Maracaibo Lake and Basin: The Geologic and Economic Heart of Venezuela
Lake Maracaibo, situated in the Maracaibo Basin of northwestern Venezuela, is a large brackish tidal estuary and an inlet of the Caribbean Sea. With its rich petroleum reserves, dynamic weather phenomena, and significant economic contributions, it is central to Venezuela's geography and economy.
Lightning, Oil, and Water: The Maracaibo Lake and Basin
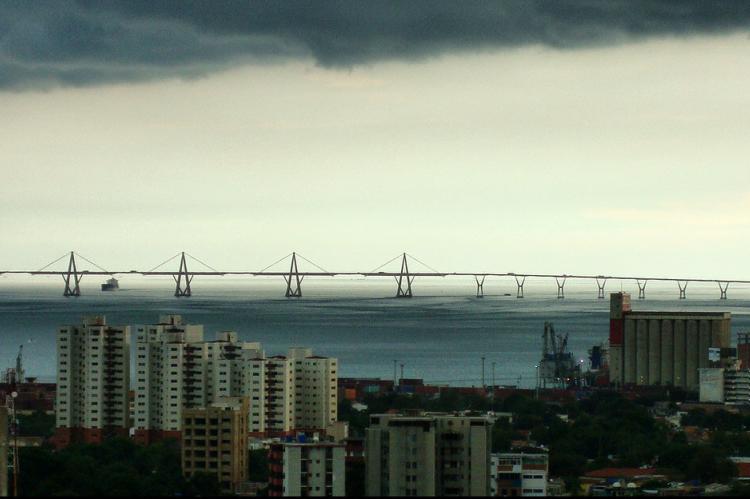
Lake Maracaibo, situated in the Maracaibo Basin of northwestern Venezuela, is a large brackish tidal estuary and an inlet of the Caribbean Sea. Connected to the Gulf of Venezuela by the Tablazo Strait, it is considered a bay or lagoon. Not only is it the largest lake in South America, but it is also one of the oldest on Earth. The lake is fed by numerous rivers, the largest being the Catatumbo. With its rich petroleum reserves, dynamic weather phenomena, and significant economic contributions, Lake Maracaibo and the Maracaibo Basin are central to Venezuela's geography and economy.
Lake Maracaibo: A Geographical Marvel
Lake Maracaibo is the largest lake in South America, covering approximately 13,210 square kilometers (5,100 square miles). Its waters are fresh in the southern portion but become brackish towards the north due to significant tidal influences. The lake is relatively shallow, with swampy lowlands surrounding its perimeter. These geographical features make it an essential resource for fishing and agriculture.
Economic Significance
The Maracaibo Basin is one of the world's richest and most centrally located petroleum-producing regions. The basin holds sizable crude oil reserves, contributing significantly to Venezuela's economy. The oil extracted from this region accounts for approximately 50% of Venezuela's crude export capacity and about 15% of the country's proven oil reserves, making Lake Maracaibo a significant profit center for Venezuela and a critical component of the global oil market.
The Catatumbo Lightning Phenomenon
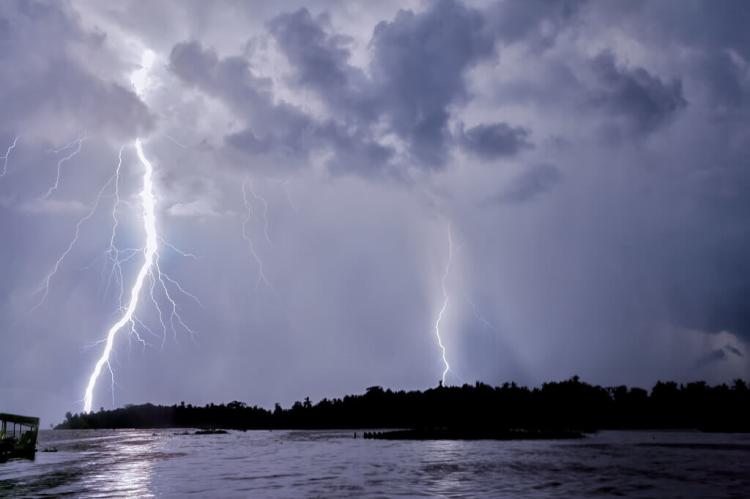
One of the most striking natural phenomena associated with Lake Maracaibo is the Catatumbo lightning. Occurring where the Catatumbo River meets the lake, this phenomenon features lightning that strikes, on average, twenty-eight times per minute for up to nine hours each day after dusk, around 300 days a year. With 250 lightning strikes per square kilometer annually, it is recognized by NASA as the "Lightning Hotspot" of the world. This spectacular display is most active in September and October and least active in January and February.
