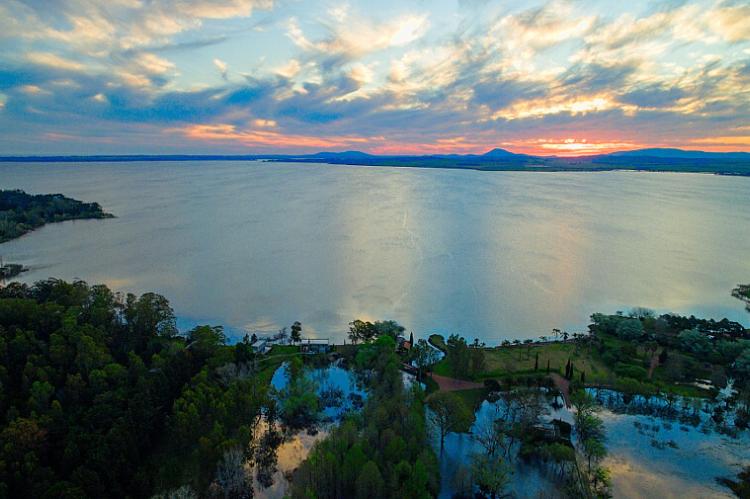
The defining feature of Uruguay's hydrography is the Río de la Plata, a massive estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay and Paraná rivers. Stretching approximately 290 kilometers (180 miles) in length and reaching widths of up to 220 kilometers (137 miles), the Río de la Plata serves as Uruguay's southern border with Argentina. Despite its name suggesting a river, the Río de la Plata functions more as a freshwater sea, carrying sediments from the interior of South America to the Atlantic Ocean.
The estuary's brackish waters create unique ecological conditions that support diverse marine life, including corvina, sole, and various species of rays. The Port of Montevideo, situated on the northern shore of the estuary, has historically served as one of South America's most important harbors, facilitating international trade and establishing Uruguay as a maritime gateway to the continent's interior.
The Uruguay River: A Natural Border
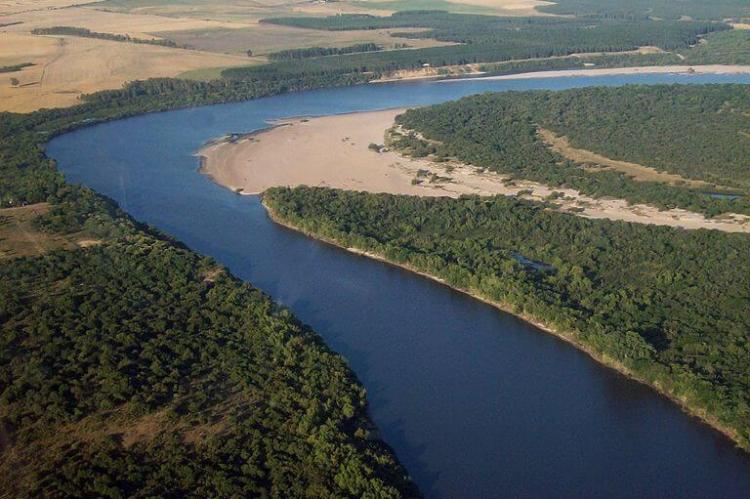
The Uruguay River forms the country's western boundary with Argentina, flowing northward from its source in Brazil's Serra Geral mountains. Along its 1,838-kilometer (1,142-mile) total length, approximately 500 kilometers (311 miles) border Uruguay. The river's flow varies significantly throughout the year, with peak discharge occurring during winter months when regional precipitation increases.
Several major tributaries feed the Uruguay River within national borders, including the Río Negro, Río Yí, and Río Tacuarembó. These waterways create fertile alluvial plains that support extensive cattle ranching and agricultural activities, particularly rice cultivation in the river's lower reaches. The Uruguay River also serves as a crucial transportation route, with commercial vessels navigating its waters to transport goods between inland regions and oceanic ports.
