The Altiplano–Puna Plateau and Basin: A High-Altitude Geological Wonderland in South America
The Altiplano–Puna plateau is a vast, high-altitude region in South America spanning Bolivia, Peru, Chile, and Argentina. It is the widest part of the Andes Mountains. The Altiplano Basin is a vast sedimentary basin between the Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Oriental mountain ranges.
The Altiplano–Puna Plateau: A Vast and Unique Landscape
The Altiplano–Puna plateau is a remarkable, expansive, high-altitude region in west-central South America, where the Andes Mountains reach their greatest width. Spanning across Bolivia, Peru, Chile, and Argentina, this vast expanse is often called the "Altiplano" and is the most extensive high plateau outside the Tibetan Plateau.
Situated at an average elevation of around 3,650 meters (12,000 feet) above sea level, the Altiplano is a series of intermontane basins bounded by the towering Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Oriental ranges of the Andes. To the southwest, the Altiplano is flanked by the Atacama Desert, one of the driest regions on Earth, while to the east, it is separated from the humid Amazon Rainforest by the Cordillera Oriental.
The northern part of the Altiplano is dominated by the iconic Lake Titicaca, a large, high-altitude freshwater lake shared by Peru and Bolivia. Further south, the landscape is characterized by salt flats, including the massive Salar de Uyuni, the world's largest salt flat. These salt flats and saline lakes are the remnants of ancient lakes that have dried up, leaving their mineral-rich deposits behind.
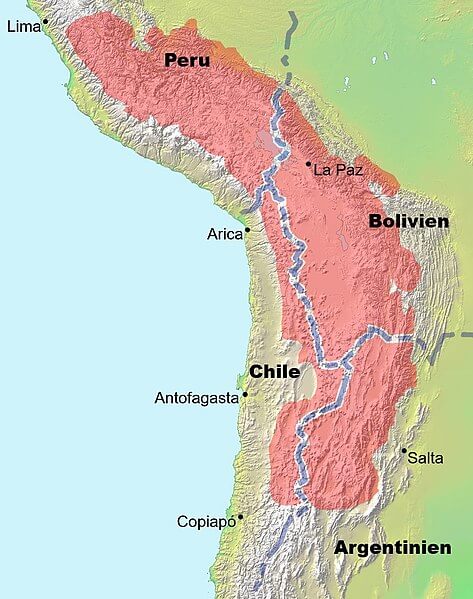
Map showing the location (in red) of the Altiplano Plateau in South America.
The Altiplano Basin: A Complex Sedimentary Feature
The Altiplano Basin, located between the Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Oriental mountain ranges, is a vast sedimentary basin that has evolved over geological time. Covering an area of approximately 154,176 square kilometers (59,528 square miles), it is a complex tectonic feature shaped by the horizontal shortening of the Earth's crust.
The Cordillera Occidental overrides the northern portion of the basin along the Pasani Fault, while the Cordillera Oriental has overridden the basin's northern edge along the Ayaviri Fault. Further south, the largely buried Coniri Fault defines the basin's boundary with the Cordillera Oriental block, characterized by the largely buried Coniri Fault.
The great thickness of sediments accumulated within the Altiplano Basin is primarily the result of the erosion of the Cordillera Oriental mountain range. This erosion has contributed to the basin's formation and evolution over time, and the basin's sedimentary deposits provide a valuable record of the region's geological history.
The Altiplano Basin's unique geological setting and the complex interplay between the Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Oriental have shaped the landscape and influenced the development of the region's diverse ecosystems and human settlements. Understanding the basin's complex tectonic history and sedimentary processes is crucial for understanding the broader Altiplano–Puna plateau and its significance within the Andes mountain range.
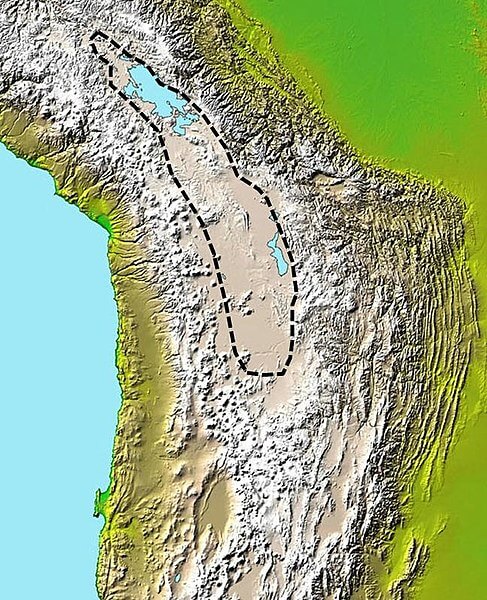
Map depicting the approximate extent of the sedimentary basin in the Altiplano.
Volcanic Activity and Tectonic Processes
The Altiplano–Puna plateau is a geologically active region shaped by the ongoing tectonic processes forming the Andes Mountains. The western edge of the plateau is dominated by the massive, active volcanoes of the Central Volcanic Zone, including Ampato, Tutupaca, Parinacota, Guallatiri, Paruma, Uturunku, and Licancabur.
The southern part of the Altiplano–Puna is particularly noteworthy for the Altiplano–Puna volcanic complex, a significant caldera and silicic ignimbrite volcanic field. This volcanic activity is a testament to the region's dynamic and ongoing geological processes, resulting in the uplift and deformation of the Altiplano–Puna plateau over time.
The complex tectonic history of the Altiplano–Puna is also reflected in the formation of the Altiplano Basin, a vast sedimentary basin located between the Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Oriental ranges. The basin has evolved through the horizontal shortening of the Earth's crust, with the adjacent mountain ranges overriding its northern and southern edges of the basin being overridden by the adjoining mountain ranges.
Human Settlement and Economic Activities
Despite the harsh, high-altitude environment, the Altiplano–Puna plateau has been home to human settlements for thousands of years. Several pre-Columbian cultures, including the Chiripa, Tiwanaku, and the Inca Empire, thrived in this region, leaving a rich cultural legacy.
Today, the Altiplano–Puna region is home to several major cities, including El Alto, La Paz, and Oruro in Bolivia and Puno in Peru. The region's economy is based on various activities, including llama and vicuña herding (for wool and as pack animals), mining, and urban services.
The dominant vegetation of the Altiplano–Puna consists of hardy grasses and shrubs, which have supported the region's Indigenous wildlife, including the alpaca and the llama. These animals have played a crucial role in the lives of the region's inhabitants, providing them with valuable resources and serving as pack animals for centuries.
The Significance of the Altiplano–Puna
The Altiplano–Puna plateau is a remarkable and unique geographical and geological feature shaped by the dynamic interplay of tectonic forces, volcanic activity, and the erosion of the surrounding mountain ranges. This high-altitude region has been the home of Indigenous cultures for millennia and continues to be a vital part of South America's economy and ecosystem of South America.
Understanding the complex geological history and processes that have formed the Altiplano–Puna is crucial for understanding the broader context of the Andes Mountain range and the evolution of the South American continent. The region's diverse landscapes, resources, and cultural heritage make it a remarkable and vital study area for geologists, ecologists, and anthropologists alike.