The Maracaibo Basin
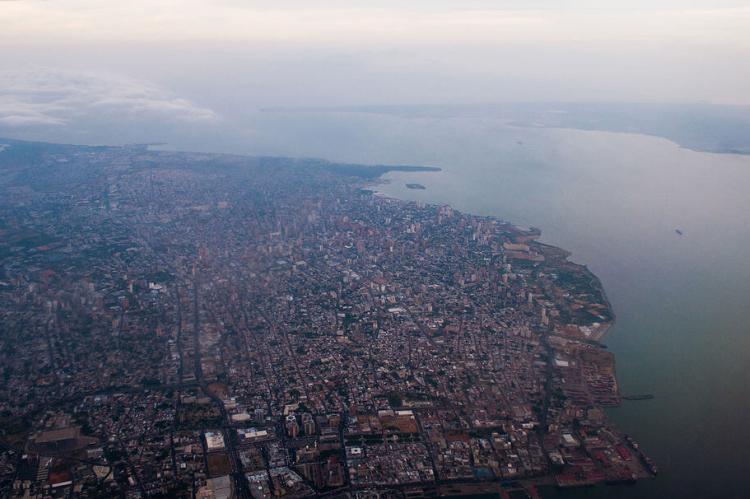
The Maracaibo Basin, also known as the Maracaibo Lowlands, covers over 36,000 square kilometers (14,000 square miles) in Venezuela's northwestern corner. This natural region is characterized by the large shallow tidal estuary of Lake Maracaibo near its center. The basin is surrounded by the two ranges of the Venezuelan Andes, the Cordillera de Mérida to the southeast and the Sierra de Perijá to the west, with the Gulf of Venezuela to the north. The Cordillera de Mérida's eastern branch extends from the Colombian border to the Venezuelan state of Lara, dividing the Maracaibo Basin from the Orinoco Basin.
Geological and Environmental Features
The Maracaibo Basin lies within a deformation region created by the Caribbean plate and South American plate boundary interactions. This geological activity has contributed to forming the basin's extensive oil reserves. The basin also features a variety of ecosystems, including mangroves, sawgrass marshes, and flooded and non-flooded forests. These habitats support diverse flora and fauna, making the region ecologically significant.
Human Impact and Conservation
Approximately a quarter of Venezuela's population resides in the Maracaibo Basin, where they engage in fishing, agriculture, and oil extraction activities. The construction of the road connecting Ciénaga and Barranquilla in the 1950s significantly impacted the region's hydrology, leading to extreme variations in the wetland ecosystem and the extinction of vast mangrove forests and swamps. However, efforts to restore local populations' hydrologic equilibrium and socio-economic conditions have been ongoing since 1994, involving local participation and scientific support to rehabilitate the mangrove ecosystems.
Conclusion
Lake Maracaibo and the Maracaibo Basin are geological marvels and vital economic and ecological regions in Venezuela. The lake's extensive oil reserves and the basin's rich biodiversity make them crucial to the country's economy and environmental health. Understanding and preserving these areas is essential for maintaining Venezuela's natural heritage and economic stability.
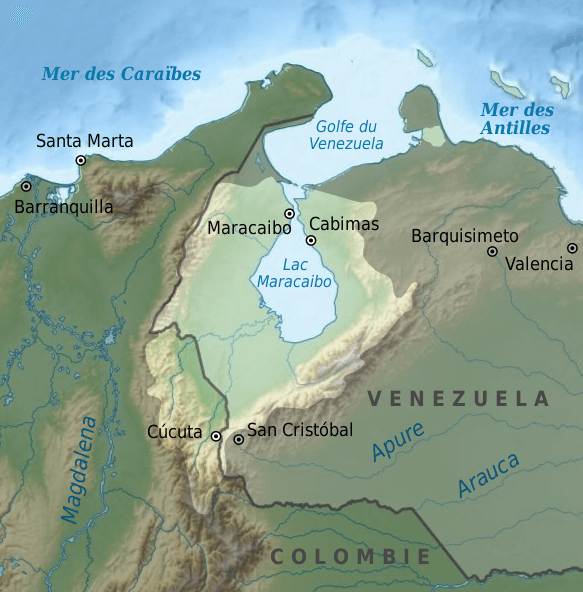
Map depicting the Lake Maracaibo watershed in northwestern Venezuela.