The Río Negro: Uruguay's Central Artery
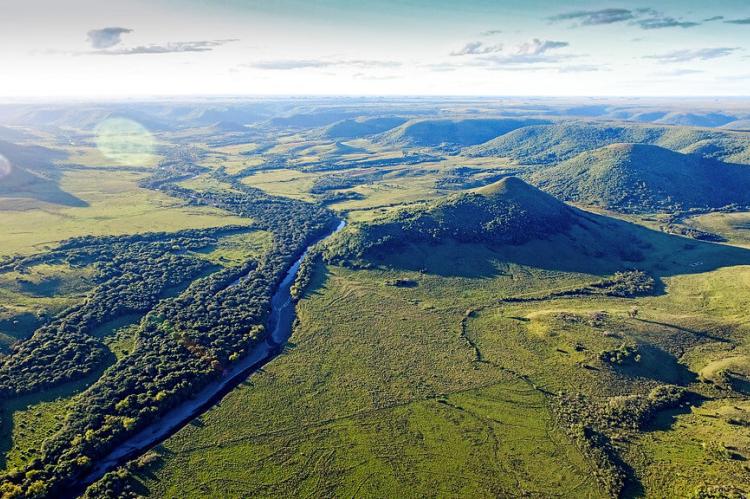
The Río Negro represents Uruguay's most significant internal waterway, stretching 750 kilometers (466 miles) from its source in the southern highlands of Brazil to its confluence with the Uruguay River. Rising just east of Bagé in Brazil, the river flows westward across the entire width of Uruguay. The river bisects the country diagonally, creating distinct northern and southern regions while serving as a vital water source for both urban and rural populations.
The Río Negro's significance extends beyond transportation and irrigation. Three major hydroelectric dams along its course—Rincón del Bonete, Baygorria, and Palmar—generate approximately 60% of Uruguay's electricity. These installations created extensive artificial lakes that have transformed local ecosystems and established new recreational opportunities for residents and tourists alike.
Coastal Lagoons: Ecological Treasures
Uruguay's Atlantic coastline features numerous coastal lagoons that serve as critical habitats for migratory birds and endemic species. Laguna de Rocha, located in Rocha department, represents one of the most ecologically significant wetlands in the region. Covering approximately 72 square kilometers (28 square miles), the lagoon alternates between freshwater and saltwater conditions depending on seasonal connections to the ocean.
Laguna Merín, shared with Brazil and covering 3,750 square kilometers (1,448 square miles) in total, represents South America's second-largest natural lagoon. The Uruguayan portion encompasses roughly 40% of the lagoon's surface area, supporting important fishing communities and serving as a habitat for over 200 bird species. These coastal wetlands play crucial roles in flood control, water purification, and carbon sequestration while providing essential breeding grounds for numerous aquatic species.
Artificial Reservoirs: Engineering Water Management
Uruguay's approach to water management includes several significant artificial reservoirs created through dam construction. The Embalse del Río Negro, formed by the Rincón del Bonete dam, covers 1,070 square kilometers (413 square miles) and represents one of South America's largest artificial lakes. These reservoirs serve multiple purposes: hydroelectric generation, flood control, irrigation support, and recreational activities.
The Paso Severino reservoir, located near Montevideo, provides drinking water for approximately 60% of Uruguay's population. Completed in 2018, the facility processes water from the Santa Lucía River system, demonstrating the country's commitment to ensuring reliable freshwater supplies for its urban centers.
Groundwater Resources: The Hidden Treasure
Beneath Uruguay's surface lies one of the world's most significant groundwater resources: the Guarani Aquifer System. This massive underground water reservoir spans approximately 1.2 million square kilometers (463,000 square miles) across Uruguay, Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay. Within Uruguay, the aquifer underlies approximately 58,500 square kilometers (22,587 square miles), accounting for roughly one-third of the country's total territory.
The Guarani Aquifer consists of interconnected sandstone formations that store an estimated 37,000 cubic kilometers (8,900 cubic miles) of freshwater. In Uruguay, the aquifer reaches depths of 50 to 1,800 meters (164 to 5,906 feet) below ground level, with water quality generally excellent and requiring minimal treatment for human consumption. The aquifer's strategic importance cannot be overstated, as it provides a reliable backup water source during drought periods and supports agricultural irrigation in regions where surface water is scarce.
Beyond the Guarani Aquifer, Uruguay possesses numerous smaller groundwater systems associated with sedimentary formations and fractured crystalline rocks. These local aquifers supply rural communities, support livestock operations, and provide water for small-scale irrigation projects throughout the country. The Mercedes Aquifer in southwestern Uruguay and the Chuy Aquifer near the Brazilian border represent important regional groundwater resources that complement the larger Guarani system.
Groundwater Systems
- Guarani Aquifer System - 58,500 km² (22,587 sq mi) in Uruguay; Depths 50-1,800 m (164-5,906 ft)
- Mercedes Aquifer - 3,200 km² (1,236 sq mi); Southwestern Uruguay, Soriano department
- Chuy Aquifer - 1,800 km² (695 sq mi); Eastern Uruguay, near the Brazilian border
- Raigón Aquifer - 2,500 km² (965 sq mi); Southern Uruguay, San José department and River Mouths
Beyond the massive Río de la Plata, Uruguay features several smaller but ecologically important estuaries where rivers meet the Atlantic Ocean. The Santa Lucía River estuary, located west of Montevideo, creates brackish water conditions that support unique plant and animal communities. Similarly, the Solís Grande River forms a small estuary that serves as a nursery habitat for various fish species.
These estuarine environments function as transition zones between freshwater and marine ecosystems, creating highly productive habitats that support both resident species and serve as stopover points for migratory birds. The mixing of nutrient-rich freshwater with saltwater creates ideal conditions for phytoplankton growth, forming the base of complex food webs that extend throughout the coastal marine environment.
Marine Environment and Coastal Waters
Uruguay's 660-kilometer (410-mile) Atlantic coastline encompasses diverse marine environments, from sandy beaches to rocky outcrops. The continental shelf extends relatively far offshore, creating productive fishing grounds that support both artisanal and industrial fisheries. Important commercial species include hake, anchovy, and various crustaceans that thrive in the nutrient-rich waters where the Río de la Plata meets the Atlantic Ocean.
Coastal upwelling phenomena bring deep, cold, nutrient-rich waters to the surface, supporting robust marine ecosystems. These conditions attract seasonal migrations of southern right whales, which use Uruguay's coastal waters as breeding and nursing grounds between June and November.
Ecological Significance and Conservation
Uruguay's water bodies support remarkable biodiversity despite the country's small size. Wetland ecosystems provide habitat for over 400 bird species, including flamingos, black-necked swans, and numerous shorebirds. The Bañados del Este, a complex of wetlands in eastern Uruguay, has been designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, recognizing its global ecological importance.
Freshwater fish populations include native species such as surubí, dorado, and various catfish species. Conservation efforts focus on maintaining water quality, protecting riparian vegetation, and managing human activities to minimize environmental impacts. Climate change poses emerging challenges, with altered precipitation patterns and increased frequency of extreme weather events affecting water availability and quality.
Economic and Cultural Importance
Water resources underpin Uruguay's economy through multiple sectors. Agriculture depends heavily on irrigation systems fed by rivers and reservoirs, particularly for rice production in the eastern regions. The country's significant hydroelectric capacity reduces dependence on fossil fuels while providing clean energy for industrial development.
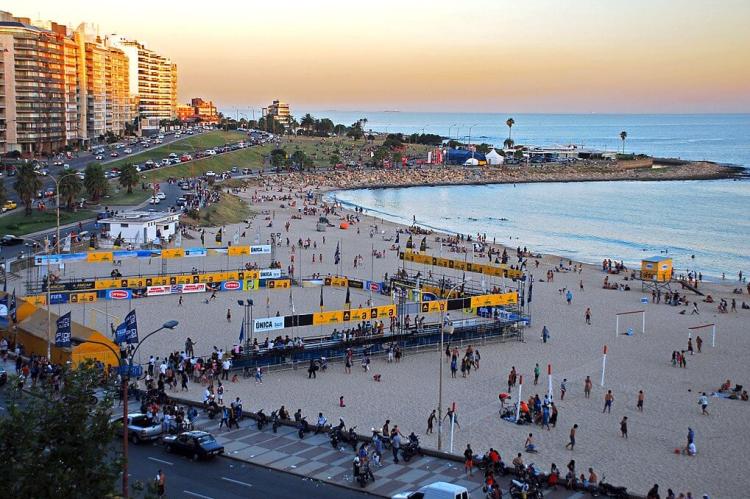
Tourism benefits substantially from Uruguay's aquatic attractions. Beach resorts along the Atlantic coast attract millions of visitors annually, while inland waterways provide opportunities for fishing, boating, and ecotourism. The cultural significance of water extends to traditional practices such as mate consumption, which requires high-quality water, and various festivals celebrating maritime heritage.
Summary
Uruguay's water bodies form an intricate network that defines the nation's physical geography, ecological character, and economic foundation. From the expansive Río de la Plata estuary to the highland streams near the Brazilian border, these aquatic systems provide essential services including freshwater supply, energy generation, transportation, and habitat for diverse wildlife. The country's coastal lagoons and Atlantic shoreline add further complexity to this hydrographic tapestry, creating unique ecosystems that support both resident and migratory species. Through careful management and conservation efforts, Uruguay continues to balance human needs with environmental protection, ensuring that these vital water resources remain sustainable for future generations. The integration of natural waterways with engineered infrastructure demonstrates how thoughtful planning can maximize the benefits of aquatic resources while maintaining ecological integrity.
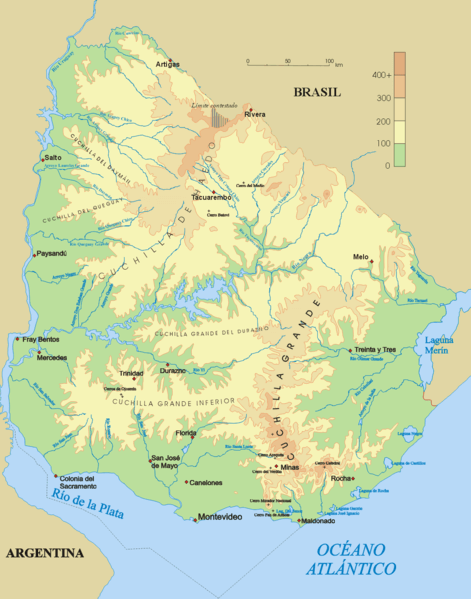
Topographical map of Uruguay.
Notable Water Bodies of Uruguay
Rivers
- Río de la Plata - 290 km (180 miles) length, up to 220 km (137 miles) width; Southern border with Argentina
- Uruguay River - 500 km (311 miles) along Uruguay border; Western boundary with Argentina
- Río Negro - 750 km (466 miles) length; Central Uruguay, flows east to west
- Río Yí - 210 km (130 miles) length; Central Uruguay, tributary of Río Negro
- Río Tacuarembó - 230 km (143 miles) length; Northern Uruguay, tributary of Río Negro
- Río Olimar - 190 km (118 miles) length; Eastern Uruguay, flows to Laguna Merín
- Santa Lucía River - 230 km (143 miles) length; Southern Uruguay, flows to Río de la Plata
- Río Cuareim - 350 km (217 miles) total length; Northern border with Brazil
- Río Arapey - 150 km (93 miles) length; Northwestern Uruguay
- Río Queguay - 220 km (137 miles) length; Northwestern Uruguay
Lakes and Lagoons
- Laguna Merín - 3,750 km² (1,448 sq mi) total, ~1,500 km² (579 sq mi) in Uruguay; Eastern border with Brazil
- Laguna de Rocha - 72 km² (28 sq mi); Rocha department, Atlantic coast
- Laguna de Castillos - 80 km² (31 sq mi); Rocha department, Atlantic coast
- Laguna Garzón - 15 km² (6 sq mi); Rocha department, Atlantic coast
- Laguna José Ignacio - 8 km² (3 sq mi); Maldonado department, Atlantic coast
- Laguna del Sauce - 50 km² (19 sq mi); Maldonado department, near Punta del Este
Artificial Reservoirs
- Embalse del Río Negro (Rincón del Bonete) - 1,070 km² (413 sq mi); Central Uruguay
- Embalse de Baygorria - 65 km² (25 sq mi); Río Negro, Durazno department
- Embalse de Palmar - 323 km² (125 sq mi); Río Negro, Soriano department
- Embalse de Salto Grande - 783 km² (302 sq mi) total; Shared with Argentina on Uruguay River
- Paso Severino Reservoir - 20 km² (8 sq mi); Santa Lucía River basin
Estuaries
- Río de la Plata Estuary - 290 km (180 miles) length, up to 220 km (137 miles) width; Southern border with Argentina
- Santa Lucía River Estuary - 15 km² (6 sq mi); West of Montevideo, Río de la Plata system
- Solís Grande River Estuary - 8 km² (3 sq mi); Canelones department, Atlantic coast
- Arroyo Pando Estuary - 5 km² (2 sq mi); Canelones department, Río de la Plata system
- Total Atlantic Coast - 660 km (410 miles); From Chuy to Colonia del Sacramento
- Río de la Plata Coastline - 425 km (264 miles); From Colonia to Montevideo to Punta del Este





